Abstract
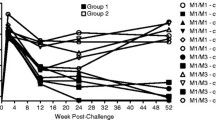
Experimental infection of Mauritian cynomolgus macaques by simian immunodeficiency virus is a representative model of HIV infection, currently in favour for evaluating the efficacy of new preventive or curative treatments. Extensive studies of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) polymorphism by microsatellites revealed seven haplotypes (H1–H7). We present statistical evidence of the influence of MHC polymorphism on the set-point plasma viral load (PVL). Our analysis was based on the study of 45 Mauritian cynomolgus macaques inoculated by intravenous or intrarectal injection of a 50 AID50 dose of the SIVmac251 virus. The animals received no treatment before or after the inoculation. MHC polymorphism was investigated by means of 20 microsatellites distributed across the MHC and by DRB genotyping using the DGGE sequencing method. Statistical analysis with Unphased software revealed that two markers located in the class IB region significantly influenced the Log PVL and that three class IB haplotypes were significantly associated with lower (H2 or H6) or higher (H4) set-point Log PVL values. Although the impact of MHC on Log PVL was found to be low (around one Log10), it is important to dispose of animals paired for their MHC genotypes, each animal tested for a given treatment and its untreated control, to minimize the influence of the MHC and clearly reveal the effect of the treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bimber BN, Moreland AJ, Wiseman RW, Hughes AL, O’Connor DH (2008) Complete characterization of killer Ig-like receptor (KIR) haplotypes in Mauritian cynomolgus macaques: novel insights into nonhuman primate KIR gene content and organization. J Immunol 181:6301–6308
Blancher A, Bonhomme M, Crouau-Roy B, Terao K, Kitano T, Saitou N (2008) Mitochondrial DNA sequence phylogeny of 4 populations of the widely distributed cynomolgus macaque (Macaca fascicularis fascicularis). J Hered 99:254–264
Blancher A, Tisseyre P, Dutaur M, Apoil PA, Maurer C, Quesniaux V, Raulf F, Bigaud M, Abbal M (2006) Study of cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis) MhcDRB (Mafa-DRB) polymorphism in two populations. Immunogenetics 58:269–282
Bonhomme M, Blancher A, Jalil MF, Crouau-Roy B (2007) Factors shaping genetic variation in the MHC of natural non-human primate populations. Tissue Antigens 70:398–411
Budde ML, Wiseman RW, Karl JA, Hanczaruk B, Simen BB, O’Connor DH (2010) Characterization of Mauritian cynomolgus macaque major histocompatibility complex class I haplotypes by high-resolution pyrosequencing. Immunogenetics 62(11–12):773–780. doi:10.1007/s00251-010-0481-9
Cafaro A, Bellino S, Titti F, Maggiorella MT, Sernicola L, Wiseman RW, Venzon D, Karl JA, O’Connor D, Monini P, Robert-Guroff M, Ensoli B (2010) Impact of viral dose and major histocompatibility complex class IB haplotype on viral outcome in Mauritian cynomolgus monkeys vaccinated with Tat upon challenge with simian/human immunodeficiency virus SHIV89.6P. J Virol 84:8953–8958
Dudbridge F (2008) Likelihood-based association analysis for nuclear families and unrelated subjects with missing genotype data. Hum Hered 66:87–98
Evans DT, Knapp LA, Jing P, Mitchen JL, Dykhuizen M, Montefiori DC, Pauza CD, Watkins DI (1999) Rapid and slow progressors differ by a single MHC class I haplotype in a family of MHC-defined rhesus macaques infected with SIV. Immunol Lett 66:53–59
Fellay J, Ge D, Shianna KV, Colombo S, Ledergerber B, Cirulli ET, Urban TJ, Zhang K, Gumbs CE, Smith JP, Castagna A, Cozzi-Lepri A, De Luca A, Easterbrook P, Gunthard HF, Mallal S, Mussini C, Dalmau J, Martinez-Picado J, Miro JM, Obel N, Wolinsky SM, Martinson JJ, Detels R, Margolick JB, Jacobson LP, Descombes P, Antonarakis SE, Beckmann JS, O’Brien SJ, Letvin NL, McMichael AJ, Haynes BF, Carrington M, Feng S, Telenti A, Goldstein DB (2009) Common genetic variation and the control of HIV-1 in humans. PLoS Genet 5:e1000791
