Abstract
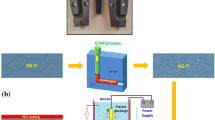
The influence of the ultrafine crystallinity of commercial purity grade 2 (as-received) titanium and titanium modified by equal channel angular pressing (modified titanium) on bacterial attachment was studied. A topographic profile analysis of the surface of the modified titanium revealed a complex morphology of the surface. Its prominent micro- and nano-scale features were 100–200-nm-scale undulations with 10–15 μm spacing. The undulating surfaces were nano-smooth, with height variations not exceeding 5–10 nm. These surface topography characteristics were distinctly different from those of the as-received samples, where broad valleys (up to 40–60 μm) were detected, whose inner surfaces exhibited asperities approximately 100 nm in height spaced at 1–2 μm. It was found that each of the three bacteria strains used in this study as adsorbates, viz. Staphylococcus aureus CIP 68.5, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9025 and Escherichia coli K12, responded differently to the two types of titanium surfaces. Extreme grain refinement by ECAP resulted in substantially increased numbers of cells attached to the surface compared to as-received titanium. This enhanced degree of attachment was accompanied with an increased level of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production by the bacteria.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes D, Fluke C (2008) Incorporating interactive three-dimensional graphics in astronomy research papers. New Astron 13:599–605
Barnes D, Fluke C, Bourke P, Parry O (2006) An advanced, three-dimensional plotting library for astronomy. Publ Astron Soc Australia 23:82–93
Bertóti I, Mohai M, Sullivan J, Saied S (1995) Surface characterisation of plasma-nitrided titanium: an XPS study. Appl Surf Sci 84:357–371
Cai K, Muller M, Bossert J, Rechtenbach A, Jandt K (2005) Surface structure and composition of flat titanium thin films as a function of film thickness and evaporation rate. Appl Surf Sci 250:252–267
Campoccia D, Montanaro L, Arciola C (2006) The significance of infection related to orthopedic devices and issues of antibiotic resistance. Biomater 27:2331–2339
Drebin R, Carpenter L, Hanrahan P (1988) Volume rendering. Comput Graph (ACM) 22:65–74
Estrin Y, Kasper C, Diederichs S, Lapovok R (2009) Accelerated growth of preosteoblastic cells on ultrafine grained titanium. J Biomed Mater Res—Part A (in press) doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.32174
Faghihi S, Azari F, Li H, Bateni M, Szpunar J, Vali H, Tabrizian M (2006) The significance of crystallographic texture of titanium alloy substrates on pre-osteoblast responses. Biomater 27:3532–3539
Fluke C, Barnes D (2008) The interactive astronomy textbook. Astron Education Rev 7(1)
Gottenbos B, Grijpma D, Van Der Mei H, Feijen J, Busscher H (2001) Antimicrobial effects of positively charged surfaces on adhering Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother 48:7–13
Hallab N, Bundy K, O'Connor K, Moses R, Jacobs J (2001) Evaluation of metallic and polymeric biomaterial surface energy and surface roughness characteristics for directed cell adhesion. Tissue Eng 7:55–70
Ivanova EP, Mitik-Dineva N, Wang J, Pham DK, Wright JP, Nicolau DV, Mocanasu RC, Crawford RJ (2008) Staleya guttiformis attachment on poly(tert-butylmethacrylate) polymeric surfaces. Micron 39:1197–1204
Kim TN, Balakrishnan A, Lee BC, Kim WS, Smetana K, Park JK, Panigrahi BB (2007) In vitro biocompatibility of equal channel angular processed (ECAP) titanium. Biomed Mater 2:S117–S120
Kim TN, Balakrishnan A, Lee BC, Kim WS, Dvorankova B, Smetana K, Park JK, Panigrahi BB (2008) In vitro fibroblast response to ultra fine grained titanium produced by a severe plastic deformation process. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19:553–557
Li B, Logan BE (2004) Bacterial adhesion to glass and metal-oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 36:81–90
Liu X, Chu PK, Ding C (2004) Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R: Reports 47:49–121
Maeyama R, Mizunoe Y, Anderson JM, Tanaka M, Matsuda T (2004) Confocal imaging of biofilm formation process using fluoroprobed Escherichia coli and flouro-stained exopolysaccharide. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A 70:274–282
Mather J, Roberts P (1998) Introduction to cell and tissue culture: theory and technique. Plenum, New York
Mitik-Dineva N, Wang J, Mocanasu RC, Stoddart PR, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP (2008) Impact of nano-topography on bacterial attachment. Biotech J 3:536–544
Mitik-Dineva N, Wang J, Truong VK, Stoddart P, Malherbe F, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP (2009) Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus attachment patterns on glass surfaces with nanoscale roughness. Curr Microbiol 58:268–273
Nishino T, Ikemoto E, Kogure K (2004) Application of atomic force microscopy to observation of marine bacteria. J Oceanogr 60:219–225
Öner D, McCarthy TJ (2000) Ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Effects of topography length scales on wettability. Langmuir 16:7777–7782
Rack HJ, Qazi JI (2006) Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R: C 26:1269–1277
Stolyarov VV, Zhu YT, Alexandrov IV, Lowe TC, Valiev RZ (2001) Influence of ECAP routes on the microstructure and properties of pure Ti. Mater Sci Eng A 299:59–67
Vadillo-Rodriguez V, Busscher HJ, Norde W, Vries J, van der Mei HC (2004) Atomic force microscopy corroboration of bond aging for adhesion of Streptococcus thermophilus to solid substrata. J Colloid Interface Sci 278:251–254
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2006) Producing bulk ultrafine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM 58:33–39
Valiev RZ, Semenova IP, Latysh VV, Rack H, Lowe TC, Petruzelka J, Dluhos L, Hrusak D, Sochova J (2008) Nanostructured titanium for biomedical applications. Adv Eng Mater 10:B15–B17
van Loosdrecht MCM, Norde W, Lyklema J, Zehnder AJB (1990) Hydrophobic and electrostatic parameters in bacterial adhesion. Aquat Sci 52:103–114
Vinogradov AY, Stolyarov VV, Hashimoto S, Valiev RZ (2001) Cyclic behavior of ultrafine-grain titanium produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 318:163–173
Whitehead KA, Verran J (2007) The effect of surface properties and application method on the retention of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on uncoated and titanium-coated stainless steel. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 60:74–80
Acknowledgment
This study was supported in part by the Australian Research Council (ARC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the linked to the electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Three-dimensional projections of CLSM images of representative S. aureus specimens on the as-received (left) and modified (right) titanium surfaces after 18-h incubation. Bacterial colonies (stained red with Rhodamine Red-X) produce EPS (stained green with concanavalin A Alexa 488) across the plate surface. Readers using version 8.0 or higher of Acrobat Reader can enable interactive, three-dimensional views of the data by clicking on the figure panels. Once enabled, 3-d mode allows the reader to rotate and zoom the view using the computer mouse (PDF 1.7 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truong, V.K., Rundell, S., Lapovok, R. et al. Effect of ultrafine-grained titanium surfaces on adhesion of bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83, 925–937 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1944-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1944-5