Abstract
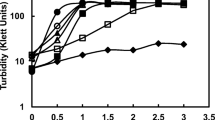
Supplementation of the divalent cations calcium and magnesium to submerged cultures of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. geldanus greatly influenced morphological development and secondary metabolite synthesis. The disparate response could be explained in terms of the differential effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions on cell surface hydrophobicity. Cultures supplemented with calcium ions were found to be hydrophobic, which resulted in cell concentration-dependent aggregation. In contrast, those grown in a magnesium-rich medium were found to be hydrophilic with the organism growing as freely dispersed filaments that synthesised geldanamycin at an optimal rate in comparison to hydrophobic pellets.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas A, Edwards C (1990) Effects of metals on Streptomyces coelicolor growth and actinorhodin production. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:675–680
Archibald A (1974) The structure, biosynthesis and function of teichoic acids. Adv Microb Physiol 11:53–95
Basak K, Majumdar S (1975) Mineral nutrition of Streptomyces kanamyceticus for kanamycin formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 8:391–395
Beveridge T (1989) Metal ions and bacteria. In: Beveridge T, Doyle R (eds) Metal ions and bacteria. Wiley, New York
Braun S, Vecht-Lifshitz S (1991) Mycelial morphology and metabolite production. Trends Biotechnol 9:63–68
Byrne K, Greenstein M (1986) Nitrogen repression of gilvocarcin V production in Streptomyces arenae 2064. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 39:594–600
Castellanos T, Ascencio F, Bashan Y (1997) Cell surface hydrophobicity and cell surface charge of Azospirillium spp. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 24:159–172
Cheng Y, Hauck L, Demain A (1995) Phosphate, ammonium, magnesium and iron nutrition of Streptomyces hygroscopicus with respect to rapamycin biosynthesis. J Ind Microbiol 14:424–427
Domingues L, Vicente A, Lima N, Teixeira J (2000) Applications of yeast flocculation in biotechnological processes. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 5:288–305
Dynesen J, Nielsen J (2003) Surface hydrophobicity of Aspergillus nidulans conidiospores and its role in pellet formation. Biotechnol Prog 19:1049–1052
Frausto da Silva J, Williams R (2001) The biological chemistry of the elements: the inorganic chemistry of life. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kelstrup J, Funder-Nielsen T (1972) Molecular interactions between the extracellular polysaccharides of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol 17:1659–1670
Lu S, Ding Y, Guo J (1998) Kinetics of fine particle aggregation in turbulence. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 78:197–235
Majeed M, Gustafsson M, Kihlstrom E, Stendahl O (1993) Roles of Ca2+ and F-actin in intracellular aggregation of Chlamydia trachomatis in eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 61:1406–1414
Mill P (1964) The nature of the interactions between flocculent cells in the flocculation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol 35:61–68
Neckers L, Schulte T, Mimnaugh E (1999) Geldanamycin as a potential anti-cancer agent: its molecular target and biochemical activity. Invest New Drugs 17:361–373
Nielsen J (1996) Modelling the morphology of filamentous microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 14:438–443
O’Cleirigh C, Walsh P, O’Shea D (2003) Morphological quantification of pellets in Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. geldanus fermentation broths using a flatbed scanner. Biotechnol Lett 25:1677–1683
Okba A, Ogata T, Matsubara H, Matsuo S, Doi K, Ogata S (1998) Effects of bacitracin and excess Mg2+ on submerged mycelial growth of Streptomyces azureus. J Ferment Bioeng 86:28–33
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Kitao C, Tanaka H, Iwai Y (1980) Stimulation of leucomycin production by magnesium phosphate and its relevance to nitrogen catabolite regulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 18:691–695
Onoda T, Enokizono J, Kaya H, Oshima A, Freestone P, Norris V (2000) Effects of calcium and calcium chelators on growth and morphology of Escherichia coli L-form NC-7. J Bacteriol 182:1419–1422
Papagianni M (2004) Fungal morphology and metabolite production in submerged mycelial processes. Biotechnol Adv 22:189–259
Papagianni M, Mattey M (2006) Morphological development of Aspergillus niger in submerged citric acid fermentation as a function of the spore inoculum level. Application of neural network and cluster analysis for characterization of mycelial morphology. Microbial Cell Factories 5:3
Pembrey R, Marshall K, Schneider R (1999) Cell surface analysis techniques: what do cell preparation protocols do to cell surface properties? Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2877–2894
Rose R (2000) The role of calcium in oral streptococcal aggregation and the implications for biofilm formation and retention. Biochim Biophys Acta 1475:76–82
Roubos J, Krabben P, De Laat W, Babuska R, Heijnen J (2002) Clavulanic acid degradation in Streptomyces clavuligerus fed-batch cultivations. Biotechnol Prog 18:451–457
Ryoo D, Choi C (1999) Surface thermodynamics of pellet formation in Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Lett 21:97–100
Singleton D, Masouka J, Hazen K (2001) Cloning and analysis of a Candida albicans gene that affects cell surface hydrophobicity. J Bacteriol 183:3582–3588
Smit G, Kijne J, Lugtenberg B (1989) Roles of flagella, lipopolysaccharide, and a Ca2+-dependent cell surface protein in attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol 171:569–572
Smit G, Straver M, Lugtenberg B, Kijne J (1992) Flocculence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells is induced by nutrient limitation, with cell surface hydrophobicity as a major determinant. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3709–3714
Thaveesri J, Daffonchio D, Liessens B, Vandermereen P, Verstraete W (1995) Granulation and sludge bed stability in upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactors in relation to surface thermodynamics. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3681–3686
Thiebault F, Coulon J (2005) Influence of carbon source and surface hydrophobicity on the aggregation of the yeast Kluyveromyces bulgaricus. Can J Microbiol 51:91–94
Vadillo-Rodriguez V, Busscher H, Norde W, De Vries J, Van der Mei H (2004) Dynamic cell surface hydrophobicity of Lactobacillus strains with and without surface layer proteins. J Bacteriol 186:6647–6650
Vecht-Lifshitz S, Magdassi S, Braun S (1989) Effects of surface active agents on pellet formation in submerged fermentations of Streptomyces tendae. J Dispers Sci Technol 10:265–275
Vecht-Lifshitz S, Magdassi S, Braun S (1990) Pellet formation and cellular aggregation in Streptomyces tendae. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:890–896
Whitaker A (1992) Actinomycetes in submerged culture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 32:23–35
Yonekawa T, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S (2005) A calmodulin-like protein in the bacterial genus Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 244:315–321
Young M, Kempe L, Bader F (1985) Effects of phosphate, glucose, and ammonium on cell-growth and lincomycin production by Streptomyces lincolnensis in chemically defined media. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:327–333
Yousef F, Espinosa-Urgel M (2007) In silico analysis of large microbial surface proteins. Res Microbiol 158(6):545–550
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank the Irish Research Council for Science, Engineering and Technology (IRCSET) for the funding provided under the Embark Postgraduate Research Scholarship Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobson, L.F., O’Shea, D.G. Antagonistic effect of divalent cations Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the morphological development of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. geldanus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81, 119–126 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1627-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1627-7