Abstract
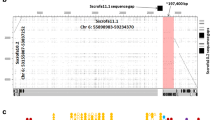
Genome analysis of the swine leukocyte antigen (SLA) region is needed to obtain information on the MHC genomic sequence similarities and differences between the swine and human, given the possible use of swine organs for xenotransplantation. Here, the genomic sequences of a 433-kb segment located between the non-classical and classical SLA class I gene clusters were determined and analyzed for gene organization and contents of repetitive sequences. The genomic organization and diversity of this swine non-class I gene region was compared with the orthologous region of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex. The length of the fully sequenced SLA genomic segment was 433 kb compared with 595 kb in the corresponding HLA class I region. This 162-kb difference in size between the swine and human genomic segments can be explained by indel activity, and the greater variety and density of repetitive sequences within the human MHC. Twenty-one swine genes with strong sequence similarity to the corresponding human genes were identified, with the gene order from the centromere to telomere of HCR - SPR1 - SEEK1 - CDSN - STG - DPCR1 - KIAA1885 - TFIIH - DDR - IER3 - FLOT1 - TUBB - KIAA0170 - NRM - KIAA1949 - DDX16 - FLJ13158 - MRPS18B - FB19 - ABCFI - CAT56. The human SEEK1 and DPCR1 genes are pseudogenes in swine. We conclude that the swine non-class I gene region that we have sequenced is highly conserved and therefore homologous to the corresponding region located between the HLA-C and HLA-E genes in the human.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadou C (1999) Evolution of the MHC class I region: the framework hypothesis. Immunogenetics 49:362–367
Anzai T, Shiina T, Kimura T, Yanagiya K, Kohara S, Shigenari A, Yamagata T, Kulski JK, Naruse TK, Fujimori Y, Fukuzumi Y, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Iwamoto C, Umehara Y, Imanishi T, Meyer A, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Bahram S, Inoko H (2003) Comparative sequencing of human and chimpanzee MHC class I regions unveils insertions/deletions as the major path to genomic divergence. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 100:7708–7713
Bernardi G (1993) The isochore organization of the human genome and its evolutionary history-a review. Gene 135:57–66
Chardon P, Renard C, Vaiman M (1999) The major histocompatibility complex in swine. Immunol Rev 167:179–192
Chardon P, Rogel-Gaillard C, Cattolico L, Duprat S, Vaiman M, and Renard C (2001) Sequence of the pig major histocompatibility region containing all non-classical class I genes. Tissue Antigens 57:55–65
Deininger PL (1983) Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem 129:216–223
Günther E, Walter L (2001) The major histocompatibility complex of the rat (R. norvegicus). Immunogenetics 53:520–542
Jurka J, Milosavljevic A (1991) Reconstruction and analysis of human Alu genes. J Mol Evol 32:105–121
Keicho N, Ohashi J, Tamiya G, Nakata K, Taguchi Y, Azuma A, Ohishi N, Emi M, Park MH, Inoko H, Tokunaga K, Kudoh S (2000) Fine localization of a major disease-susceptibility locus for diffuse panbronchiolitis. Am J Hum Genet 66:501–507
Kulski JK, Shiina T, Anzai T, Kohara S, Inoko H (2002) Comparative genomic analysis of the MHC: the evolution of class I duplication blocks, diversity and complexity from shark to man. Immunol Rev 190:95–122
Lai L, Kolber-Simonds D, Park KW, Cheong HT, Greenstein JL, Im GS, Samuel M, Bonk A, Rieke A, Day BN, Murphy CN, Carter DB, Hawley RJ, Prather RS (2002) Production of alpha-1.3-galactosyltaransferase knockout pigs by nuclear transfer cloning. Science 295:1089–1092
Matsuzaka Y, Tounai K, Denda A, Tomizawa M, Makino S, Okamoto K, Keicho N, Oka A, Kulski JK, Tamiya G (2002) Identification of novel candidate genes in the diffuse panbronchiolitis critical region of the class I human MHC. Immunogenetics 54:301–309
Mizuki N, Ando H, Kimura M, Ohno S, Miyata S, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Watanabe K, Ono A, Taguchi S, Sugawara C, Fukuzumi Y, Okumura K, Goto K, Ishihara M, Nakamura S, Yonemoto J, Kikuti YY, Shiina T, Chen L, Ando A, Ikemura T, Inoko H (1997) Nucleotide sequence analysis of the HLA class I region spanning the 237-kb segment around the HLA-B and -C genes. Genomics 42:55–66
Oka A, Tamiya G, Tomizawa M, Ota M, Katsuyama Y, Makino S, Shiina T, Yoshitome M, Iizuka M, Sasao Y, Iwashita K, Kawakubo Y, Sugai J, Ozawa A, Ohkido M, Kimura M, Bahram S, Inoko H (1999) Association analysis using refined microsatellite markers localizes a susceptibility locus for psoriasis vulgaris within a 111 kb segment telomeric to the HLA-C gene. Hum Mol Gent 8:2165–2170
Oka A, Hayashi H, Tomizawa M, Okamoto K, Hui J, Kulski JK, Beilby J, Tamiya G, Inoko H (2003) Localization of a non-melanoma skin cancer susceptibility region within the major histocompatibility complex by association analysis using microsatellite markers. Tissue Antigens 61:203–210
Peelman LJ, Chardon P, Vaiman M, Mattheeuws M, Van Zeveren A, Van de Weghe A, Bouquet Y, Campbell RD (1996) A detailed physical map of the porcine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region: comparison with human and mouse MHC class III regions. Mamm Genome 7:363–367
Rabin M, Fries R, Singer DS, Ruddle FH (1985) Assignment of the porcine major histocompatibility complex to chromosome 7 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39:206–209
