Abstract
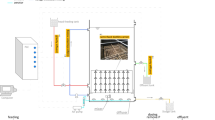
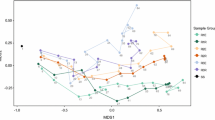
Problems with deflocculation and solids separation in biological wastewater treatment systems are linked to fluctuations in physicochemical conditions. This study examined the composition of activated sludge bacterial communities in lab-scale sequencing batch reactors treating bleached kraft mill effluent, under transient temperature conditions (30 to 45 °C) and their correlation to sludge settleability problems. The bacterial community composition of settled and planktonic biomass samples in the reactors was monitored via denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene fragments. Our analysis showed that settled biomass has a different community composition from the planktonic biomass (49 ± 7% difference based on Jaccard similarity coefficients; p < 0.01). During times of poor sludge compression, the settled and planktonic biomass became more similar. This observation supports the hypothesis that settling problems observed were due to deflocculation of normally settling flocs rather than the outgrowth of non-settling bacterial species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acinas SG, Marcelino LA, Klepac-Ceraj V, Polz MF (2004) Divergence and redundancy of 16S rRNA sequences in genomes with multiple rrn operons. J Bacteriol 186:2629–2635
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington
Burge LM (2004) Testing links between river patterns and in-channel characteristics using MRPP and ANOVA. Geomorphol 63:115–130
Carpenter WL, Vamvakias JG, Gellman I (1968) Temperature relationships in aerobic treatment and disposal of pulp and paper wastes. WPCF 40:733–739
Chow ML, Radomski CC, McDermott JM, Davies J, Axelrood PE (2002) Molecular characterization of bacterial diversity in Lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) rhizosphere soils from British Columbia forest soils differing in disturbance and geographic source. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:347–357
Cocci AA, McCarthy PJ (1998) Sequencing batch reactors in the pulp and paper industry: a bench-marking study. International environmental conference and exhibit, Vancouver, British Columbia, April 5–8, 1998, TAPPI Press, Norcross, pp 1203–1208
Davis KE, Joseph SJ, Janssen PH (2005) Effects of growth medium, inoculum size, and incubation time on culturability and isolation of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:826–834
DeLong EF, Franks DG, Alldredge AL (1993) Phylogenetic diversity of aggregate-attached vs. free-living marine bacterial assemblage. Limnol Oceanogr 38:924–934
Farrelly V, Rainey FA, Stackebrandt E (1995) Effect of genome size and rrn gene copy number on PCR amplification of 16S rRNA genes from a mixture of bacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2798–2801
Feldman SR, Lewis JP (2005) Effects of fire on the structure and diversity of a Spartina argentinensis tall grassland. Appl Veg Sci 8:77–84
Gremion F, Chatzinotas A, Harms H (2003) Comparative 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA sequence analysis indicates that Actinobacteria might be a dominant part of the metabolically active bacteria in heavy metal-contaminated bulk and rhizosphere soil. Environ Microbiol 5:896–907
Haig SM, Wagner RS, Forsman ED, Mullins TD (2001) Geographic variation and genetic structure in Spotted Owls. Conserv Genet 2:25–40
Jenkins D, Richard MG, Daigger GT (1993) Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking and foaming, 2nd edn. Lewis, Chelsea
Kjellerup BV, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (2001) Monitoring and troubleshooting of non-filamentous settling and dewatering problems in an industrial activated sludge treatment plant. Water Sci Technol 44:155–162
Liu X-C, Zhang Y, Yang M, Wang Z-Y, Lv W-Z (2007) Analysis of bacterial community structures in two sewage treatment plants with different sludge properties and treatment performance by nested PCR-DGGE method. J Environ Sci 19:60–66
McCune B, Grace JB (2002) MRPP (Multi-Response Permutation Procedures) in analysis of ecological communities. MjM Software Design, Glenden Beach, Oregon, pp 188–198
Morgan-Sagastume F, Allen DG (2003) Effects of temperature transient conditions on aerobic biological treatment of wastewater. Water Res 37:3590–3601
Morgan-Sagastume F, Allen DG (2005) Activated sludge deflocculation under temperature upshifts from 30 to 45 °C. Water Res 39:1061–1074
Morgan-Sagastume F, Larsen P, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2008) Characterization of the loosely attached fraction of activated sludge bacteria. Water Res 42:843–854
Müller E, Kriebitzch K, Wilderer PA, Wuertz S (2002) Community structure of micro- and macroflocs in pin-point sludge and the influence of sludge age and potassium addition on microfloc formation. Water Sci Technol 46:405–412
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Utterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nadarajah N, Allen DG, Fulthorpe RR (2007) Effects of transient temperature conditions on the divergence of activated sludge bacterial community structure and function. Water Res 41:2563–2571
Piao Z, Yang L, Zhao L, Yin S (2008) Actinobacterial community structure in soils receiving long-term organic and inorganic amendments. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:526–530
Schmid M, Thill A, Purkhold U, Walcher M, Bottero JY, Ginestet P, Nielsen PH, Wuertz S, Wagner M (2003) Characterization of activated sludge flocs by confocal laser scanning microscopy and image analysis. Water Res 37:2043–2052
Severns PM (2005) Response of a terrestrial mollusc community to an autumn prescribed burn in a rare wetland prairie of western Oregon, USA. J Molluscan Stud 71:181–187
Suzuki MT, Giovannoni SJ (1996) Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:625–630
Tresse O, Lorrain MJ, Rho D (2002) Population dynamics of free-floating and attached bacteria in a styrene-degrading biotrickling filter analyzed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:585–590
von Wintzingerode F, Goebel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:213–229
Werker AG, Hall ER (1998) Using microbial fatty acids to quantify, characterize and compare biofilm and suspended microbial populations in wastewater treatment systems. Water Sci Technol 38:273–280
Wilen BM, Nielsen JL, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (2000) Influence of microbial activity on the stability of activated sludge flocs. Colloids Surf B 18:145–156
Zhang T, Fang HHP (2000) Digitization of DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) profile and cluster analysis of microbial communities. Biotechnol Lett 22:399–405
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the members of the “Minimizing the Impact of Pulp and Paper Mill Discharges Consortium” and “Environmental Consortium” at the Pulp and Paper Centre, University of Toronto: Aracruz Celulose S.A., Bowater Canadian Forest Products Inc., Carter Holt Harvey Tasman, Domtar Inc., EKA Chemicals Inc., Georgia-Pacific Corporation, Irving Pulp and Paper Ltd., Japan Carlit Co. Ltd., ERCO Worldwide, Tembec Inc., Votorantim Celulose e Papel SA, and Tembec Inc. In addition, financial support from Ontario Graduate Scholarship and the Ontario Graduate Scholarship in Science and Technology to Nalina Nadarajah is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadarajah, N., Allen, D.G. & Fulthorpe, R.R. Composition of activated sludge settling and planktonic bacterial communities treating industrial effluent and their correlation to settling problems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 1205–1214 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2829-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2829-3