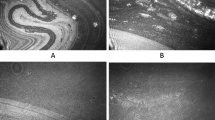
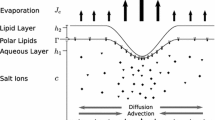
Abstract
The surface properties of meibomian secretion (MGS), the major constituent of the tear film (TF) lipid layer, are of key importance for TF stability. The interfacial properties of canine, cMGS, and feline, fMGS, meibum films were studied using a Langmuir surface balance. These species were selected because they have blinking frequency and TF stability similar to those of humans. The sample’s performance during dynamic area changes was evaluated by surface pressure (π)-area (A) isocycles and the layer structure was monitored with Brewster angle microscopy. The films’ dilatational rheology was probed via the stress-relaxation technique. The animal MGS showed similar behavior both between each other and with human MGS (studied previously). They form reversible, non-collapsible, multilayer thick films. The relaxations of canine, feline, and human MGS films were well described by double exponential decay reflecting the presence of two processes: (1) fast elastic process, with characteristic time τ < 10 s and (2) slow viscous process, with τ > 100 s—emphasizing the meibum layers viscoelasticity. The temperature decrease from 35 to 25 °C resulted in decreased thickness and lateral expansion of all MGS layers accompanied with increase of the π/A hysteresis and of the elastic process contribution to π relaxation transients. Thus, MGS films of mammals with similar blinking frequency and TF stability have similar surface properties and stress relaxations unaltered by the interspecies MGS compositional variations. Such knowledge may impact the selection of animal mimics of human MGS and on a better understanding of lipid classes’ impact on meibum functionality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreau K, Callan C, Kottaiyan R, Zhang A, Yoon G, Aquavella JV, Zavislan J, Hindman HB (2016) Temperatures of the ocular surface, lid, and periorbital regions of Sjögren’s, evaporative, and aqueous-deficient dry eyes relative to normals. Ocul Surf 14(1):64–73
Barabino S, Dana MR (2004) Animal models of dry eye: a critical assessment of opportunities and limitations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1641–1646
Barabino S, Chen W, Dana MR (2004) Tear film and ocular surface tests in animal models of dry eye: uses and limitations. Exp Eye Res 79:613–621
Barnes HA (2000) A handbook of elementary rheology. Institute of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, University of Wales, Aberystwyth
Biondi F, Dornbusch PT, Sampaio M, Montiani-Ferreira F (2015) Infrared ocular thermography in dogs with and without keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Vet Ophthalmol 18:28–34
Borchman D, Foulks GN, Yappert MC, Mathews J, Leake K, Bell J (2009) Factors affecting evaporation rates of tear film components measured in vitro. Eye Contact Lens 35:32–37
Brown SI, Dervichian DG (1969) The oils of the meibomian glands: physical and surface characteristics. Arch Ophthalmol 82:537–540
Brown SH, Kunnen CM, Papas EB, Lazon de la Jara P, Willcox MD, Blanksby SJ, Mitchell TW (2016) Intersubject and interday variability in human tear and meibum lipidomes: a pilot study. Ocul Surf 14:43–48
Butovich IA (2008) On the lipid composition of human meibum and tears: comparative analysis of nonpolar lipids. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:3779–3789
Butovich IA, Borowiak AM, Eule JC (2011) Comparative HPLC-MS analysis of canine and human meibomian lipidomes: many similarities, a few differences. Sci Rep 1:24
Cerretani CF, Ho NH, Radke CJ (2013) Water-evaporation reduction by duplex films: application to the human tear film. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 197–198:33–57
Dennison SR, Phoenix AJ, Phoenix DA (2012) Effect of salt on the interaction of Hal18 with lipid membranes. Eur Biophys J 41(9):769–776
Dota A, Takaoka-Shichijo Y, Nakamura M (2013) Gefarnate stimulates mucin-like glycoprotein secretion in conjunctival tissue and ameliorates corneal epithelial damage in animal dry-eye models. Clin Ophthalmol Auckl NZ 7:211–217
Efron N, Young G, Brennan NA (1989) Ocular surface temperature. Curr Eye Res 8:901–906
Georgiev GA, Kutsarova E, Jordanova A, Krastev R, Lalchev Z (2010) Interactions of meibomian gland secretion with polar lipids in Langmuir monolayers. Colloids Surf B 78:317–327
Georgiev GA, Yokoi N, Koev K, Kutsarova E, Ivanova S, Kyumurkov A, Jordanova A, Krastev R, Lalchev Z (2011) Surface chemistry study of the interactions of benzalkonium chloride with films of meibum, corneal cells lipids, and whole tears. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:4645–4654
Georgiev GA, Yokoi N, Ivanova S, Krastev R, Lalchev Z (2012) Surface chemistry study of the interactions of pharmaceutical ingredients with human meibum films. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:4605–4615
Georgiev GA, Yokoi N, Ivanova S, Dimitrov T, Andreev K, Krastev R, Lalchev Z (2013) Surface chemistry study of the interactions of hyaluronic acid and benzalkonium chloride with meibomian and corneal cell lipids. Soft Matter 9:10841–10856
