Abstract
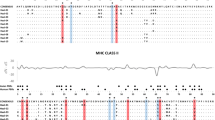
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is integral to the vertebrate adaptive immune system. Characterizing diversity at functional MHC genes is invaluable for elucidating patterns of adaptive variation in wild populations, and is particularly interesting in species of conservation concern, which may suffer from reduced genetic diversity and compromised disease resilience. Here, we use next generation sequencing to investigate MHC class II B (MHCIIB) diversity in two sister taxa of New Zealand birds: South Island saddleback (SIS), Philesturnus carunculatus, and North Island saddleback (NIS), Philesturnus rufusater. These two species represent a passerine family outside the more extensively studied Passerida infraorder, and both have experienced historic bottlenecks. We examined exon 2 sequence data from populations that represent the majority of genetic diversity remaining in each species. A high level of locus co-amplification was detected, with from 1 to 4 and 3 to 12 putative alleles per individual for South and North Island birds, respectively. We found strong evidence for historic balancing selection in peptide-binding regions of putative alleles, and we identified a cluster combining non-classical loci and pseudogene sequences from both species, although no sequences were shared between the species. Fewer total alleles and fewer alleles per bird in SIS may be a consequence of their more severe bottleneck history; however, overall nucleotide diversity was similar between the species. Our characterization of MHCIIB diversity in two closely related species of New Zealand saddlebacks provides an important step in understanding the mechanisms shaping MHC diversity in wild, bottlenecked populations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas AK, Lichtman AH (2001) Basic immunology: functions and disorders of the immune system. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia
Alcaide M, Edwards SV, Negro JJ (2007) Characterization, polymorphism, and evolution of MHC class IIB genes in birds of prey. J Mol Evol 65:541–554
Alley M, Hale K, Cash W, Ha H, Howe L (2010) Concurrent avian malaria and avipox virus infection in translocated South Island saddlebacks (Philesturnus carunculatus carunculatus). N Z Vet J 58:218–223
Altizer S, Harvell D, Friedle E (2003) Rapid evolutionary dynamics and disease threats to biodiversity. Trends Ecol Evol 18:589–596
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anmarkrud J, Johnsen A, Bachmann L, Lifjeld J (2010) Ancestral polymorphism in exon 2 of bluethroat (Luscinia svecica) MHC class II B genes. J Evol Biol 23:1206–1217
Babik W, Taberlet P, Ejsmond M, Radwan J (2009) New generation sequencers as a tool for genotyping of highly polymorphic multilocus MHC system. Mol Ecol Res 9:713–719
Barker FK, Cibois A, Schikler P, Feinstein J, Cracraft J (2004) Phylogeny and diversification of the largest avian radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11040–11045
Bernatchez L, Landry C (2003) MHC studies in nonmodel vertebrates: what have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J Evol Biol 16:363–377
Binladen J, Gilbert M, Bollback J, Panitz F, Bendixen C, Nielsen R, Willerslev E (2007) The use of coded PCR primers enables high-throughput sequencing of multiple homolog amplification products by 454 parallel sequencing. PLoS One 2:e197
Blankenberg D, Gordon A, Von Kuster G, Coraor N, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A (2010) Manipulation of FASTQ data with Galaxy. Bioinformatics 26:1783–1785
Bollmer JL, Dunn PO, Whittingham LA, Wimpee C (2010) Extensive MHC class II B gene duplication in a passerine, the common yellowthroat (Geothlypis trichas). J Hered 101:448–460
Borg ÅA, Pedersen SA, Jensen H, Westerdahl H (2011) Variation in MHC genotypes in two populations of house sparrow (Passer domesticus) with different population histories. Ecol Evol 1:145–159
