Abstract
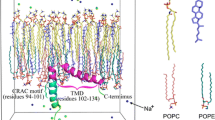
Caveolins (cav1–3) are essential membrane proteins found in caveolae. The caveolin scaffolding domain of cav-1 includes a short sequence containing a CRAC motif (V94TKYWFYR101) at its C-terminal end. To investigate the role of this motif in the caveolin–membrane interaction at the atomic level, we performed a detailed structural and dynamics characterization of a cav-1(V94-L102) nonapeptide encompassing this motif and including the first residue of cav-1 hydrophobic domain (L102), in dodecylmaltoside (DM) or dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) micelles, as membrane mimics. Cav-1(V94-L102) partitioned better in DPC and in DM/anionic lipid micelles than in DM micelles, as shown by fluorescence titration and CD. NMR data revealed that this peptide folded as an amphipathic helix located in the polar head group region of DPC micelles. The two tyrosine side-chains, flanked by arginine and lysine residues, are situated on one face of this helix, whereas the phenylalanine and tryptophan side-chains are located on the opposite face. Fluorescence studies showed significant Trp subnanosecond rotations, the presence of several rotamers, and a heterogeneous location within the water/micelle interface. NMR studies of the shorter cav-1(V94-R101) peptide and of the homologous sequence of cav-2(I79SKYVMYKF87) allowed the description of the effect of L102 and of the amino acid variations occurring in cav-2 on the structure and localization in DPC micelles. Based on the topological model of caveolins, our results suggest that the cav-1 and cav-2 nonapeptides studied form interfacial α-helix membrane anchors in which the K/RhhhYK/Rh motif, also found in cav-3, may play a significant role.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BrDM:
-
7,8-Dibromododecylmaltoside
- BrUM:
-
10,11-Dibromoundecanoylmaltoside
- cmc:
-
Critical micellar concentration
- CD:
-
Circular dichroism
- CRAC:
-
Cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus
- cav-n :
-
Caveolin-n with n = 1, 2 or 3
- DM:
-
n-Dodecyl-β-d-maltoside
- DMPA:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate
- DMPC:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- DMPG:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)]
- DMPS:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-l-serine
- DPC:
-
Dodecylphosphocholine
- DSS:
-
Dimethylsilapentane-sulfonic acid
- FWHM:
-
Full width at half maximum
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum correlated spectroscopy
- MALDI/TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight
- MEM:
-
Maximum entropy method
- N-MAD:
-
N-terminal membrane attachment domain
- NATA:
-
N-acetyltryptophanamide
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy
- POPC:
-
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- POPS:
-
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-l-serine]
- POPG:
-
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)]
- TOCSY:
-
Total correlated spectroscopy
References
Arbuzova A, Wang L, Wang J, Hangyas-Mihalyne G, Murray D, Honig B, McLaughlin S (2000) Membrane binding of peptides containing both basic and aromatic residues. Experimental studies with peptides corresponding to the scaffolding region of caveolin and the effector region of MARCKS. Biochemistry 39:10330–10339
Ben-Tal N, Honig B, Peitzsch RM, Denisov G, McLaughlin S (1996) Binding of small basic peptides to membranes containing acidic lipids: theoretical models and experimental results. Biophys J 71:561–575
Beswick V, Guerois R, Cordier-Ochsenbein F, Coïc YM, Tam HD, Tostain J, Noël JP, Sanson A, Neumann JM (1999) Dodecylphosphocholine micelles as a membrane-like environment: new results from NMR relaxation and paramagnetic relaxation enhancement analysis. Eur Biophys J 28:48–58
Bhattacharyya K, Bagchi B (2000) Slow dynamics of constrained water in complex geometries. J Phys Chem A 104:10603–10613
Bocquet N, Nury H, Baaden M, Le Poupon C, Changeux JP, Delarue M, Corringer PJ (2009) X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation. Nature 457:111–114
Bouhss A, Vincent M, Munier H, Gilles AM, Takahashi M, Bârzu O, Danchin A, Gallay J (1996) Conformational transitions within the calmodulin-binding site of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase studied by time-resolved fluorescence of Trp242 and circular dichroism. Eur J Biochem 237:619–628
