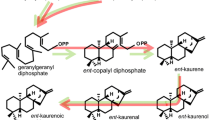
Abstract
This review focuses on studies with bacteria for which biosynthesis/production of the plant hormones gibberellins have been demonstrated. Actual data on gibberellin metabolism by bacteria are analyzed in comparison with the biosynthetic pathways known for vascular plants and fungi. The potential involvement of gibberellins produced by symbiotic and soil-endophytic microorganisms in plant growth promotion and yield increase is also discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atzorn R, Crozier A, Wheeler C, Sandberg G (1988) Production of gibberellins and Indole 3-acetic acid by Rhizobium phaseoli in relation to nodulation of Phaseolus vulgaris roots. Planta 175:532–538
Bashan Y, Levanony H (1990) Current status of Azospirillum inoculation technology: Azopirillum as a challenge for agriculture. Can J Microbiol 36:591–608
Bastián F, Cohen A, Piccoli P, Luna V, Baraldi R, Bottini R (1998) Production of indole-3-acetic acid and gibberellins A1 and A3 by Acetobacter diazotrophicus and Herbaspirillum seropedicae in chemically-defined culture media. Plant Growth Regul 24:7–11
Bastián F, Rapparini F, Baraldi R, Piccoli P, Bottini R (1999) Inoculation with Acetobacter diazotrophicus increases glucose and fructose content in shoots of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Symbiosis 27:147–156
Bottini R, Luna V (1993) Bud dormancy in deciduous fruit trees. Curr Top Plant Physiol 1:147–159
Bottini R, Fulchieri M, Pearce D, Pharis RP (1989) Identification of Gibberellins A1, A3, and isoA3 in cultures of Azospirillum lipoferum. Plant Physiol 90:45–47
Cacciari I, Lippi D, Pietrosanti T (1989) Phytohormone-like substances produced by single and mixed diazotrophic cultures of Azospirillum sp. and Arthrobacter. Plant Soil 115:151–153
Candau R, Avalos J, Cerdá-Olmedo E (1992) Regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis in Gibberella fujikuroi. Plant Physiol 100:1184–1188
Cassán F (2003) Activación de giberelinas in vivo por bacterias endofíticas a través de la deconjugación de glucosíl conjugados y la 3β-hidroxilación. PhD Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto
Cassán F, Bottini R, Schneider G, Piccoli P (2001a) Azospirillum brasilense and Azospirillum lipoferum hydrolyze conjugates of GA20 and metabolize the resultant aglycones to GA1 in seedlings of rice dwarf mutants. Plant Physiol 125:2053–2058
Cassán F, Lucangeli C, Bottini R, Piccoli P (2001b) Azospirillum spp. Metabolize [17,17-2H2]Gibberellin A20 to [17,17-2H2]Gibberellin A1 in vivo in dy rice mutant seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 42:763–767
Cassán FD, Piccoli P, Bottini R (2003) Promoción del crecimiento vegetal por Azospirillum sp. a través de la producción de giberelinas. Un modelo alternativo para incrementar la producción agrícola. In: Albanesi A, Kunst C, Anriquez A, Luna S, Ledesma R (eds) Microbiología Agrícola. Un aporte de la investigación en Argentina para la sociedad. Universidad Nacional de Santiago del Estero, Santiago, pp 1–16
Cohen A, Travaglia C, Reinoso H, Piccoli P, Bottini R (2001) Azospirillum inoculation and inhibition of gibberellin and ABA synthesis in maize seedlings under drought. Proc Plant Growth Regul Soc Am 28:88–93
Creus C, Sueldo R, Barassi C (1997) Shoot growth and water status in Azospirillum-inoculated wheat seedlings grown under osmotic and salt stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:939–944
Crozier A, Kamiya Y, Bishop G, Yokota T (2000) Biosynthesis of hormones and elicitor molecules. In: Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiology, Rockville, pp 850–929
Curtis PJ, Cross BE (1954) Gibberellic acid. A new metabolite from the culture filtrates of Gibberella fujikuroi. Chem Ind 1066
Davies PJ (1995) The plant hormones: their nature, occurrence and functions. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones. Physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1–12
De-Polli H, Matsui E, Döbereiner J, Salatti E (1977) Confirmation of nitrogen fixation in two tipical grasses by 15N2 incorporation. Soil Biol Biochem 9:119–123
