Abstract
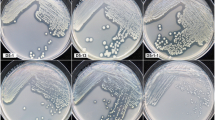
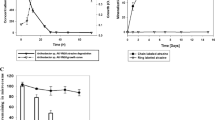
Six previously undescribed microorganisms capable of atrazine degradation were isolated from an agricultural soil that received repeated exposures of the commonly used herbicides atrazine and acetochlor. These isolates are all Gram-positive and group with microorganisms in the genera Nocardioides and Arthrobacter, both of which contain previously described atrazine degraders. All six isolates were capable of utilizing atrazine as a sole nitrogen source when provided with glucose as a separate carbon source. Under the culture conditions used, none of the isolates could utilize atrazine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source. We used several polymerase-chain-reaction-based assays to screen for the presence of a number of atrazine-degrading genes and verified their identity through sequencing. All six isolates contain trzN and atzC, two well-characterized genes involved in the conversion of atrazine to cyanuric acid. An additional atrazine-degrading gene, atzB, was detected in one of the isolates as well, yet none appeared to contain atzA, a commonly encountered gene in atrazine impacted soils and atrazine-degrading isolates. Interestingly, the deoxyribonucleic acid sequences of trzN and atzC were all identical, implying that their presence may be the result of horizontal gene transfer among these isolates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST, a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Angle JS, McGrath SP, Chaney RL (1991) New culture medium containing ionic concentrations of nutrients similar to concentrations found in soil solution. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3674–3676
Cai B, Han Y, Liu B, Ren Y, Jiang S (2003) Isolation and characterization of an atrazine-degrading bacterium from industrial wastewater in China. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:272–276
Crain AD, Guillette LJ, Rooney AA, Pickford DB (1997) Alterations in steroidogenesis in alligators (Alligator mississippiensis) exposed naturally and experimentally to environmental contaminants. Environ Health Perspect 105:528–533
Crawford JJ, Traina SJ, Tuovinen OH (2000) Bacterial degradation of atrazine in redox potential gradients in fixed-film sand columns. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:624–634
Devers M, Henry S, Hartmann A, Martin-Laurent F (2005) Horizontal gene transfer of atrazine-degrading genes (atz) from Agrobacteriumtumefaciens St96-4 pADP1::Tn5 to bacteria of maize-cultivated soil. Pest Manag Sci 61:870–880
de Souza ML, Seffernick J, Martinez B, Sadowsky MJ, Wackett LP (1998a) The atrazine catabolism genes atzABC are widespread and highly conserved. J Bacteriol 180:1951–1954
de Souza ML, Wackett LP, Sadowsky MJ (1998b) The atzABC genes encoding atrazine catabolism are located on a self-transmissible plasmid in Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2323–2326
Ferris MJ, Muyzer G, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:340–346
Fruchey I, Shapir N, Sadowsky MJ, Wackett LP (2003) On the origins of cyanuric acid hydrolase: purification, substrates, and prevalence of AtzD from Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3653–3657
Garcia-Gonzalez V, Govantes F, Shaw LJ, Burns RG, Santero E (2003) Nitrogen control of atrazine utilization in Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6987–6993
Hayes TB, Collins A, Lee M, Mendoza M, Noriega N, Stuart AA, Vonk A (2002) Hermaphroditic, demasculinized frogs after exposure to the herbicide atrazine at low ecologically relevant doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:5476–5480
Kiyohara H, Nagao K, Yana K (1982) Rapid screen for bacteria degrading water-insoluble, solid hydrocarbons on agar plates. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:454–457
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Mandelbaum RT, Wackett LP, Allen DL (1993) Mineralization of the s-triazine ring of atrazine by stable bacterial mixed cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1695–1701
Mandelbaum RT, Allen DL, Wackett LP (1995) Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas sp. strain that mineralizes the s-triazine herbicide atrazine. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1451–1459
