Abstract
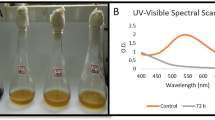
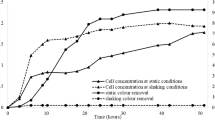
Wastewaters from textile processing and dye-stuff manufacture industries contain substantial amounts of salts in addition to azo dye residues. To examine salinity effects on dye-degrading bacteria, a study was carried out with four azo dyes in the presence of varying concentrations of NaCl (0–100 g l−1) with a previously isolated bacterium, Shewanella putrefaciens strain AS96. Under static, low oxygen conditions, the bacterium decolorized 100 mg dye l−1 at salt concentrations up to 60 g NaCl l−1. There was an inverse relationship between the velocity of the decolorization reaction and salt concentration over the range between 5 and 60 g NaCl l−1 and at dye concentrations between 100 and 500 mg l−1. The addition of either glucose (C source) or NH4NO3 (N source) to the medium strongly inhibited the decolorization process, while yeast extract (4 g l−1) and Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O (1 g l−1) both enhanced decolorization rates. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis demonstrated the presence of 1-amino-2-naphthol, sulfanilic acid and nitroaniline as the major metabolic products of the azo dyes, which could be further degraded by a shift to aerobic conditions. These findings show that Shewanella could be effective for the treatment of dye-containing industrial effluents containing high concentrations of salt.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulenta F, Gossett JM, Papini MP, Rossetti S, Majone M (2005) Comparative study of methanol, butyrate, and hydrogen as electron donors for long-term dechlorination of tetrachloroethene in mixed anerobic cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:743–753
Beliaev AS, Klingeman DM, Klappenbach JA, Wu L, Romine MF, Tiedje JM, Nealson KH, Fredrickson JK, Zhou J (2005) Global transcriptome analysis of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 exposed to different terminal electron acceptors. J Bacteriol 187:7138–7145
Boer CG, Obici L, Souza CG, Peralta RM (2004) Decolourization of synthetic dyes by solid state cultures of Lentinula (Lentinus) edodes producing manganese peroxidase as the main lignolytic enzyme. Bioresour Technol 94:107–112
Bozal N, Montes MJ, Tudela E, Jime’nez F, Guinea J (2002) Shewanella frigidimarina and Shewanella livingstonensis sp. nov. isolated from Antarctic coastal areas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:195–205
Carliell CM, Barclay SJ, Naidoo N, Buckley CA, Mulholland DA, Senior E (1994) Anaerobic decolorisation of reactive dyes in conventional sewage treatment processes. Water SA 20:341–344
Carliell CM, Barcaly SJ, Shaw C, Wheatley AD, Buckley CA (1998) The effect of salts used in textile dyeing on microbial decolourisation of a reactive azo dye. Environ Technol 19:1133–1137
Chang JS, Lin YC (2001) Decolorization kinetics of recombinant E. coli strain harboring azo dye decolorization determinants for Rhodococcus sp. Biotechnol Lett 23:631–636
Chung KT, Cerniglia CE (1992) Mutagenicity of azo dyes: structure–activity relationships. Mutat Res 277:201–220
De Baere LA, Devocht M, Assche PV, Verstraete W (1984) Influence of high NaCl and NH4Cl salt levels on methanogenic associations. Water Res 18:543–648
DiChristina TJ, Moore CM, Haller CA (2002) Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction by Shewanella putrefaciens requires ferE, a Homolog of the pulE (gspE) type II protein secretion gene. J Bacteriol 184:142–151
EPA (1997) Profile of the textile industry. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Green AG (1949) The analysis of dyestuffs and their identification in dyed and coloured material, lake-pigments and foodstuffs etc. Charles Griffin, London
Holt HM, Gahrn-Hansen B, Bruun B (2005) Shewanella algae and Shewanella putrefaciens: clinical and microbiological characteristics. Clin Microbiol Infect 11:347–352
Ince H, Tezcanli G (1999) Treatability of textile dye-bath effluents by advanced oxidation: preparation for reuse. Water Sci Technol 40:183–190
Ivanova EP, Sawabe T, Gorshkova NM, Svetashev VI, Mikhailov VV, Nicolau DV, Christen R (2001) Shewanella japonica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1027–1033
