Abstract
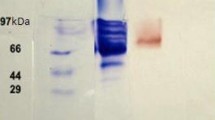
The white-rot fungus Daedalea quercina produced the ligninolytic enzymes laccase and Mn-dependent peroxidase. Laccase was purified using anionexchange and size-exclusion chromatographies. SDS-PAGE showed the purified laccase to be a monomeric protein of 69 kDa (71 kDa using gel filtration) with an isoelectric point near 3.0. The optimum pH for activity was bellow 2.0 for 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (K m=38 μM), 4.0 for 2,6-dimethoxyphenol (K m=48 μM), 4.5 for guaiacol (K m=93 μM) and 7.0 for syringaldazine (K m=131 μM). The temperature optimum was between 60 and 70 °C depending on the pH and buffer used. The enzyme was stable up to 45 °C, and stability was higher at alkaline pH. Enzyme activity was increased by the addition of Cu2+ and inhibited by Mn2+, sodium azide, dithiothreitol, and cysteine. Laccase from Daedalea quercina was able to decolorize the synthetic dyes Chicago sky blue, poly B-411, remazol brilliant blue R, trypan blue and reactive blue 2.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldrian P (2003) Interactions of heavy metals with white-rot fungi. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:78–91
Baldrian P, Gabriel J (2003) Lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus in the presence of cadmium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220:235–240
Chet I, Trojanowski J, Hüttermann A (1985) Decolourisation of the dye poly B-411 and its correlation with lignin degradation by fungi. Microbios Lett 29:37–43
Eggert C, Temp U, Eriksson K-EL (1996) The lignolytic system of the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: Purification and characterization of the laccase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1151–1158
Hatakka A (1994) Lignin-modifing enzymes from selected white-rot fungi: production and role in lignin degradation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:125–135
Katagiri N, Tsutsumi Y, Nishida T (1995) Correlation of brightening with cumulative enzyme activity related to lignin biodegradation during biobleaching of kraft pulp by white rot fungi in the solid-state fermentation system. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:617–622
Leonowicz A, Matuszewska A, Luterek J, Ziegenhagen D, Wojtas-Wasilewska M, Cho N-S, Hofrichter M, Rogalski J (1999) Biodegradation of lignin by white rot fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 27:175–185
Lo SC, Ho YS, Buswell JA (2001) Effect of phenolic monomers on the production of laccases by the edible mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju, and partial characterization of a major laccase component. Mycologia 93:413–421
Munoz C, Guillen F, Martinez AT, Martinez MJ. Induction and characterization of laccase in the ligninolytic fungus Pleurotus eryngii. Curr Microbiol 34:1–5
Nagai M, Sato T, Watanabe H, Saito K, Kawata M, Enei H (2002) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes, and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:327–335
Ngo TT, Lenhoff HM (1980) A sensitive and versatile chromogenic assay for peroxidase and peroxidase-coupled reactions. Anal Biochem 105:389–397
Niku-Paavola ML, Raaska L Itävaara M (1990) Detection of white rot fungi by a non-toxic stain. Mycol Res 94:27–31
Novotný Č, Vyas BRM, Erbanová P, Kubátová A, and Šašek V (1997) Removal of PCBs by various white rot fungi in liquid cultures. Folia Microbiol 42:136–140
Paszczynski A, Crawford RL (2000) Recent advances in the use of fungi in environmental remediation and biotechnology. Soil Biochem 10:379–422
Schliephake K, Mainwaring DE, Lonergan GT, Jones IK, Baker WL (2000) Transformation and degradation of the disazo dye Chicago Sky Blue by a purified laccase from Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:100–107
Thurston CF (1994) The structure and function of fungal laccases. Microbiology 140:19–26
Tien M, Kirk TK (1988) Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods Enzymol 161B:238–248
Xu F (1997) Effects of redox potential and hydroxide inhibition on the pH activity profile of fungal laccases. J Biol Chem 272:924–928
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Academy of Sciences (B5020202) and by the Institutional Research Concept no. AV0Z5020903 of the Institute of Microbiology, ASCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldrian, P. Purification and characterization of laccase from the white-rot fungus Daedalea quercina and decolorization of synthetic dyes by the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63, 560–563 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1434-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1434-0