Brochon JC (1994) Maximum entropy method of data analysis in time-resolved spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol 240:262–311
Brown LR, Bosch C, Wüthrich K (1981) Location and orientation relative to the micelle surface for glucagon in mixed micelles with dodecylphosphocholine: EPR and NMR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 642:296–312
Burstein EA, Emelyanenko VI (1996) Log-normal description of fluorescence spectra of organic fluorophores. Photochem Photobiol 64:316–320
Burstein EA, Abornev SM, Reshetnyak YK (2001) Decomposition of protein tryptophan fluorescence spectra into log-normal components. I. Decomposition algorithms. Biophys J 81:1699–1709
Chen Y, Barkley MD (1998) Toward understanding tryptophan fluorescence in proteins. Biochemistry 37:9976–9982
Cohen AW, Hnasko R, Schubert W, Lisanti MP (2004) Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol Rev 84:1341–1379
Coïc YM, Vincent M, Gallay J, Baleux F, Mousson F, Beswick V, Neumann JM, de Foresta B (2005) Single-spanning membrane protein insertion in membrane mimetic systems: role and localization of aromatic residues. Eur Biophys J 35:27–39
de Foresta B, Legros N, Plusquellec D, Le Maire M, Champeil P (1996) Brominated detergents as tools to study protein–detergent interactions. Eur J Biochem 241:343–354
de Foresta B, Gallay J, Sopkova J, Champeil P, Vincent M (1999) Tryptophan octyl ester in detergent micelles of dodecylmaltoside: fluorescence properties and quenching by brominated detergent analogs. Biophys J 77:3071–3084
de Foresta B, Tortech L, Vincent M, Gallay J (2002) Location and dynamics of tryptophan in transmembrane alpha-helix peptides: a fluorescence and circular dichroism study. Eur Biophys J 31:185–197
Drummond CJ, Warr GG, Grieser F, Ninham BW, Fennell Evans D (1985) Surface properties and micellar interfacial microenvironment of n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside. J Phys Chem 89:2103–2109
Dupuy C, Auvray X, Petipas C, Rico-Lattes I, Lattes A (1997) Anomeric effects on the structure of micelles of alkyl maltosides in water. Langmuir 13:3965–3967
East JM, Lee AG (1982) Lipid selectivity of the calcium and magnesium ion dependent adenosinetriphosphatase, studied with fluorescence quenching by a brominated phospholipid. Biochemistry 21:4144–4151
Eftink MR (1991) Fluorescence techniques for studying protein structure. Methods Biochem Anal 35:127–205
Eisenberg D, Weiss RM, Terwilliger TC (1984) The hydrophobic moment detects periodicity in protein hydrophobicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:140–144
Epand RM, Sayer BG, Epand RF (2003) Peptide-induced formation of cholesterol-rich domains. Biochemistry 42:14677–14689
Epand RM, Sayer BG, Epand RF (2005) Caveolin scaffolding region and cholesterol-rich domains in membranes. J Mol Biol 345:339–350
Fernandez-Vidal M, Jayasinghe S, Ladokhin AS, White SH (2007) Folding amphipathic helices into membranes: amphiphilicity trumps hydrophobicity. J Mol Biol 370:459–470
Gallay J, Vincent M, de la Sierra IML, Munier-Lehmann H, Renouard M, Sakamoto H, Barzu O, Gilles AM (2004) Insight into the activation mechanism of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase by calmodulin using fluorescence spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 271:821–833
Hristova K, White SH (2005) An experiment-based algorithm for predicting the partitioning of unfolded peptides into phosphatidylcholine bilayer interfaces. Biochemistry 44:12614–12619
Krittanai C, Johnson WC (1997) Correcting the circular dichroism spectra of peptides for contributions of absorbing side chains. Anal Biochem 253:57–64
Lakowicz JR (1999) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Kluwer, New York
Lauterwein J, Bösch C, Brown LR, Wüthrich K (1979) Physicochemical studies of the protein–lipid interactions in melittin-containing micelles. Biochim Biophys Acta 556:244–264
Le Lan C, Neumann JM, Jamin N (2006) Role of the membrane interface on the conformation of the caveolin scaffolding domain: a CD and NMR study. FEBS Lett 580:5301–5305
le Maire M, Champeil P, Møller JV (2000) Interaction of membrane proteins and lipids with solubilizing detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta 1508:86–111