Dobert RC, Rood SB, Blevins DG (1992) Gibberellins and the legume-Rhizobium symbiosis. I. Endogenous gibberellins of lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) stems and nodules. Plant Physiol 98:221–224
Döbereiner J, Mariel IE, Nery M (1976) Ecological distribution of Spirillum lipoferum Beinjerick. Can J Microbiol 22:1464–1473
Flouri F, Sini K, Balis C (1995) Interactions between Azospirillum and Phialophora radicicola. NATO ASI Ser G 37:231–237
Fulchieri M, Lucangeli C, Bottini R (1993) Inoculation with Azospirillum lipoferum affects growth and gibberellin status of corn seedling roots. Plant Cell Physiol 34:1305–1309
Glick BR, Patten CL, Holquin G, Penrose DM (1999) Biochemical and genetic mechanisms used by plant growth promoting bacteria. Imperial College, London
Gutiérrez-Mañero F, Ramos-Solano B, Probanza A, Mehouachi J, Tadeo FR, Talon M (2001) The plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus licheniformis produce high amounts of physiologically active gibberellins. Physiol Plant 111:206–211
Hedden P, Phillips A (2000) Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed genes. Trends Plant Sci 5:523–530
Janzen R, Rood S, Dormar J, McGill W (1992) Azospirillum brasilense produces gibberellins in pure culture and chemically-medium and in co-culture on straw. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1061–1064
King RW, Evans LT (2003) Gibberellins and flowering of grasses and cereals: prising open the lid of the “Florigen” black box. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 54:307–328
Kucey RMN (1988) Plant growth-altering effects of Azospirillum brasilense and Bacillus C-11-25 on two wheat cultivars. J Appl Bacteriol 64:187–196
Linnemannstöns P, Voß T, Hedden P, Gaskin P, Tudzynski B (1999) Deletions in the gibberellin biosynthesis gene cluster of Gibberella fujikuroi by restriction enzyme-mediated integration and conventional transformation-mediated mutagenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2558–2564
Litchtenthaler HK (1999) The 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Phsyiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–65
Lucangeli C, Bottini R (1996) Reversion of dwarfism in dwarf-1 maize (Zea mays L.) and dwarf-x rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutants by endophytic Azospirillum spp. Biocell 20:223–228
Lucangeli C, Bottini R (1997) Effects of Azospirillum spp. on endogenous gibberellin content and growth of maize (Zea mays L.) treated with uniconazole. Symbiosis 23:63–72
Ludden PW, Okon Y, Burris RH (1978) The nitrogenase system of Spirillum lipoferum. Biochem J 173:1001–1003
MacMillan J (1997) Biosynthesis of the gibberellin plant hormones. Nat Prod Rep 14:221–243
MacMillan J (2002) Occurrence of gibberellins in vascular plants, fungi and bacteria. J Plant Growth Regul 20:387–442
Macmillan J, Suter PJ (1958) The occurrence of gibberellin A1 in higher plants: isolation from the seed of runner bean (Phaseolus multiflorus). Naturwissenschaften 45:46
Mende K, Homann V, Tudzynski B (1997) The geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase gene of Gibberella fujikuroi: isolation and expression. Mol Gen Genet 255:96–105
Okon Y, Labandera-González C (1994) Agronomic applications of Azospirillum: an evaluation of 20 years worldwide field inoculation. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1591–1601
Okon Y, Albrecht SL, Burris RH (1976a) Factors affecting growth and nitrogen fixation of Spirillum lipoferum. J Bacteriol 127:1248–1254
Okon Y, Albrecht SL, Burris RH (1976b) Carbon and ammonia metabolism of Spirillum lipoferum. J Bacteriol 128:592–597
Pharis RP, King RW (1985) Gibberellins and reproductive development in seed plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 36:517–568
Piccoli P, Bottini R (1994a) Metabolism of 17,17-[2H2]gibberellin A20 to 17,17-[2H2]gibberellin A1 by Azospirillum lipoferum cultures. AgriScientia XI:13–15
Piccoli P, Bottini R (1994b) Effects of C/N relationships, N content, pH, and time of culture on growth and gtibberellin production of Azospirillum lipoferum cultures. Symbiosis 17:229–236
Piccoli P, Bottini R (1996) Light enhancement of gibberellin production by Azospirillum lipoferum cultures. Biocell 20:200–207
