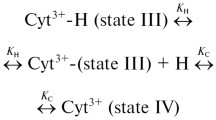Abstract
Circular dichroism, nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance, UV-vis absorption, and resonance Raman (RR) spectroscopic techniques were employed to study protein and heme structural changes of cytochrome c (Cyt-c) induced by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) monomers and micelles via hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, respectively. Both modes of interactions cause the transition to the conformational state B2, which is implicated to be involved in the physiological processes of Cyt-c. At sub-micellar concentrations of SDS, specific binding of only ca. three SDS monomers, which is likely to occur at the hydrophobic peptide segment 81–85, is sufficient for a complete conversion to a B2 state in which Met80 is replaced by His33 (His26). These heme pocket structural changes are not linked to secondary structure changes of the protein brought about by nonspecific binding of SDS monomers in different regions of the protein. Upon binding of micelles, B2 high-spin species can also be stabilized by electrostatic interactions. In addition, the micelle interaction domain is located on the front surface of Cyt-c, which includes a ring-like arrangement of lysine residues appropriate for binding one micelle. According to freeze-quench RR and stopped-flow experiments, state B2 is formed on the long millisecond timescale and reveals a complex dependence on the SDS concentration that can be interpreted in terms of competitive binding of monomers and micelles.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alden RG, Crawford BA, Doolen R, Ondrias MR, Shelnutt JA (1989) Ruffling of nickel(II)-octaethlporphyrin in solution. J Am Chem Soc 111:2070–2072
Ali V, Prakash K, Kulkarni S, Ahmad A, Madhusudan KP, Bhakuni V (1999) 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid (ANS) induces folding of acid unfolded cytochrome c to molten globule state as a result of electrostatic interactions. Biochemistry 38:13635–13642
Bushnell GW, Louie GV, Brayer GD (1990) High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J Mol Biol 214:585–595
Cartling B (1983) Intermediate and stable redox states of cytochrome c studied by low-temperature resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biophys J 43:191–205
Colón W, Wakem LP, Sherman F, Roder H (1997) Identification of the predominant non-native histidine ligand in unfolded cytochrome c. Biochemistry 36:12535–12541
Das TK, Mazumdar S, Mitra S (1998) Characterization of a partially unfolded structure of cytochrome c induced by sodium dodecyl sulphate and the kinetics of its refolding. Eur J Biochem 254:662–670
Davies AM, Guillemette JG, Smith M, Greenwood C, Thurgood AGP, Mauk AG, Moore GR (1993) Redesign of the interior hydrophilic region of mitochondrial cytochrome c by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 32:5431–5435
de Jongh HHJ, Killian JA, de Kruijff B (1992) A water-lipid interface induces a highly dynamic folded state in apocytochrome c and cytochrome c, which may represent a common folding intermediate. Biochemistry 31:1636–1643
Di Paola M, Cocco T, Lorusso M (2000) Arachidonic acid causes cytochrome c release from heart mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:128–133
Döpner S, Hildebrandt P, Mauk AG, Lenk H, Stempfle W (1996) Analysis of vibrational spectra of multicomponent systems. Application to pH-dependent resonance Raman spectra of ferricytochrome c. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 52:573–584
Döpner S, Hildebrandt P, Rosell FI, Mauk AG, von Walter M, Buse G, Soulimane T (1999) The structural and functional role of lysine residues in the binding domain of cytochrome c in the electron transfer to cytochrome c oxidase. Eur J Biochem 261:379–391
Elöve GA, Bhuyan AK, Roder H (1994) Kinetic mechanism of cytochrome c folding: involvement of the heme and its ligands. Biochemistry 33:6925–6935
Emerson MF, Holtzer A (1967) On the ionic strength dependence of micelle number. J Phys Chem 71:1898–1907
Ferguson-Miller S, Babcock GT (1996) Heme/copper terminal oxidases. Chem Rev 96:2889–2907
Gębicka L, Gębicki JL (1999) Kinetic studies on the interaction of ferricytochrome c with anionic surfactants. J Protein Chem 18:165–172
Geren LM, Beasley JR, Fine BR, Saunders AJ, Hibdon S, Pielak GJ, Durham B, Millett F (1995) Design of a ruthenium cytochrome c derivative to measure electron transfer to the initial acceptor in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem 270:2466–2472
Goto Y, Calciano LJ, Fink AL (1990) Acid-induced folding of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:573–577
Hancock JT, Desikan R, Neill SJ (2001) Does the redox status of cytochrome c act as a fail-safe mechanism in the regulation of programmed cell death? Free Radical Biol Med 31:697–703