Fellay J, Shianna KV, Ge D, Colombo S, Ledergerber B, Weale M, Zhang K, Gumbs C, Castagna A, Cossarizza A, Cozzi-Lepri A, De Luca A, Easterbrook P, Francioli P, Mallal S, Martinez-Picado J, Miro JM, Obel N, Smith JP, Wyniger J, Descombes P, Antonarakis SE, Letvin NL, McMichael AJ, Haynes BF, Telenti A, Goldstein DB (2007) A whole-genome association study of major determinants for host control of HIV-1. Science 317:944–947
Florese RH, Wiseman RW, Venzon D, Karl JA, Demberg T, Larsen K, Flanary L, Kalyanaraman VS, Pal R, Titti F, Patterson LJ, Heath MJ, O’Connor DH, Cafaro A, Ensoli B, Robert-Guroff M (2008) Comparative study of Tat vaccine regimens in Mauritian cynomolgus and Indian rhesus macaques: influence of Mauritian MHC haplotypes on susceptibility/resistance to SHIV(89.6P) infection. Vaccine 26:3312–3321
Giraldo-Vela JP, Rudersdorf R, Chung C, Qi Y, Wallace LT, Bimber B, Borchardt GJ, Fisk DL, Glidden CE, Loffredo JT, Piaskowski SM, Furlott JR, Morales-Martinez JP, Wilson NA, Rehrauer WM, Lifson JD, Carrington M, Watkins DI (2008) The major histocompatibility complex class II alleles Mamu-DRB1*1003 and -DRB1*0306 are enriched in a cohort of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaque elite controllers. J Virol 82:859–870
Goulder PJ, Watkins DI (2008) Impact of MHC class I diversity on immune control of immunodeficiency virus replication. Nat Rev Immunol 8:619–630
Houghton P (1988) Virus-free African cynomolgus macaques. Lab Animal 70:36–40
Karl JA, Wiseman RW, Campbell KJ, Blasky AJ, Hughes AL, Ferguson B, Read DS, O’Connor DH (2008) Identification of MHC class I sequences in Chinese-origin rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 60:37–46
Karlsson I, Malleret B, Brochard P, Delache B, Calvo J, Le Grand R, Vaslin B (2007) Dynamics of T-cell responses and memory T cells during primary simian immunodeficiency virus infection in cynomolgus macaques. J Virol 81:13456–13468
Lawler SH, Sussman RW, Taylor LL (1995) Mitochondrial DNA of the Mauritian macaques (Macaca fascicularis): an example of the founder effect. Am J Phys Anthropol 96:133–141
Ling B, Veazey RS, Luckay A, Penedo C, Xu K, Lifson JD, Marx PA (2002) SIV(mac) pathogenesis in rhesus macaques of Chinese and Indian origin compared with primary HIV infections in humans. AIDS 16:1489–1496
Loffredo JT, Bean AT, Beal DR, Leon EJ, May GE, Piaskowski SM, Furlott JR, Reed J, Musani SK, Rakasz EG, Friedrich TC, Wilson NA, Allison DB, Watkins DI (2008) Patterns of CD8+ immunodominance may influence the ability of Mamu-B*08-positive macaques to naturally control simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 replication. J Virol 82:1723–1738
Loffredo JT, Maxwell J, Qi Y, Glidden CE, Borchardt GJ, Soma T, Bean AT, Beal DR, Wilson NA, Rehrauer WM, Lifson JD, Carrington M, Watkins DI (2007) Mamu-B*08-positive macaques control simian immunodeficiency virus replication. J Virol 81:8827–8832
Maness NJ, Yant LJ, Chung C, Loffredo JT, Friedrich TC, Piaskowski SM, Furlott J, May GE, Soma T, Leon EJ, Wilson NA, Piontkivska H, Hughes AL, Sidney J, Sette A, Watkins DI (2008) Comprehensive immunological evaluation reveals surprisingly few differences between elite controller and progressor Mamu-B*17-positive simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques. J Virol 82:5245–5254
Matsubayashi K, Gotoh S, Kawamoto Y, Watanabe T, Nozawa K, Takasaka M, Narita T, Griffiths O, Stanley MA (1992) Clinical examinations on crab-eating macaques in Mauritius. Primates 33:281–288
Mee ET, Badhan A, Karl JA, Wiseman RW, Cutler K, Knapp LA, Almond N, O’Connor DH, Rose NJ (2009a) MHC haplotype frequencies in a UK breeding colony of Mauritian cynomolgus macaques mirror those found in a distinct population from the same geographic origin. J Med Primatol 38:1–14
Mee ET, Berry N, Ham C, Aubertin A, Lines J, Hall J, Stebbings R, Page M, Almond N, Rose NJ (2010) Mhc haplotype M3 is associated with early control of SHIVsbg infection in Mauritian cynomolgus macaques. Tissue Antigens 76:223–229