Martinez B, Tomkins J, Wackett LP, Wing R, Sadowsky MJ (2001) Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the atrazine catabolic plasmid pADP-1 from Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP. J Bacteriol 183:5684–5697
Mulbry WW, Zhu H, Nour SM, Topp E (2002) The triazine hydrolase gene trzN from Nocardioides sp. strain C190: cloning and construction of gene-specific primers. FEMS Microbiol Lett 206:75–79
Piutti S, Semon E, Landry D, Hartmann A, Dousset S, Lichtfouse E, Topp E, Soulas G, Martin-Laurent F (2003) Isolation and characterization of Nocardioides sp. SP12, an atrazine-degrading bacterial strain possessing the gene trzN from bulk and maize rhizosphere soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 221:111–117
Radosevich M, Traina SJ, Hao Y-L, Tuovinen OH (1995) Degradation and mineralization of atrazine by a soil bacterial isolate. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:297–302
Ralebitso RK, Senior E, van Verseveld HW (2002) Microbial aspects of atrazine degradation in natural environments. Biodegradation 13:11–19
Rousseaux S, Hartmann A, Soulas G (2001) Isolation and characterization of new Gram-negative and Gram-positive atrazine degrading bacteria from different French soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:211–222
Rousseaux S, Soulas G, Hartmann A (2002) Plasmid localisation of atrazine-degrading genes in newly described Chelatobacter and Arthrobacter strains. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41:69–75
Sajjaphan K, Shapir N, Wackett LP, Palmer M, Blackmon B, Tomkins J, Sadowsky MJ (2004) Arthrobacter aurescens TC1 atrazine catabolism genes trzN, atzB and atzC are linked on a 160-kilobase region and are functional in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4402–4407
Satsuma K (2006) Characterisation of new strains of atrazine-degrading Nocardioides sp. isolated from Japanese riverbed sediment using naturally derived river ecosystem. Pest Manag Sci 62:340–349
Shapir N, Goux S, Mandelbaum RT, Pussemier L (2000) The potential of soil microorganisms to mineralize atrazine as predicted by MCH-PCR followed by nested PCR. Can J Microbiol 46:425–432
Solomon KR, Baker DB, Richards RP, Dixon KR, Klaine SJ, La Point TW, Kendall RJ, Weisskopf CP, Giddings JM, Giesy JP, Hall LW, Williams WM (1996) Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:31–76
Strong LC, Rosendahl C, Johnson G, Sadowsky MJ, Wackett LP (2002) Arthrobacter aurescens TC1 metabolizes diverse s-triazine ring compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5973–5980
Struthers JK, Jauachandran K, Moorman TB (1998) Biodegradation of atrazine by Agrobacterium radiobacter J14a and use of this strain in bioremediation of contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3368–3375
Topp E, Gutzman DW, Bourgoin B, Millette J, Gamble DS (1995) Rapid mineralization of the herbicide atrazine in alluvial sediments and enrichment cultures. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:743–747
Topp E, Mulbry WM, Zhu H, Nour SM, Cuppels D (2000a) Characterization of s-triazine herbicide metabolism by a Nocardioides sp. isolated from agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3134–3141
Topp E, Zhu H, Nour SM, Houot S, Lewis M, Cuppels D (2000b) Characterization of an atrazine-degrading Pseudaminobacter sp. isolated from Canadian and French agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2773–2782
Vanderheyden V, Debongnie P, Puissemier L (1997) Accelerated degradation and mineralization of atrazine in surface and subsurface soil materials. Pest Sci 49:237–242
Widmer SK, Spalding RF (1995) A natural gradient transport study of selected herbicides. J Environ Qual 24:445–453
Acknowledgments
Soil samples were kindly provided by Steve Comfort. HPLC assistance was provided by Dale LeCaptain and Jessie Thompson. This project was supported by CMU’s Summer Scholar’s Program and by the National Research Initiative of the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service, grant number 2001-35107-13592.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vibber, L.L., Pressler, M.J. & Colores, G.M. Isolation and characterization of novel atrazine-degrading microorganisms from an agricultural soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 921–928 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0871-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0871-6