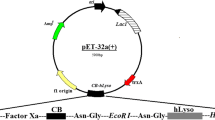
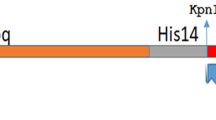
Abstract
The amino acid composition of halophilic enzymes is characterized by an abundant content of acidic amino acid, which confers to the halophilic enzymes extensive negative charges at neutral pH and high aqueous solubility. This negative charge prevents protein aggregation when denatured and thereby leads to highly efficient protein refolding. β-Lactamase from periplasmic space of moderate halophile (BLA), a typical halophilic enzyme, can be readily expressed as a native, active form in Escherichia coli cytoplasm. Similar to other halophilic enzymes, BLA is soluble upon denaturation by heat or urea treatments and, hence, can be efficiently refolded. Such high solubility and refolding efficiency make BLA a potential fusion partner for expression of aggregation-prone heterologous proteins to be expressed in E. coli. Here, we succeeded in the soluble expression of several “difficult-to-express” proteins as a BLA fusion protein and verified biological activities of human interleukin 1α and human neutrophil α-defensin, HNP-1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnau J, Lauritzen C, Petersen GE, Pedersen J (2006) Current strategies for the use of affinity tags and tag removal for the purification of recombinant proteins. Protein Expr Purif 48:1–13
Chou CP (2007) Engineering cell physiology to enhance recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:521–532
Daumy GO, Merenda JM, McColl AS, Andrews GC, Franke AE, Geoghegan KF, Otterness IG (1989) Isolation and characterization of biologically active murine interleukin-1 alpha derived from expression of a synthetic gene in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 998:32–42
Esposito D, Chatterjee DK (2006) Enhancement of soluble protein expression through the use of fusion tags. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:353–358
Ishibashi M, Tokunaga H, Arakawa T, Tokunaga M (2001a) Expression, purification, and characterization of the active immunoglobulin-like domain of human granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor receptor in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 21:317–322
Ishibashi M, Tokunaga H, Hiratsuka K, Yonezawa Y, Tsurumaru H, Arakawa T, Tokunaga M (2001b) NaCl-activated nucleoside diphosphate kinase from extremely halophilic archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum, maintains native conformation without salt. FEBS Lett 493:134–138
Iwata T, Tanaka R, Suetsugu M, Ishibashi M, Tokunaga H, Kikuchi M, Tokunaga M (2004) Efficient secretion of human lysozyme from the yeast, Kluyveromyces lactis. Biotechnol Lett 26:1803–1808
Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock RE (2006) Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:491–511
Kanaya E, Higashizaki T, Ozawa F, Hirai K, Nishizawa M, Tokunaga M, Tsukui H, Hatanaka H, Hishinuma F (1989) Synthesis and secretion of human nerve growth factor by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 83:65–74
Kapust RB, Waugh DS (1999) Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein is uncommonly effective at promoting the solubility of polypeptides to which it is fused. Protein Sci 8:1668–1674
Kato S, Ishibashi M, Tatsuda D, Tokunaga H, Tokunaga M (2001) Efficient expression, purification and characterization of mouse salivary alpha-amylase secreted from methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Yeast 18:643–655
Kennedy SP, Ng WV, Salzberg SL, Hood L, DasSarma S (2001) Understanding the adaptation of Halobacterium species NRC-1 to its extreme environment through computational analysis of its genome sequence. Genome Res 11:1641–1650
Kobayashi K, Kamekura M, Kanlayakrit W, Onishi H (1986) Production, purification, and characterization of an amylase from the moderate halophile, Micrococcus varians subspecies halophilus. Microbios 46:165–177
Kushner DJ (1985) The Halobacteriaceae. Bacteria 8:171–214
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lanyi JK (1974) Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 38:272–290
Lehrer RI, Rosenman M, Harwig SS, Jackson R, Eisenhauer P (1991) Ultrasensitive assays for endogenous antimicrobial polypeptides. Immunol Methods 137:167–173
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mevarech M, Frolow F, Gloss LM (2000) Halophilic enzymes: proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys Chem 86:155–164
Nagayoshi C, Ishibashi M, Kita Y, Matsuoka M, Nishimoto I, Tokunaga M (2005) Expression, refolding and characterization of human brain serine racemase in Escherichia coli with N-terminal His-tag. Protein Pept Lett 12:487–490