Brown J, Jardetzky T, Gorga J, Stern L, Urban R, Strominger J, Wiley D (1993) 3-Dimensional structure of the human class-II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature 364:33–39
Burri R, Hirzel HN, Salamin N, Roulin A, Fumagalli L (2008) Evolutionary patterns of MHC class II B in owls and their implications for the understanding of avian MHC evolution. Mol Biol Evol 25:1180–1191
Burri R, Salamin N, Studer RA, Roulin A, Fumagalli L (2010) Adaptive divergence of ancient gene duplicates in the avian MHC class II β. Mol Biol Evol 27:2360–2374
Canal D, Alcaide M, Anmarkrud J, Potti J (2010) Towards the simplification of MHC typing protocols: targeting classical MHC class II genes in a passerine, the pied flycatcher Ficedula hypoleuca. BMC Res Notes 3:236
Casquet J, Thebaud C, Gillespie RG (2012) Chelex without boiling, a rapid and easy technique to obtain stable amplifiable DNA from small amounts of ethanol–stored spiders. Mol Ecol Resour 12:136–141
Cooper A, Poinar HN (2000) Ancient DNA: do it right or not at all. Science 289:1139–1139
Delport W, Poon AFY, Frost SDW, Pond SLK (2010) Datamonkey 2010: a suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 26:2455–2457
Drummond A, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A, Duran C, Field M, Heled J, Kearse M, Markowitz S, Moir R, Stones-Havas S, Sturrock S, Thierer T, Wilson A (2012) Geneious v5.6.5 created by Biomatters. Available from http://www.geneious.com
Edwards SV, Grahn M, Potts WK (1995a) Dynamics of Mhc evolution in birds and crocodilians: amplification of class II genes with degenerate primers. Mol Ecol 4:719–729
Edwards SV, Wakeland E, Potts W (1995b) Contrasting histories of avian and mammalian Mhc genes revealed by class II B sequences from songbirds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:12200–12204
Edwards SV, Gasper J, March M (1998) Genomics and polymorphism of Agph-DAB1, an Mhc class II B gene in red-winged blackbirds (Agelaius phoeniceus). Mol Biol Evol 15:236–250
Edwards SV, Hess CM, Gasper J, Garrigan D (1999) Toward an evolutionary genomics of the avian Mhc. Immunol Rev 167:119–132
Eimes J, Bollmer J, Dunn P, Whittingham L, Wimpee C (2010) MHC class II diversity and balancing selection in greater prairie-chickens. Genetica 138:265–271
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Ewing B, Hillier LD, Wendl MC, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Falk K, Rötzschke O, Stevanovié S, Jung G, Rammensee HG (1991) Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature 351:290–296
Galan M, Guivier E, Caraux G, Charbonnel N, Cosson J-F (2010) A 454 multiplex sequencing method for rapid and reliable genotyping of highly polymorphic genes in large-scale studies. BMC Genomics 11:296
Garrigan D, Hedrick PW (2003) Perspective: detecting adaptive molecular polymorphism: lessons from the MHC. Evolution 57:1707–1722
Giardine B, Riemer C, Hardison RC, Burhans R, Elnitski L, Shah P, Zhang Y, Blankenberg D, Albert I, Taylor J (2005) Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res 15:1451–1455
Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J (2010) Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol 11:R86
Hale K (2008) Disease outbreak amongst South Island saddlebacks (Philesturnus carunculatus carunculatus) on Long Island. DOC Research & Development Series 289. Department of Conservation, Wellington, New Zealand
Hale K, Briskie J (2009) Rapid recovery of an island population of the threatened South Island Saddleback Philesturnus c. carunculatus after a pathogen outbreak. Bird Conserv Int 19:239–253
Heather B, Robertson H (1996) The field guide to the birds of New Zealand. Viking, Auckland
Hedrick PW (1994) Evolutionary genetics of the major histocompatibility complex. Am Nat 143:945–964
Hess CM, Edwards SV (2002) The evolution of the major histocompatibility complex in birds. Bioscience 52:423–431
Hooson S, Jamieson IG (2003) The distribution and current status of New Zealand saddleback Philesturnus carunculatus. Bird Conserv Int 13:79–95