Li H, Papadopoulos V (1998) Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor function in cholesterol transport. Identification of a putative cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid sequence and consensus pattern. Endocrinology 139:4991–4997
Liu P, Rudick M, Anderson RG (2002) Multiple functions of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem 277:41295–41298
Livesey AK, Brochon JC (1987) Analyzing the distribution of decay constants in pulse-fluorimetry using the maximum entropy method. Biophys J 52:693–706
London E, Feigenson GW (1981) Fluorescence quenching in model membranes. 2. Determination of local lipid environment of the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry 20:1939–1948
Lund S, Orlowski S, de Foresta B, Champeil P, le Maire M, Møller JV (1989) Detergent structure and associated lipid as determinants in the stabilization of solubilized Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 264:4907–4915
Moors SL, Hellings M, De Maeyer M, Engelborghs Y, Ceulemans A (2006) Tryptophan rotamers as evidenced by X-ray, fluorescence lifetimes, and molecular dynamics modeling. Biophys J 91:816–823
Muñoz V, Serrano L (1995) Elucidating the folding problem of helical peptides using empirical parameters. II. Helix macrodipole effects and rational modification of the helical content of natural peptides. J Mol Biol 245:275–296
Murray D, Hermida-Matsumoto L, Buser CA, Tsang J, Sigal CT, Ben-Tal N, Honig B, Resh MD, McLaughlin S (1998) Electrostatics and the membrane association of Src: theory and experiment. Biochemistry 37:2145–2159
Nanga RP, Brender JR, Xu J, Veglia G, Ramamoorthy A (2008) Structures of rat and human islet amyloid polypeptide IAPP1–19 in micelles by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 47:12689–12697
Neumoin A, Arshava B, Becker J, Zerbe O, Naider F (2007) NMR studies in dodecylphosphocholine of a fragment containing the seventh transmembrane helix of a G-protein-coupled receptor from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biophys J 93:467–482
Pace CN, Vajdos F, Fee L, Grimsley G, Gray T (1995) How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 4:2411–2423
Pan CP, Barkley MD (2004) Conformational effects on tryptophan fluorescence in cyclic hexapeptides. Biophys J 86:3828–3835
Parton RG, Simons K (2007) The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:185–194
Parton RG, Hanzal-Bayer M, Hancock JF (2006) Biogenesis of caveolae: a structural model for caveolin-induced domain formation. J Cell Sci 119:787–796
Peitzsch RM, McLaughlin S (1993) Binding of acylated peptides and fatty acids to phospholipid vesicles: pertinence to myristoylated proteins. Biochemistry 32:10436–10443
Perrin F (1936) Mouvement brownien d’un ellipsoide (II). Rotation libre et dépolarisation des fluorescences. Translation et diffusion de molécules ellipsoidales. J Phys et le Radium 7:1–11
Phoenix DA, Harris F, Daman OA, Wallace J (2002) The prediction of amphiphilic alpha-helices. Curr Protein Pept Sci 3:201–221
Powl AM, East JM, Lee AG (2005) Heterogeneity in the binding of lipid molecules to the surface of a membrane protein: hot spots for anionic lipids on the mechanosensitive channel of large conductance MscL and effects on conformation. Biochemistry 44:5873–5883
Reshetnyak YK, Burstein EA (2001) Decomposition of protein tryptophan fluorescence spectra into log-normal components. II. The statistical proof of discreteness of tryptophan classes in proteins. Biophys J 81:1710–1734
Roche S, Bressanelli S, Rey FA, Gaudin Y (2006) Crystal structure of the low-pH form of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G. Science 313:187–191
Rogers DM, Hirst JD (2004) First-principles calculations of protein circular dichroism in the near ultraviolet. Biochemistry 43:11092–11102
Rosevear P, VanAken T, Baxter J, Ferguson-Miller S (1980) Alkyl glycoside detergents: a simpler synthesis and their effects on kinetic and physical properties of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry 19:4108–4115
Rouvière N, Vincent M, Craescu CT, Gallay J (1997) Immunosuppressor binding to the immunophilin FKBP59 affects the local structural dynamics of a surface beta-strand: time-resolved fluorescence study. Biochemistry 36:7339–7352
Santos NC, Prieto M, Castanho MA (2003) Quantifying molecular partition into model systems of biomembranes: an emphasis on optical spectroscopic methods. Biochim Biophys Acta 1612:123–135