Piccoli P, Masciarelli O, Bottini R (1996) Metabolism of 17,17[2H2]-Gibberellins A4, A9, and A20 by Azospirillum lipoferum in chemically-defined culture medium. Symbiosis 21:167–178
Piccoli P, Lucangeli D, Schneider G, Bottini R (1997) Hydrolysis of [17,17-2H2]Gibberellin A20-Glucoside and [17,17-2H2]Gibberellin A20-glucosyl ester by Azospirillum lipoferum cultured in a nitrogen-free biotin-based chemically-defined medium. Plant Growth Regul 23:179–182
Piccoli P, Masciarelli O, Bottini R (1999) Gibberellin Production by Azospirillum lipoferum cultured in chemically-defined medium as affected by oxygen availability and water status. Symbiosis 27:135–146
Probanza A, García JAL, Palomino MR, Ramos B, Manero FJG (2002) Pinus pinea L. seedling growth and bacterial rhizosphere structure after inoculation with PGPR Bacillus (B. licheniformis CECT 5106 and B. pumilus CECT 5105). Appl Soil Ecol 20:75–84
Reinoso H, Dauría C, Luna V, Pharis R, Bottini R (2002) Dormancy in peach (Prunus persica L.) flower buds VI. Effects of gibberellins and an acylcyclohexanedione (Cimectacarb) on bud morphogenesis in field experiments with orchard trees and on cuttings. Can J Bot 80:656–663
Rojas MC, Hedden P, Gaskin P, Tudzynski B (2001) The P450-1 gene of Gibberella fujikuroi encodes a multifunctional enzyme in gibberellin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5838–5843
Schneider G (1983) Gibberellin conjugates. In: Crozier A (ed) The biochemistry and physiology of gibberellins, vol 1. Praeger, New York, pp 389–456
Sponsel VM (2002) The deoxy xylulose phosphate pathway for the biosynthesis of plastidic isoprenoids: early days in our understanding of the early stages of gibberellin biosynthesis. J Plant Growth Regul 20:332–345
Sponsel VM (2003) Gibberellins. In: Henry HL, Norman AW (eds) Encyclopedia of hormones, vol 2. Academic, pp 29–40
Sponsel VM, Hedden P (2004) Gibberellin biosynthesis and catabolism. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones: biosynthesis, signal transduction, action! Kluwer, Dordrecht
Tamura S (1990) Historical aspects of gibberellins. In: Takahashi N, Phinney BO, MacMillan J (eds) Gibberellins. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–8
Tanimoto E (1987) Gibberellin-dependent root elongation in Lactuca sativa: recovery from growth retardant-suppressed elongation with thickening by low concentration of GA3. Plant Cell Physiol 28:963–973
Trewavas A (2000) Signal perception and transduction. In: Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiology, Rockville, pp 930–987
Tudzynski B, Hedden P, Carrera E, Gaskin P (2001) The P450-4 Gene of Gibberella fujikuroi encodes ent-kaurene oxidase in the gibberellin biosynthesis pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3514–3522
Tudzynski B, Rojas MC, Gaskin P, Hedden P (2002) The gibberellin 20-oxidase of Gibberella fujikuroi is a multifunctional monooxygenase. J Biol Chem 277:21246–21253
Tudzynski B, Mihlan M, Rojas MC, Linnemannstons P, Gaskin P, Hedden P (2003) Characterization of the final two genes of the gibberellin biosynthesis gene cluster of Gibberella fujikuroi: des and P450-3 encode GA4 desaturase and the 13-hydroxylase, respectively. J Biol Chem 278:28635–28643
Tully RE, van Berkum P, Lovins KW, Keister DL (1998) Identification and sequencing of a cytochrome P450 gene cluster from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1398:243–255
Yanni YG, Rizk RY, Abd El-Fattah FK, Squartini A, Corich V, Giacomini A, de Bruijn F, Rademaker J, Maya-Flores J, Ostrom P, Vega-Hernández M, Hollingsworth RI, Martínez-Molina E, Mateos P, Velázquez E, Wopereis J, Triplett E, Umali-García M, Anarna JA, Rolfe BG, Ladha JK, Hill J, Mujoo R, Ng PK, Dazzo FB (2001) The beneficial plant growth-promoting association of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii with rice roots. Funct Plant Biol 28:845–870
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bottini, R., Cassán, F. & Piccoli, P. Gibberellin production by bacteria and its involvement in plant growth promotion and yield increase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65, 497–503 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1696-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1696-1