Abstract
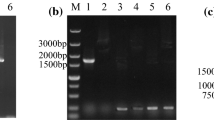
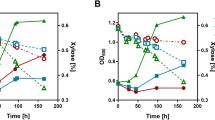
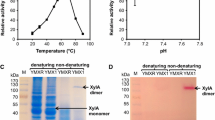
The cellobiose phosphorylase (cepA) gene from Clostridium stercorarium was cloned and successfully expressed under transcriptional control of the phosphoglycerate kinase gene (PGK1) promoter and terminator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y294. The recombinant CepA enzyme showed optimal activity at 60 °C and pH 5 and displayed a K m value of 92.85 mM and 1.69 mM on cellobiose and pNPG, respectively. A codon-optimised synthetic cepA gene was also expressed; however, it did not enhance cellobiose utilisation. Transport of cellobiose was subsequently facilitated through the heterologous expression of the lac12 of Kluyveromyces lactis. Strains co-producing the heterologous CepA and Lac12 were able to grow on cellobiose as sole carbon source. This is the first report of successful intracellular utilisation of cellobiose by S. cerevisiae producing a cellobiose phosphorylase and of cellobiose transport into S. cerevisiae via the K. lactis lac12 encoded permease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander JK (1961) Characteristics of cellobiose phosphorylase. J Bacteriol 81:903–910
Bennetzen JL, Hall BD (1982) Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem 257:3026–3031
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carbone A, Zinovyev A, Kepes F (2003) Codon adaptation index as a measure of dominating codon bias. Bioinformatics 19:2005–2015
Collins JC, Permuth SF, Brooker RJ (1989) Isolation and characterization of lactose permease mutants with an enhanced recognition of maltose and diminished recognition of cellobiose. J Biol Chem 264:14698–14703
Crous JM, Pretorius IS, van Zyl WH (1995) Cloning and expression of an Aspergillus kawachii endo-1, 4-β-xylanase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 28:467–473
Den Haan R, McBride JE, La Grange DC, Lynd LR, Van Zyl WH (2007) Functional expression of cellobiohydrolases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae towards one-step conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1291–1299
Freer SN (1991) Fermentation and aerobic metabolism of cellodextrins by yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:655–659
Freer SN, Greene RV (1990) Transport of glucose and cellobiose by Candida wickerhamii and Clavispora lusitaniae. J Biol Chem 265:12864–12868
Fujita Y, Takahashi S, Ueda M, Tanaka A, Okada H, Morikawa Y, Kawaguchi T, Arai M, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2002) Direct and efficient production of ethanol from cellulosic material with a yeast strain displaying cellulolytic enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5136–5141
Galazka JM, Tian C, Beeson WT, Martinez B, Glass NL, Cate JH (2010) Cellodextrin transport in yeast for improved biofuel production. Science 330:84–86
Gonde P, Blondin B, Leclerc M, Ratomahenina R, Arnaud A, Galzy P (1984) Fermentation of cellodextrins by different yeast strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:265–269
Gustafsson CS, Govindarajan S, Minshull J (2004) Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol 22:346–353
Ha SJ, Galazka JM, Rin Kim S, Choi JH, Yang X, Seo JH, Glass NL, Cate JH, Jin YS (2011) Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of simultaneous cellobiose and xylose fermentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:504–509
Hill J, Donald KA, Griffiths DE, Donald G (1991) DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5791
Kosaric N, Pieper HJ, Vardar-Sukan F (2001) The biotechnology of ethanol. Classical and future applications. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Kubicek CP, Messner R, Gruber F, Mandels M, Kubicek-Pranz EM (1993) Triggering of cellulase biosynthesis by cellulose in Trichoderma reesei. Involvement of a constitutive, sophorose-inducible, glucose-inhibited β-diglucoside permease. J Biol Chem 268:19364–19368
la Grange DC, Pretorius IS, van Zyl WH (1996) Expression of a Trichoderma reesei β-xylanase gene (XYN2) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1036–1044
Lynd LR, Wyman CE, Gerngross TU (1999) Biocommodity engineering. Biotechnol Prog 15:777–793
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, van Zyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:577–583
McBride JE, Zietsman JJ, van Zyl WH, Lynd LR (2005) Utilization of cellobiose by recombinant β-glucosidase-expressing strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization and evaluation of the sufficiency of expression. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:93–101
Rajashekhara E, Kitaoka M, Kim YK, Hayashi K (2002) Characterization of a cellobiose phosphorylase from a hyperthermophilic eubacterium, Thermotoga maritima MSB8. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:2578–2586
Rajoka MI, Shaukat F, Ghauri MT, Shahid R (2003) Kinetics of β-glucosidase production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinants harboring heterologous bgl genes. Biotechnol Lett 25:945–948
Reichenbecher M, Lottspeich F, Bronnenmeier K (1997) Purification and properties of a cellobiose phosphorylase (CepA) and a cellodextrin phosphorylase (CepB) from the cellulolytic thermophile Clostridium stercorarium. Eur J Biochem 247:262–267
Reizer J, Reizer A, Saier MH Jr (1990) The cellobiose permease of Escherichia coli consists of three proteins and is homologous to the lactose permease of Staphylococcus aureus. Res Microbiol 141:1061–1067
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Skory CD, Freer SN, Bothast RJ (1996) Expression and secretion of the Candida wickerhamii extracellular β-glucosidase gene, bglB, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 30:417–422
Sreekrishna K, Dickson RC (1985) Construction of strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that grow on lactose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7909–7913
Stambuk BU, Batista AS, de Araujo PS (2000) Kinetics of active sucrose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 89:212–214
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Tanaka K, Kawaguchi T, Imada Y, Ooi T, Arai M (1994) Purification and properties of cellobiose phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Ferment Bioeng 79:212–216
Tautz D, Renz M (1983) An optimized freeze–squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem 132:14–19
Tingle M, Halvorson HO (1971) A comparison of β-glucanase and β-glucosidase in Saccharomyces lactis. Biochim Biophys Acta 250:165–171
Tingle M, Halvorson HO (1972) Biochemical and genetic characterization of 3 β-glucosidase mutants in Saccharomyces lactis. J Bacteriol 110:196–201
van der Rest ME, Kamminga AH, Nakano A, Anraku Y, Poolman B, Konings WN (1995) The plasma membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: structure, function, and biogenesis. Microbiol Rev 59:304–322
van Rensburg P, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (1998) Engineering yeast for efficient cellulose degradation. Yeast 14:67–76
van Rooyen R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, la Grange DC, van Zyl WH (2005) Construction of cellobiose-growing and fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. J Biotechnol 120:284–295
Yernool DA, McCarthy JK, Eveleigh DE, Bok JD (2000) Cloning and characterization of the glucooligosaccharide catabolic pathway β-glucan glucohydrolase and cellobiose phosphorylase in the marine hyperthermophile Thermotoga neapolitana. J Bacteriol 182:5172–5179
Zhang YH, Lynd LR (2004) Kinetics and relative importance of phosphorolytic and hydrolytic cleavage of cellodextrins and cellobiose in cell extracts of Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1563–1569
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Research Foundation (NRF) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadie, C.J., Rose, S.H., den Haan, R. et al. Co-expression of a cellobiose phosphorylase and lactose permease enables intracellular cellobiose utilisation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90, 1373–1380 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3164-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3164-z