Abstract
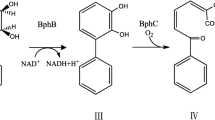
Commercial formulations of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) consist of a mixture of four isomers: α, β, γ, and δ. All four isomers are toxic and recalcitrant pollutants. β-HCH is more problematic due to its longer persistence in the environment. Sphingomonas sp. BHC-A was able to degrade not only α-, γ-, and δ-HCH but also β-HCH. To clone a gene responsible for the degradation of β-HCH, a Tn5 mutation was introduced into BHC-A, and one mutant BHC-A45 defective in β-HCH degradation was selected. Sequencing analysis showed this mutant had a Tn5 insertion at the site of one haloalkane dehalogenase gene, designated linB2. linB2 was overexpressed in Escherichia coli and the 32-kDa product LinB2 showed the conversion activity of not only β-HCH to β-2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorocyclohexanol (β-PCHL) but also β-PCHL to β-2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-1,4-cyclohexanediol.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai-zhi Ma, Jun Wu, Guo-shun Zhang, Ting Wang, Shun-peng Li (2005) Isolation and characterization of a HCH degradation Sphingomonas sp. strain BHC-A. Acta Microbiol Sin 45:728–732
Bhuyan S, Sreedharan B, Adhya TK, Sethunathan N (1993) Enhanced biodegradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH) in HCH (commercial) acclimatized flooded soil: factors affecting its development and persistence. Pestic Sci 38:49–55
de Bruijn FJ (1987) Transposon Tn5 mutagenesis to map genes. Methods Enzymol 154:175–196
de Bruijn FJ, Lupski JR (1984) The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids—a review. Gene 27:131–149
Endo R, Kamakura M, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2005) Identification and characterization of genes involved in the downstream degradation pathway of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Bacteriol 187:847–853
Gupta A, Kaushik CP, Kaushik A (2000) Degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH; α, β, γ and δ) by Bacillus circulans and Bacillus brevis isolated from soil contaminated with HCH. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1803–1805
Gupta A, Kaushik CP, Kaushik A (2001) Degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by two strains of Alcaligenes faecalis isolated from a contaminated site. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66:794–800
Hynkova K, Nagata Y, Takagi M, Damborsky J (1999) Identification of the catalytic triad in the haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. FEBS Lett 446:177–181
Imai R, Nagata Y, Fukuda M, Takagi M, Yano K (1991) Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas paucimobilis gene encoding a 17-kilodalton polypeptide that eliminates HCl molecules from γ-hexachlorocyclohexane. J Bacteriol 173:6811–6819
Iwasaki I, Utsumi S, Ozawa T (1952) New colorimetric determination of chloride using mercuric thiocyanate and ferric ion. Bull Chem Soc Japan 25:226
Jensen AA, Slorach SA (1991) Chemical contaminants in human milk. CRC, Boca Raton, FL
Johri AK, Dua M, Tuteja D, Saxena R, Saxena DM, Lal R (1996) Genetic manipulations of microorganisms for the degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane. FEMS Microbiol Rev 19:69–84
Johri AK, Dua M, Tuteja D, Saxena R, Saxena DM, Lal R (1998) Degradation of alpha, beta, gamma and delta-hexachlorocyclohexanes by Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Biotechnol Lett 20:885–887
Kumari R, Subudhi S, Suar M, Dhingra G, Raina V, Dogra C, Lal S, van der Meer JR, Holliger C, Lal R (2002) Cloning and characterization of lin genes responsible for the degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain B90. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6021–6028
Langenhoff AAM, Staps JJM, Pijls CGJM, Alphenaar A, Zwiep G, Rijnaarts HHM (2002) Intrinsic and stimulated in situ biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). Water Air and Soil Pollut Focus 2:171–181
Li YF, Macdonald RW, Jantunen LM, Harner T, Bidleman TF, Strachan WM (2002) The transport of beta-hexachlorocyclohexane to the western Arctic Ocean: a contrast to alpha-HCH. Sci Total Environ 27:229–246
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Miyauchi K, Suh S, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1998) Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone reductive dehalogenase gene which is involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 180:1354–1359
Miyauchi K, Adachi Y, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1999) Cloning and sequencing of a novel meta-cleavage dioxygenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 181:6712–6719
Miyauchi K, Lee HS, Fukuda M, Takagi M, Nagata Y (2002) Cloning and characterization of linR, involved in regulation of the downstream pathway for γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1803–1807
Nagasawa S, Kikuchi R, Nagata Y, Takagi M, Matsuo M (1993) Aerobic mineralization of γ-HCH by Pseudomonas paucimobilis UT26. Chemosphere 26:1719–1728
Nagata Y, Hatta T, Imai R, Kimbara K, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1993a) Purification and characterization of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH) dehydrochlorinase (LinA) from Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1582–1583
Nagata Y, Nariya T, Ohtomo R, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1993b) Cloning and sequencing of a dehalogenase gene encoding an enzyme with hydrolase activity involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 175:6403–6410
Nagata Y, Ohtomo R, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1994) Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dioldehydrogenase gene involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 176:3117–3125
Nagata Y, Miyauchi K, Damborsky J, Manova K, Ansorgova A, Takagi M (1997) Purification and characterization of a haloalkane dehalogenase of a new substrate class from a γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3707–3710
Nagata Y, Futamura A, Miyauchi K, Takagi M (1999a) Two different types of dehalogenases, LinA and LinB, involved in γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 are localized in the periplasmic space without molecular processing. J Bacteriol 181:5409–5413
Nagata Y, Hynkova K, Damborsky J, Takagi M (1999b) Construction and characterization of histidine-tagged haloalkane dehalogenase (LinB) of a new substrate class from a γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Protein Expr Purif 17:299–304
Nagata Y, Miyauchi K, Takagi M (1999c) Complete analysis of genes and enzymes for γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:380–390
Nagata Y, Prokop Z, Sato Y, Jerabek P, Kumar A, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Damborsky J (2005) Degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2183–2185
Nigam U, Siddqui KJ (2001) Organochlorine insecticide residues in dairy milk samples collected in Lucknow, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66:678–682
Sahu SK, Patnaik KK, Sharmila M, Sethunathan N (1990) Degradation of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane by a soil bacterium under aerobic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3620–3622
Selvaraj G, Iyer VN (1983) Suicide plasmid vehicles for insertion mutagenesis in Rhizobium meliloti and related bacteria. J Bacteriol 156:1292–1300
Smatanova I, Nagata Y, Svensson LA, Takagi M, Marek J (1999) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr D55:1231–1233
Suar M, Hauser A, Poiger T, Buser HR, Muller MD, Dogra C, Raina V, van der Holliger C (2005) Enantioselective transformation of alpha-hexachlorocyclohexane by the dehydrochlorinases LinA1 and LinA2 from the soil bacterium Sphingomonas paucimobilis B90A. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8514–8518
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Y. Nagata, Tohoku University, for providing the authentic mass spectrum of β-PCHL. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (projects nos. 40471073 and 30400013), the 863 hi-tech research and development program of Ministry of Science and Technology [projects nos. 2003AA241150, 2004AA246070, 2004(249), and 2004(514)] and the hi-tech research program of JiangSu Science & Technology Department of The People’s Republic of China (project nos. BE2002345, BE2003343, and BG2005322).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Hong, Q., Han, P. et al. A gene linB2 responsible for the conversion of β-HCH and 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorocyclohexanol in Sphingomonas sp. BHC-A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 1097–1105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0579-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0579-z