Georgiev GA, Yokoi N, Ivanova S, Tonchev V, Nencheva Y, Krastev R (2014) Surface relaxations as a tool to distinguish the dynamic interfacial properties of films formed by normal and diseased meibomian lipids. Soft Matter 10:5579–5588
Green-Church KB, Butovich I, Willcox M, Borchman D, Paulsen F, Barabino S, Glasgow BJ (2011) The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the subcommittee on tear film lipids and lipid–protein interactions in health and disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:1979–1993
Haworth KM, Nichols JJ, Thangavelu M, Sinnott LT, Nichols KK (2011) Examination of human meibum collection and extraction techniques. Optom Vis Sci Off Publ Am Acad Optom 88:525–533
Huehnerfuss H, Alpers W (1983) Molecular aspects of the system water/monomolecular surface film and the occurrence of a new anomalous dispersion regime at 1.43 GHz. J Phy Chem 87:5251–5258
Ivanova T, Minkov I, Panaiotov I, Saulnier P, Proust JE (2003) Dilatational properties and morphology of surface films spread from clinically used lung surfactants. Colloid Polym Sci 282:1258–1267
Ivanova S, Tonchev V, Yokoi N, Yappert MC, Borchman D, Georgiev GA (2015) Surface properties of squalene/meibum films and nmr confirmation of squalene in tears. Int J Mol Sci 16:21813–21831
Iwata S, Lemp MA, Holly FJ, Dohlman CH (1969) Evaporation rate of water from the precorneal tear film and cornea in the rabbit. Invest Ophthalmol 8:613–619
Kaercher T, Honig D, Mobius D (1993) Brewster angle microscopy. a new method of visualizing the spreading of meibomian lipids. Int Ophthalmol 17:341–348
Lam SM, Tong L, Duan X, Petznick A, Wenk MR, Shui G (2014) Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J Lipid Res 55:289–298
Leiske DL, Raju SR, Ketelson HA, Millar TJ, Fuller GG (2010) The interfacial viscoelastic properties and structures of human and animal meibomian lipids. Exp Eye Res 90:598–604
Leiske DL, Miller CE, Rosenfeld L, Cerretani C, Ayzner A, Lin B, Meron M, Senchyna M, Ketelson HA, Meadows D, Srinivasan S, Jones L, Radke CJ, Toney MF, Fuller GG (2012) Molecular structure of interfacial human meibum films. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 28:11858–11865
Maggs DJ (2008) Chapter 5—basic diagnostic techniques. In: Ofri DJMEM (ed) Slatter’s fundamentals of veterinary ophthalmology, 4th edn. W.B. Saunders, Saint Louis, pp 81–106
Maggs DJ, Miller PE, Ofri R (2007) Slatter’s fundamentals of veterinary ophthalmology, 4th edn. Saunders Elseiver, St Louis, p 496
Margadant DL, Kirkby K, Andrew SE, Gelatt KN (2003) Effect of topical tropicamide on tear production as measured by Schirmer’s tear test in normal dogs and cats. Vet Ophthalmol 6:315–320
McLaughlin SA, Brightman AH 2nd, Helper LC, Primm ND, Brown MG, Greeley S (1988) Effect of removal of lacrimal and third eyelid glands on Schirmer tear test results in cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc 193:820–822
McMahon A, Lu H, Butovich IA (2013) The spectrophotometric sulfo-phospho-vanillin assessment of total lipids in human meibomian gland secretions. Lipids 48:513–525
Mishima S, Maurice DM (1961) The oily layer of the tear film and evaporation from the corneal surface. Exp Eye Res 1:39–45
Mochizuki H, Yamada M, Hatou S, Tsubota K (2009) Turnover rate of tear-film lipid layer determined by fluorophotometry. Br J Ophthalmol 93:1535–1538
Montés-Micó R, Alió JL, Muñoz G, Charman WN (2004) Temporal changes in optical quality of air-tear film interface at anterior cornea after blink. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1752–1757
Moore CP, Frappier BL, Linton LL (l996) Distribution and course of ducts of the canine third eyelid gland: effects of two surgical replacement techniques. Vet Comp Ophthalmol 6:258–264
Mudgil P, Millar TJ (2011) Surfactant properties of human meibomian lipids. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:1661–1670
Murata H (2012) Rheology—theory and application to biomaterials. Polym 404–424. doi:10.5772/48393
Murata H, Hamada T, Djulaeha E, Nikawa H (1998) Rheology of tissue conditioners. J Prosthet Dent 79:188–199
Németh J, Erdélyi B, Csákány B, Gáspár P, Soumelidis A, Kahlesz F, Lang Z (2002) High-speed videotopographic measurement of tear film build-up time. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1783–1790
Paananen RO, Rantamäki AH, Parshintsev J, Holopainen JM (2015) The effect of ambient ozone on unsaturated tear film wax esters. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(13):8054–8062
Panaiotov I, Ivanova T, Proust J, Boury F, Denizot B, Keough K, Taneva S (1996) Effect of hydrophobic protein SP-C on structure and dilatational properties of the model monolayers of pulmonary surfactant. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 6:243–260
Petrov PG, Thompson JM, Rahman IB, Ellis RE, Green EM, Miano F, Winlove CP (2007) Two-dimensional order in mammalian pre-ocular tear film. Exp Eye Res 84:1140–1146
Phadatare SP, Momin M, Nighojkar P, Askarkar S, Singh KK (2015) A comprehensive review on dry eye disease: diagnosis, medical management, recent developments, and future challenges. Adv Pharm 2015:12