Schibli DJ, Nguyen LT, Kernaghan SD, Rekdal O, Vogel HJ (2006) Structure–function analysis of tritrpticin analogs: potential relationships between antimicrobial activities, model membrane interactions, and their micelle-bound NMR structures. Biophys J 91:4413–4426
Schlegel A, Schwab RB, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1999) A role for the caveolin scaffolding domain in mediating the membrane attachment of caveolin-1. The caveolin scaffolding domain is both necessary and sufficient for membrane binding in vitro. J Biol Chem 274:22660–22667
Seelig J (2004) Thermodynamics of lipid-peptide interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1666:40–50
Sillen A, Engelborghs Y (1998) The correct use of “average” fluorescence parameters. Photochem Photobiol 67:475–486
Sjögren H, Ericsson CA, Evenas J, Ulvenlund S (2005) Interactions between charged polypeptides and nonionic surfactants. Biophys J 89:4219–4233
Sowmya BL, Jagannadham MV, Nagaraj R (2006) Interaction of synthetic peptides corresponding to the scaffolding domain of caveolin-3 with model membranes. Biopolymers 84:615–624
Tamm LK (1991) Membrane insertion and lateral mobility of synthetic amphiphilic signal peptides in lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1071:123–148
Tieleman DP, van der Spoel D, Berendsen HJC (2000) Molecular dynamics simulations of dodecylphosphocholine micelles at three different aggregate sizes: micellar structure and chain relaxation. J Phys Chem B 104:6380–6388
Tortech L, Jaxel C, Vincent M, Gallay J, de Foresta B (2001) The polar headgroup of the detergent governs the accessibility to water of tryptophan octyl ester in host micelles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1514:76–86
Vincent M, Gallay J (1995) Solvent relaxation around the excited state of indole: analysis of fluorescence lifetime distributions and time-dependence spectral shifts. J Phys Chem 99:14931–14941
Vincent M, de Foresta B, Gallay J (2005) Nanosecond dynamics of a mimicked membrane-water interface observed by time-resolved stokes shift of LAURDAN. Biophys J 88:4337–4350
Vincent M, Gallay J, Jamin N, Garrigos M, de Foresta B (2007) The predicted transmembrane fragment 17 of the human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) behaves as an interfacial helix in membrane mimics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:538–552
Vivian JT, Callis PR (2001) Mechanisms of tryptophan fluorescence shifts in proteins. Biophys J 80:2093–2109
Warr GG, Drummond CJ, Grieser F, Ninham BW, Fennell Evans D (1986) Aqueous solution properties of nonionic n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside micelles. J Phys Chem 90:4581–4586
Willis KJ, Neugebauer W, Sikorska M, Szabo AG (1994) Probing alpha-helical secondary structure at a specific site in model peptides via restriction of tryptophan side-chain rotamer conformation. Biophys J 66:1623–1630
Wimmer R, Andersen KK, Vad B, Davidsen M, Molgaard S, Nesgaard LW, Kristensen HH, Otzen DE (2006) Versatile interactions of the antimicrobial peptide novispirin with detergents and lipids. Biochemistry 45:481–497
Wishart DS, Bigam CG, Yao J, Abildgaard F, Dyson HJ, Oldfield E, Markley JL, Sykes BD (1995) 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shift referencing in biomolecular NMR. J Biomol NMR 6:135–140
Woodman SE, Schlegel A, Cohen AW, Lisanti MP (2002) Mutational analysis identifies a short atypical membrane attachment sequence (KYWFYR) within caveolin-1. Biochemistry 41:3790–3795
Wüthrich K (1986) NMR of proteins and nucleic acids. John Wiley, New York
Wymore T, Gao XF, Wong T (1999) Molecular dynamics simulation of the structure and dynamics of a dodecylphosphocholine micelle in aqueous solution. J Mol Struct 485–486:195–210
Zhang Q, Horst R, Geralt M, Ma X, Hong WX, Finn MG, Stevens RC, Wüthrich K (2008) Microscale NMR screening of new detergents for membrane protein structural biology. J Am Chem Soc 130:7357–7363
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to the memory of J-M Neumann, who died during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Lan, C., Gallay, J., Vincent, M. et al. Structural and dynamic properties of juxta-membrane segments of caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 at the membrane interface. Eur Biophys J 39, 307–325 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0548-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0548-4