Abstract
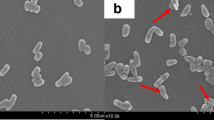
A comparative investigation was performed on the effects of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) on the growth, biocatalytic activity, and cell integrity of Arthrobacter simplex TCCC 11037 (ASP) and Mycobacterium sp. NRRL B-3683 (MSP). The addition of HP-β-CD to ASP medium improved its cell wall permeability for lipophilic compounds but significantly inhibited its growth and biocatalytic activity. On the other hand, the addition of HP-β-CD to MSP broth had lesser effects. Atomic force microscopy scanning analysis revealed that HP-β-CD damaged the cell integrity in ASP, especially the outermost cell surface structure, but not in MSP, which remained intact, owing to the differences in their cell wall and cell membrane composition. Protein leaking and lipid content in ASP increased with increased HP-β-CD concentration, indicating possible alterations in ASP cell membrane features caused by HP-β-CD. These alterations may also explain the slow cell growth and decreased cell ΔΨm in ASP upon the addition of HP-β-CD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DL, Fisher JF (1995) Advances in microbial steroid biotransformation. Steroids 60:290–294
Brennan PJ, Nikaido H (1995) The envelope of mycobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 64:29–63
Chatterjee D (1997) The mycobacterial cell wall: structure biosynthesis and sites of drug action. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1:579–588
Donova MV, Nikolayeva VM, Dovbnya DV, Gulevskaya SA, Suzina NE (2007) Methyl-b-cyclodextrin alters growth, activity and cell envelope features of sterol-transforming mycobacteria. Microbiology 153:1981–1992
Egorova OV, Nikolayeva VM, Sukhodolskaya GV, Donova MV (2009) Transformation of C19-steroids and testosterone production bysterol-transforming strains of Mycobacterium spp. J Mol Catal B Enzym 57:198–203
Fernandes P, Cruz A, Angelova B, Pinheiro HM, Cabral JMS (2003) Microbial conversion of steroid compounds: recent developments. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:688–705
Greenberg-Ofrath N, Terespolosky Y, Kahane I, Bar R (1993) Cyclodextrins as carriers of cholesterol and fatty acids in cultivation of mycoplasmas. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:547–551
Harper JB, Eastona CJ, Lincolnb SF (2000) Cyclodextrins to increase the utility of enzymes in organic synthesis. Curr Org Chem 4:429–454
Heipieper HJ, Neumann G, Cornelissen S (2007) Solvent-tolerant bacteria for biotransformations in two-phase fermentation systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:961–973
Hesselink PGM, Vliet SV, Vries HO (1989) Optimization of steroid side chain cleavage by cyclodextrins. Enzyme Microb Technol 11:398–404
Irie T, Otagiri M, Sunada M, Uekama K, Ohtani Y, Yamada Y, Sugiyama Y (1982) Cyclodextrin-induced haemolysis and shape changes of human erythrocytes in vitro. J Pharmacobio Dyn 5:741–744
Jadoun J, Bar R (1993a) Microbial transformations in a cyclodextrin medium. Part 3. Cholesterol oxidation by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:230–240
Jadoun J, Bar R (1993b) Microbial transformations in a cyclodextrin medium. Part 4. Enzyme and microbial oxidation of cholesterol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:477–482
Ma YH, Wang M, Fan Z, Shen YB, Zhang LT (2009) The influence of host–guest inclusion complex formation on the biotransformation of cortisone acetate Δ1-dehydrogenation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 117:146–151
Machała MK, Ziołkowski A, Galewicz AR, Lisowska K, Sedlaczek L (2001) Polycations increase the permeability of Mycobacterium vaccae cell envelopes to hydrophobic compounds. Microbiology 147:2769–2781
Manosroi A, Saowakhon S, Manosroi J (2008) Enhancement of androstadienedione production from progesterone by biotransformation using the hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexation technique. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 108:132–136
Minnikin DE (1991) Chemical principles in the organization of the lipid components in the mycobacterial cell envelope. Res Microbiol 142:423–427
Mishra KP (2002) Radiation induced permeability changes in liposome and thymocytes: potential and relevance to biological dosimetry. Adv ESR Appl 18:261–264
Molnar I, Choi KP, Yamashita M (1995) Molecular cloning, expression in Streptomyces lividans, and analysis of a gene cluster from Arthrobacter simplex encoding 3-ketosteroid-∆1-dehydrogenase, 3-ketosteroid-∆5-isomerase and a hypothetical regulatory protein. Mol Microbiol 15:895–905
Nikaido H, Jarlier V (1991) Permeability of the mycobacterial cell wall. Res Microbiol 142:437–443
Roglič U, Znidarsic-Plazl P, Plazl I (2005) The influence of β-cyclodextrin on the kinetics of progesterone transformation by Rhizopus nigricans. Biocatal Biotransform 23:299–305
Scaduto JR, Grotyohann LW (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76:469–477
Shen YB, Wang M, Wang YL, Luo JM (2009) Effect of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on the side-chain bioconversion of phytosterols by Mycobacterium sp. NRRL B-3683. Chem Eng Chin Univ 23:440–444
Singer Y, Shity H, Bar R (1991) Microbial transformations in a cyclodextrin medium. Part 2. Reduction of androstenedione to testosterone by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:731–737
Szejtli J (1988) Cyclodextrin technology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 188–190
Szentirrnai A (1990) Microbial physiology of side-chain degradation of sterols. J Ind Microbiol Biot 6:101–116
Wang M, Zhang LT, Shen YB, Ma YH, Zheng Y, Luo JM (2009) Effects of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on steroids 1-en-dehydrogenation biotransformation by Arthrobacter simplex TCCC 11037. J Mol Catal B Enzym 59:58–63
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20776111, 21076158), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-08-0911), and the Foundation for Excellent Doctoral Dissertations of TianJin University of Science and Technology in 2010 (No. B201001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, L. et al. Effects of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on cell growth, activity, and integrity of steroid-transforming Arthrobacter simplex and Mycobacterium sp.. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90, 1995–2003 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3214-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3214-6