Huelsenbeck J, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Hughes A, Nei M (1988) Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature 335:167–170
Hughes A, Nei M (1989) Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:958–962
Hughes A, Yeager M (1998) Natural selection at the major histocompatibility complex loci of vertebrates. Annu Rev Genet 32:415–435
Ikemura T (1985) Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol 2:13–34
Judo MSB, Wedel AB, Wilson C (1998) Stimulation and suppression of PCR-mediated recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1819–1825
Kalbe M, Eizaguirre C, Dankert I, Reusch TBH, Sommerfeld RD, Wegner KM, Milinski M (2009) Lifetime reproductive success is maximized with optimal major histocompatibility complex diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 276:925
Kanagawa T (2003) Bias and artifacts in multitemplate polymerase chain reactions (PCR). J Biosci Bioeng 96:317–323
Kosakovsky Pond SL, Frost SDW (2005) Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol Biol Evol 22:1208–1222
Kosakovsky Pond SL, Frost SDW, Muse SV (2005) HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 21:676–679
Kosakovsky Pond SL, Posada D, Gravenor MB, Woelk CH, Frost SDW (2006) GARD: a genetic algorithm for recombination detection. Bioinformatics 22:3096–3098
Lambert D, King T, Shepherd L, Livingston A, Anderson S, Craig J (2005) Serial population bottlenecks and genetic variation: translocated populations of the New Zealand saddleback (Philesturnus carunculatus rufusater). Conserv Genet 6:1–14
Learn B, Graftstrom R (1989) Methyl-directed repair of frameshift heteroduplexes in cell extracts from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 171:6473–6481
Lenz TL, Becker S (2008) Simple approach to reduce PCR artefact formation leads to reliable genotyping of MHC and other highly polymorphic loci—implications for evolutionary analysis. Gene 427:117–123
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Matsumura M, Fremont DH, Peterson PA, Wilson IA (1992) Emerging principles for the recognition of peptide antigens by MHC class I molecules. Science 257:927–934
Meglécz E, Piry S, Desmarais E, Galan M, Gilles A, Guivier E, Pech N, Martin JF (2011) SESAME (SEquence Sorter & AMplicon Explorer): genotyping based on high-throughput multiplex amplicon sequencing. Bioinformatics 27:277–278
Meyer M, Stenzel U, Hofreiter M (2008) Parallel tagged sequencing on the 454 platform. Nat Protoc 3:267–278
Miller HC, Lambert DM (2004a) Gene duplication and gene conversion in class II MHC genes of New Zealand robins (Petroicidae). Immunogenetics 56:178–191
Miller HC, Lambert DM (2004b) Genetic drift outweighs balancing selection in shaping post-bottleneck major histocompatibility complex variation in New Zealand robins (Petroicidae). Mol Ecol 13:3709–3721
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Piertney SB, Oliver MK (2006) The evolutionary ecology of the major histocompatibility complex. Heredity 96:7–21
Promerová M, Babik W, Bryja J, Albrecht T, Stuglik M, Radwan J (2011) Evaluation of two approaches to genotyping major histocompatibility complex class I in a passerine—CE-SSCP and 454 pyrosequencing. Mol Ecol Resour 12:285–292
Rothberg JM, Hinz W, Rearick TM, Schultz J, Mileski W, Davey M, Leamon JH, Johnson K, Milgrew MJ, Edwards M, Hoon J, Simons JF, Marran D, Myers JW, Davidson JF, Branting A, Nobile JR, Puc BP, Light D, Clark TA, Huber M, Branciforte JT, Stoner IB, Cawley SE, Lyons M, Fu Y, Homer N, Sedova M, Miao X, Reed B, Sabina J, Feierstein E, Schorn M, Alanjary M, Dimalanta E, Dressman D, Kasinskas R, Sokolsky T, Fidanza JA, Namsaraev E, McKernan KJ, Williams A, Roth GT, Bustillo J (2011) An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing. Nature 475:348–352
Sepil I, Moghadam HK, Huchard E, Sheldon BC (2012) Characterization and 454 pyrosequencing of major histocompatibility complex class I genes in the great tit reveal complexity in a passerine system. BMC Evol Biol 12:68