Junnarkar N, Murty DS, Bhatt NS, Madamwar D (2006) Decolorization of diazo dye Direct Red 81 by a novel bacterial consortium. World J Microbiol Biotech 22:163–168
Kalme SD, Parshetti GK, Jadhav SU, Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of benzidine based dye Direct Blue-6 by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Bioresor Technol 98:1405–1410
Karigi F, Dincer AR (1998) Saline wastewater treatment by halophile-supplemented activated sludge culture in an aerated rotating biodisc contactor. Enzyme Microbial Technol 122:427–433
Kerin EJ, Gilmour CC, Roden E, Suzuki MT, Coates JD, Mason RP (2006) Mercury methylation by dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7919–7921
Khalid A, Arshad M, Crowley DE (2008) Accelerated decolorization of structurally different azo dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:361–369
Klonowska A, Heulin T, Vermeglio A (2005) Selenite and tellurite reduction by Shewanella oneidensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5607–5609
Lourenco ND, Novais JM, Pinheiro HM (2000) Reactive textile dye colour removal in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 42:321–328
Manu B, Chauhari S (2003) Decolorization of indigo and azo dyes in semicontinuous reactors with long hydraulic retention time. Process Biochem 38:1213–1221
Ozturk A, Abdullah MI (2006) Toxicological effect of indole and its azo dye derivatives on some microorganisms under aerobic conditions. Sci Total Environ 358:137–142
Panswad T, Anan C (1999) Impact of high chloride wastewater on an anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic process with and without inoculation of chloride acclimated seeds. Water Res 33:1165–1172
Pearce CI, Christie R, Boothman C, von Canstein H, Guthrie JT, Lloyd JR (2006) Reactive azo dye reduction by Shewanella strain J18 143. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:692–703
Peyton BM, Wilson T, Yonge DR (2002) Kinetics of phenol biodegradation in high salt solutions. Water Res 36:4811–4820
Tan NCG, Borger A, Slender P, Svitelskaya AV, Lettinga G, Field JA (2000) Degradation of azo dye Mordant Yellow 10 in a sequential anaerobic and bioaugmented aerobic bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 42:337–344
Venkateswaran K, Moser DP, Dollhopf ME, Lies DP, Saffarini DA, MacGregor BJ, Ringelberg DB, White DC, Nishijima M, Sano H, Burghardt J, Stackebrandt E, Nealson KH (1999) Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Shewanella and description of Shewanella oneidensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:705–724
Xiao X, Wang P, Zeng X, Bartlett DH, Wang F (2007) Shewanella psychrophila sp. nov. and Shewanella piezotolerans sp. nov., isolated from west Pacific deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:60–65
Xu M, Guo J, Cen Y, Zhong X, Cao W, Sun G (2005) Shewanella decolorationis sp. nov., a dye decolorizing bacterium isolated from activated sludge of a waste-water treatment plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:363–368
Xu M, Guo J, Sun G (2007) Biodegradation of textile azo dye by Shewanella decolorationis S12 under microaerophilic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:719–726
Yang SH, Lee JH, Ryu JS, Kato C, Kim SJ (2007) Shewanella donghaensis sp. nov., a psychrophilic, piezosensitive bacterium producing high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acid, isolated from deep-sea sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:208–212
Yoon JH, Yeo SH, Kim IG, Oh TK (2004) Shewanella marisflavi sp. nov. and Shewanella aquimarina sp. nov., slightly halophilic organisms isolated from sea water of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2347–2352
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study was provided by the Higher Education Commission, Pakistan. We thank Dr. Sakkyun Han for supplying the S. oneidensis strain JM6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalid, A., Arshad, M. & Crowley, D.E. Decolorization of azo dyes by Shewanella sp. under saline conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 1053–1059 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1498-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1498-y