Mee ET, Berry N, Ham C, Sauermann U, Maggiorella MT, Martinon F, Verschoor EJ, Heeney JL, Le Grand R, Titti F, Almond N, Rose NJ (2009b) Mhc haplotype H6 is associated with sustained control of SIVmac251 infection in Mauritian cynomolgus macaques. Immunogenetics 61:327–339
Muhl T, Krawczak M, Ten Haaft P, Hunsmann G, Sauermann U (2002) MHC class I alleles influence set-point viral load and survival time in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. J Immunol 169:3438–3446
O’Connor DH, Mothe BR, Weinfurter JT, Fuenger S, Rehrauer WM, Jing P, Rudersdorf RR, Liebl ME, Krebs K, Vasquez J, Dodds E, Loffredo J, Martin S, McDermott AB, Allen TM, Wang C, Doxiadis GG, Montefiori DC, Hughes A, Burton DR, Allison DB, Wolinsky SM, Bontrop R, Picker LJ, Watkins DI (2003) Major histocompatibility complex class I alleles associated with slow simian immunodeficiency virus disease progression bind epitopes recognized by dominant acute-phase cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte responses. J Virol 77:9029–9040
Sauermann U, Siddiqui R, Suh YS, Platzer M, Leuchte N, Meyer H, Matz-Rensing K, Stoiber H, Nurnberg P, Hunsmann G, Stahl-Hennig C, Krawczak M (2008) Mhc class I haplotypes associated with survival time in simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected rhesus macaques. Genes Immun 9:69–80
Sauermann U, Stahl-Hennig C, Stolte N, Muhl T, Krawczak M, Spring M, Fuchs D, Kaup FJ, Hunsmann G, Sopper S (2000) Homozygosity for a conserved Mhc class II DQ-DRB haplotype is associated with rapid disease progression in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques: results from a prospective study. J Infect Dis 182:716–724
Smith SM, Holland B, Russo C, Dailey PJ, Marx PA, Connor RI (1999) Retrospective analysis of viral load and SIV antibody responses in rhesus macaques infected with pathogenic SIV: predictive value for disease progression. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 15:1691–1701
Trichel AM, Rajakumar PA, Murphey-Corb M (2002) Species-specific variation in SIV disease progression between Chinese and Indian subspecies of rhesus macaque. J Med Primatol 31:171–178
Watanabe A, Shiina T, Shimizu S, Hosomichi K, Yanagiya K, Kita YF, Kimura T, Soeda E, Torii R, Ogasawara K, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2007) A BAC-based contig map of the cynomolgus macaque (Macaca fascicularis) major histocompatibility complex genomic region. Genomics 89:402–412
Wiseman RW, Wojcechowskyj JA, Greene JM, Blasky AJ, Gopon T, Soma T, Friedrich TC, O’Connor SL, O’Connor DH (2007) Simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 infection of major histocompatibility complex-identical cynomolgus macaques from Mauritius. J Virol 81:349–361
Wojcechowskyj JA, Yant LJ, Wiseman RW, O’Connor SL, O’Connor DH (2007) Control of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 is not predicted by inheritance of Mamu-B*17-containing haplotypes. J Virol 81:406–410
Yant LJ, Friedrich TC, Johnson RC, May GE, Maness NJ, Enz AM, Lifson JD, O’Connor DH, Carrington M, Watkins DI (2006) The high-frequency major histocompatibility complex class I allele Mamu-B*17 is associated with control of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 replication. J Virol 80:5074–5077
Acknowledgements
We are pleased to thank Béatrice Atlan, Audrey Dauba, Stéphanie Despiau-Schiavinato and Sylvie Hébrard, Benoit Delache and Patricia Brochard for their excellent technical assistance. We thank Takashi Shiina for the location of the markers on the cynomolgus MHC map. We thank also Christophe Joubert and the animal facility staff of the CEA. We thank the Agence Nationale de Recherches sur le SIDA et les Hépatites Virales (ANRS) for its financial support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aarnink, A., Dereuddre-Bosquet, N., Vaslin, B. et al. Influence of the MHC genotype on the progression of experimental SIV infection in the Mauritian cynomolgus macaque. Immunogenetics 63, 267–274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-010-0504-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-010-0504-6