Nagayoshi C, Ishibashi M, Tokunaga M (2009) Purification and characterization of human brain serine racemase expressed in moderately halophilic bacteria. Protein Pept Lett 16:201–206
Onozaki K, Matsushima K, Aggarwal BB, Oppenheim JJ (1985) Human interleukin 1 is a cytocidal factor for several tumor cell lines. J Immunol 135:3962–3968
Rehaume LM, Hancock RE (2008) Neutrophil-derived defensins as modulators of innate immune function. Crit Rev Immunol 28:185–200
Sahdev S, Khattar SK, Saini KS (2008) Production of active eukaryotic proteins through bacterial expression systems: a review of the existing biotechnology strategies. Mol Cell Biochem 307:249–264
Schägger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:368–379
Tanaka R, Mizukami M, Ishibashi M, Tokunaga H, Tokunaga M (2003) Cloning and expression of the ccdA-associated thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase (catA) gene from Brevibacillus choshinensis: stimulation of human epidermal growth factor production. J Biotechnol 103:1–10
Terpe K (2006) Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:211–222
Tokunaga M, Kawamura A, Yonekyu S, Kishida M, Hishinuma F (1993) Secretion of mouse alpha-amylase from fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: presence of chymostatin-sensitive protease activity in the culture medium. Yeast 9:379–387
Tokunaga M, Ishibashi M, Tatsuda D, Tokunaga H (1997a) Secretion of mouse alpha-amylase from Kluyveromyces lactis. Yeast 13:699–706
Tokunaga M, Miyawaki H, Shiraishi Y, Tokunaga H (1997b) Purification and characterization of a GroEL homologue from the moderately eubacterial halophile Pseudomonas sp. #43. FEMS Microbiol Lett 152:321–326
Tokunaga H, Yamakawa M, Mizukami M, Takagi H, Tokunaga M (1998) Molecular cloning of the dnaK locus, and purification and characterization of a DnaK protein from Bacillus brevis HPD31. Biochim Biophys Acta 1387:65–79
Tokunaga H, Hara S, Arakawa T, Ishibashi M, Gupta RS, Tokunaga M (1999) Identification and partial purification of DnaK homologue from extremely halophilic archaebacteria, Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Protein Chem 18:837–844
Tokunaga H, Ishibashi M, Arakawa T, Tokunaga M (2004a) Highly efficient renaturation of beta-lactamase isolated from moderately halophilic bacteria. FEBS Lett 558:7–12
Tokunaga H, Mitsuo K, Ichinose S, Omori A, Ventosa A, Nakae T, Tokunaga M (2004b) Salt-inducible multidrug efflux pump protein in the moderately halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4424–4431
Tokunaga H, Mitsuo K, Kamekura M, Tokunaga M (2004c) Major outer membrane proteins in moderately halophilic eubacteria of genera Chromohalobacter and Halomonas. J Basic Microbiol 44:232–240
Tokunaga H, Arakawa T, Fukada H, Tokunaga M (2006) Opposing effects of NaCl on reversibility and thermal stability of halophilic beta-lactamase from a moderate halophile, Chromohalobacter sp. 560. Biophys Chem 119:316–320
Tokunaga H, Arakawa T, Tokunaga M (2008a) Engineering of halophilic enzymes: two acidic amino acid residues at the carboxy-terminal region confer halophilic characteristics to Halomonas and Pseudomonas nucleoside diphosphate kinases. Protein Sci 17:1603–1610
Tokunaga H, Ishibashi M, Arisaka F, Arai S, Kuroki R, Arakawa T, Tokunaga M (2008b) Residue 134 determines the dimer-tetramer assembly of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from moderately halophilic bacteria. FEBS Lett 582:1049–1054
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Waugh DS (2005) Making the most of affinity tags. Trends Biotechnol 23:316–320
Widmann M, Christen P (2000) Comparison of folding rates of homologous prokaryotic and eukaryotic proteins. J Biol Chem 275:18619–18622
Zhang YB, Howitt J, McCorkle S, Lawrence P, Springer K, Freimuth P (2004) Protein aggregation during overexpression limited by peptide extensions with large net negative charge. Protein Expr Purif 36:207–216
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Salt Science Research Foundation (Program for Research on Halophilic Organisms), and Grant in Aid for Science Research (20580372) from MEXT Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokunaga, H., Saito, S., Sakai, K. et al. Halophilic β-lactamase as a new solubility- and folding-enhancing tag protein: production of native human interleukin 1α and human neutrophil α-defensin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 649–658 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2325-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2325-9