Seutin G, White BN, Boag PT (1991) Preservation of avian blood and tissue samples for DNA analyses. Can J Zool 69:82–90
Sharp PM, Li WH (1987) The rate of synonymous substitution in enterobacterial genes is inversely related to codon usage bias. Mol Biol Evol 4:222–230
Sommer S (2005) The importance of immune gene variability (MHC) in evolutionary ecology and conservation. Front Zool 2:1–18
Spurgin L, Richardson D (2010) How pathogens drive genetic diversity: MHC, mechanisms and misunderstandings. Proc R Soc B (Biol Sci) 277:979–988
Sutton JT, Nakagawa S, Robertson BC, Jamieson IG (2011) Disentangling the roles of natural selection and genetic drift in shaping variation at MHC immunity genes. Mol Ecol 20:4408–4420
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Taylor SS, Jamieson IG (2008) No evidence for loss of genetic variation following sequential translocations in extant populations of a genetically depauperate species. Mol Ecol 17:545–556
Taylor SS, Jamieson IG, Wallis GP (2007) Historic and contemporary levels of genetic variation in two New Zealand passerines with different histories of decline. J Evol Biol 20:2035–2047
Thompson J, Higgins D, Gibson T (1994) CLUSTAL-W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thompson JR, Marcelino LA, Polz MF (2002) Heteroduplexes in mixed-template amplifications: formation, consequence and elimination by ‘reconditioning PCR’. Nucleic Acids Res 30:2083–2088
Walsh PS, Metzger DA, Higuchi R (1991) Chelex-100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques 10:506–513
Wegner KM, Kalbe M, Kurtz J, Reusch TBH, Milinski M (2003) Parasite selection for immunogenetic optimality. Science 301:1343–1343
Wittzell H, Bernot A, Auffray C, Zoorob R (1999) Concerted evolution of two MHC class II B loci in pheasants and domestic chickens. Mol Biol Evol 16:479–490
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591
Yang Z, Bielawski JP (2000) Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol 15:496–503
Yuhki N, O'Brien SJ (1990) DNA variation of the mammalian major histocompatibility complex reflects genomic diversity and population history. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:836–840
Zagalska-Neubauer M, Babik W, Stuglik M, Gustafsson L, Cichon M, Radwan J (2010) 454 sequencing reveals extreme complexity of the class II major histocompatibility complex in the collared flycatcher. BMC Evol Biol 10:395
Zylstra P, Rothenfluh HS, Weiller GF, Blanden RV, Steele EJ (1998) PCR amplification of murine immunoglobulin germline V genes: strategies for minimization of recombination artefacts. Immunol Cell Biol 76:395–405
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Sabrina Taylor, Craig Millar, and Kevin Parker for providing blood samples from contemporary specimens. Canterbury Museum, American Museum of Natural History, and Naturhistorisches Museum Wien graciously supplied toepad samples from historic specimens (Accessions AV.309, 669746, NMW52.593, and NMW51.174). We are very grateful to Martyn Kennedy for input regarding phylogenetic analysis. Three anonymous reviewers provided constructive comments that greatly improved the manuscript. This research was funded by Landcare Research (contract no. C09X0503), University of Otago, and Allan Wilson Centre for Molecular Ecology and Evolution. J. Sutton is supported by scholarships from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and New Zealand Ministry of Education (NZIDRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 2.03 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sutton, J.T., Robertson, B.C., Grueber, C.E. et al. Characterization of MHC class II B polymorphism in bottlenecked New Zealand saddlebacks reveals low levels of genetic diversity. Immunogenetics 65, 619–633 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0708-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0708-7