Pichot R, Watson RL, Norton IT (2013) Phospholipids at the interface: current trends and challenges. Int J Mol Sci 14:11767–11794
Raju SR, Palaniappan CK, Ketelson HA, Davis JW, Millar TJ (2013) Interfacial dilatational viscoelasticity of human meibomian lipid films. Curr Eye Res 38:817–824
Rantamäki AH, Wiedmer SK, Holopainen JM (2013) Melting points–the key to the anti-evaporative effect of the tear film wax esters. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54(8):5211–5217
Rosenfeld L, Fuller GG (2012) Consequences of interfacial viscoelasticity on thin film stability. Langmuir 28(40):14238–14244
Rosenfeld L, Cerretani C, Leiske DL, Toney MF, Radke CJ, Fuller GG (2013) Structural and rheological properties of meibomian lipid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2720–2732
Rysa P, Sarvaranta J (1974) Corneal temperature in man and rabbit. Observations made using an infra-red camera and a cold chamber. Acta Ophthalmol 52:810–816
Schrader S, Mircheff AK, Geerling G (2008) Animal models of dry eye. Dev Ophthalmol 41:298–312
Schwartz B, Feller MR (1962) Temperature gradients in the rabbit eye. Investig Ophthalmol 1:513–521
Shchipunov YA, Kolpakov AF (1991) Phospholipids at the oil/water interface: adsorption and interfacial phenomena in an electric field. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 35:31–138
Shrestha RK, Borchman D, Foulks GN, Yappert MC, Milliner SE (2011) Analysis of the composition of lipid in human meibum from normal infants, children, adolescents, adults, and adults with meibomian gland dysfunction using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:7350–7358
Smaby JM, Kulkarni VS, Momsen M, Brown RE (1996) The interfacial elastic packing interactions of galactosylceramides, sphingomyelins, and phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J 70:868–877
Svitova TF, Lin MC (2013) Racial variations in interfacial behavior of lipids extracted from worn soft contact lenses. Optom Vis Sci Off Publ Am Acad Optom 90:1361–1369
Tan J-H, Ng EYK, Rajendra Acharya U, Chee C (2009) Infrared thermography on ocular surface temperature: a review. Infrared Phys Technol 52:97–108
Tiffany JM (2003) Tears in health and disease. Eye 17:923–926
Tiffany JM, Winter N, Bliss G (1989) Tear film stability and tear surface tension. Curr Eye Res 8:507–515
Tschoegl N (1989) The modelling of multimodal distributions of respondance times the phenomenological theory of linear viscoelastic behavior. Springer, Berlin, pp 489–507
Tsubota K (1998) Tear dynamics and dry eye. Prog Retin Eye Res 17:565–596
Uchino M, Uchino Y, Dogru M, Kawashima M, Yokoi N, Komuro A, Sonomura Y, Kato H, Kinoshita S, Schaumberg DA, Tsubota K (2014) Dry eye disease and work productivity loss in visual display users: the Osaka study. Am J Ophthalmol 157:294–300
van Hunsel J, Joos P (1989) Study of the dynamic interfacial tension at the oil/water interface. Colloid Polym Sci 267:1026–1035
Wei XE, Markoulli M, Millar TJ, Willcox MD, Zhao Z (2012) Divalent cations in tears, and their influence on tear film stability in humans and rabbits. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:3280–3285
Wei XE, Markoulli M, Zhao Z, Willcox MD (2013) Tear film break-up time in rabbits. Clin Exp Optom 96:70–75
Wilke N, Maggio B (2006) Effect of externally applied electrostatic fields on the surface topography of ceramide-enriched domains in mixed monolayers with sphingomyelin. Biophys Chem 122:36–42
Wizert A, Iskander DR, Cwiklik L (2014) Organization of lipids in the tear film: a molecular-level view. PLoS One 9:e92461
Yokoi N, Takehisa Y, Kinoshita S (1996) Correlation of tear lipid layer interference patterns with the diagnosis and severity of dry eye. Am J Ophthalmol 122:818–824
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Collaborative study grant by Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan and in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (25462728) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan. We expresses personal gratitude to Prof. Christian Vassillieff (Department of Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy, St. Kliment Ohridski University of Sofia) for the numerous discussions on the technique of stress-relaxation and on the viscoelasticity of lipid films. VT acknowledges the useful discussions with Prof. Isak Avramov (Institute of Physical Chemistry, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences) on relaxation theory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Concerning the representative data on human meibum these were taken from our previous studies (Georgiev et al. 2010, 2012, 2013, 2014; Ivanova et al. 2015). For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eftimov, P., Yokoi, N., Tonchev, V. et al. Surface properties and exponential stress relaxations of mammalian meibum films. Eur Biophys J 46, 129–140 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1146-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1146-x