Renard C, Vaiman M, Chiannikulchai N, Cattolico L, Robert C, Chardon P (2001) Sequence of the pig major histocompatibility region containing the classical class I genes. Immunogenetics 53:490–500
Rogel-Gaillard C, Bourgeaux N, Billault A, Vaiman M, Chardon P (1999) Construction of a swine BAC library: application to the characterization and mapping of porcine type C endoviral elements. Cytogenet Cell Genet 85:205–211
Rogic S, Mackworth AK, Ouellette FB (2001) Gene-finding programs on mammalian sequences. Genome Res 11:817–832
Sachs DH (1994) The pig as a potential xenograft donor. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 43:185–191
Sambrook JG, Russell R, Umrania Y, Edwards YJ, Campbell RD, Elgar G, Clark MS (2002) Fugu orthologues of human major histocompatibility complex genes: a genome survey. Immunogenetics 54:367–380
Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA, Smit A, Riemer C, Bouck J, Gibbs R, Hardison R, Miller W (2000) PipMaker-A web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 10:577–586
Shiina T, Tamiya G, Oka A, Yamagata T, Yamagata N, Kikkawa E, Goto K, Mizuki N, Watanabe K, Fukuzumi Y, Taguchi S, Sugawara C, Ono A, Chen L, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Ando A, Ikemura T, Kimura M, Inoko H (1998) Nucleotide sequencing analysis of the 146 kb segment around the IkBL and MICA genes at the centromeric end of the HLA class I region. Genomics 47:372–382
Shiina T, Tamiya G, Oka A, Takishima N, Yamagata T, Kikkawa E, Iwata K, Tomizawa M, Okuaki N, Kuwano Y, Watanabe K, Fukuzumi Y, Itakura S, Sugawara C, Ono A, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Ando A, Ikemura T, Soeda E, Kimura M, Bahram S, Inoko H (1999) Molecular dynamics of MHC genesis unraveled by sequence of the 1,796,938-bp HLA class I region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13282–13287
Shimamura M, Abe H, Nikaido M, Ohshima K, Okada M (1999) Genealogy of families of SINEs in Cetaceans and Artiodactyls: the presence of a huge superfamily of tRNA(Glu)-derived families of SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 16:1046–1060
Smith TP, Rohrer GA, Alexander LJ, Troyer DL, Kirby-Dobbels KR, Janzen MA, Cornwell DL, Louis CF, Schook LB, Beattie CW (1995) Directed integration of the physical and genetic linkage maps of the swine chromosome 7 reveals that SLA spans the centromere. Genome Res 5:259–271
Takahashi H, Awata T, Yasue H (1992) Characterization of swine short interspersed repetitive sequences. Anim Genet 23:443–448
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Ullu E, Tschudi C (1984) Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes. Nature 312:171–172
Velten F, Rogel-Gaillard C, Renard C, Pontarotti P, Tazi-Ahnini R, Vaiman M, Chardon P (1998) A first map of the porcine major histocompatibility complex class I region. Tissue Antigens 51:183–194
Velten F, Renald C, Rogel-Gaillard C, Vaiman M, Schrezenmeir J, Chardon P (1999) Spatial arrangement of pig MHC class I sequences. Immunogenetics 49:919–930
Weiner AM (1980) An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell 22:209–218
Xu XC, Naziruddin B, Sasaki H, Smith DM. Mohanakumar T (1999) Allele-specific and peptide-dependent recognition of swine leukocyte antigen class I by human cytotoxic T-cell clines. Transplantation 68:473–479
Xu Y, Rothchild MF, Warmer CM (1992) Mapping of the SLA complex of the miniature swine mapping of the SLA gene complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Mamm Genome 2:2–10
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Yasunari Matsuzaka, Akihiro Denda, and Gen Tamiya, for helpful information regarding the human novel genes surrounding the CDSN gene. We also wish to thank Dr. Tetsushi Yamagata and Tatsuya Anzai for useful discussion. This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Sports, Science, Culture and Technology, Japan, and the Animal Genome Research Project of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to DDBJ, EMBL and GenBank databases under accession numbers AB113354, AB113355, AB113356, AB113357
Electronic database information
Electronic database information
-
http://ftp.genome.washington.edu/cgi-bin/RepeatMasker; RepeatMasker program
-
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/; BLAST search programs.
-
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/fasta33/; BLAST search programs
-
http://genes.mit.edu/GENSCAN.html; GENSCAN search programs
-
http://bio.cse.psu.edu; PipMaker programs
-
http://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/E-mail/clustalw-j.html; CLUSTALW programs
-
http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/cards/; Human genes database
-
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/; Site for Map Viewer and GenBank database
-
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ LocusLink/; LocusLink database
-
http://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/; CLUSTALW programs and GenBank database
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shigenari, A., Ando, A., Renard, C. et al. Nucleotide sequencing analysis of the swine 433-kb genomic segment located between the non-classical and classical SLA class I gene clusters. Immunogenetics 55, 695–705 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0627-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0627-0