Heimburg T, Marsh D (1993) Investigation of secondary and tertiary structural changes of cytochrome c in complexes with anionic lipids using amide hydrogen exchange measurements: an FTIR study. Biophys J 65:2408–2417
Hildebrandt P, Stockburger M (1989a) Cytochrome c at charged interfaces. 1. Conformational and redox equilibria at the electrode electrolyte interface probed by surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry 28:6710–6721
Hildebrandt P, Stockburger M (1989b) Cytochrome c at charged interfaces. 2. Complexes with negatively charged macromolecular systems studied by resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry 28:6722–6728
Hildebrandt P, Heimburg T, Marsh D (1990) Quantitative conformational analysis of cytochrome c bound to phospholipid vesicles studied by resonance Raman spectroscopy. Eur Biophys J 18:193–201
Hiramatsu K, Yang JT (1983) Cooperative binding of hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and sodium dodecyl sulfate to cytochrome c and the resultant change in protein conformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 743:106–114
Jemmerson R, Liu J, Hausauer D, Lam KP, Mondino A, Nelson RD (1999) A conformational change in cytochrome c of apoptotic and necrotic cells is detected by monoclonal antibody binding and mimicked by association of the native antigen with synthetic phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 38:3599–3609
Kitagawa T, Ozaki Y (1987) Infrared and Raman spectra of metalloporphyrins. Struct Bonding 64:73–114
Koppenol WH, Rush JD, Mills JD, Margoliash E (1991) The dipole moment of cytochrome c. Mol Biol Evol 8:545–558
Makinen MW, Churg AK (1983) Structural and analytical aspects of the electronic spectra of hemeproteins. In: Lever ABP, Gray HB (eds) Iron porphyrins. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass., USA, pp 141–219
Malatesta F, Antonini G, Sarti P, Brunori M (1995) Structure and function of a molecular machine: cytochrome c oxidase. Biophys Chem 54:1–33
Muga A, Mantsch HH, Surewicz WK (1991) Membrane binding induces destabilization of cytochrome c structure. Biochemistry 30:7219–7224
Murgida DH, Hildebrandt P (2001) Heterogeneous electron transfer of cytochrome c on coated silver electrodes. Electric field effects on structure and redox potentials. J Phys Chem B 105:1578–1586
Oellerich S (2001) PhD thesis. MPI für Strahlenchemie Mülheim/University of Essen
Oellerich S, Bill E, Hildebrandt P (2000) Freeze-quench resonance Raman and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy for studying enzyme kinetics: application to azide binding to myoglobin. Appl Spectrosc 54:1480–1484
Oellerich S, Wackerbarth H, Hildebrandt P (2002) Spectroscopic characterization of non-native conformational states of cytochrome c. J Phys Chem B 106:6566–6580
Otzen DE, Oliveberg M (2002) Burst phase expansion of the native protein prior to global unfolding in SDS. J Mol Biol 315:1231–1240
Parthasarathi N, Hansen C, Yamaguchi S, Spiro TG (1987) Metalloporphyrin core size resonance Raman marker bands revisited: implications for the interpretation of hemoglobin photoproduct Raman frequencies. J Am Chem Soc 109:3865–3871
Pettigrew GW, Moore GR (1987) Cytochromes c: biological aspects. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Pinheiro TJT (1994), The interaction of horse heart cytochrome c with phospholipid bilayers: structural and dynamic effects. Biochimie 76:489–500
Pinheiro TJT, Elöve GA, Watts A, Roder H (1997) Structural and kinetic description of cytochrome c unfolding induced by the interaction with lipid vesicles. Biochemistry 36:13122–13132
Purring-Koch C, McLendon G (2000) Cytochrome c binding to Apaf-1: the effects of dATP and ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11923–11931
Purring C, Zou H, Wang X, McLendon G (1999) Stoichiometry, free energy, and kinetic aspects of cytochrome c: Apaf-1 binding in apoptosis. J Am Chem Soc 121:7435–7436
Reynolds JA, Tanford C (1970) Binding of dodecyl sulfate to proteins at high binding ratios. Possible implications for the state of proteins in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 66:1002–1007
Rivas L, Murgida DH, Hildebrandt P (2002) Conformational and redox equilibria and dynamics of cytochrome c immobilized on electrodes via hydrophobic interactions. J Phys Chem B 106:4823–4830
Roberts VA, Pique ME (1999) Definition of the interaction domain for cytochrome c on cytochrome c oxidase. III. Prediction of the docked complex by a complete, systematic search. J Biol Chem 274:38051–38060
Sanghera N, Pinheiro TJT (2000) Unfolding and refolding of cytochrome c driven by the interaction with lipid micelles. Protein Sci 9:1194–1202
Scott RA, Mauk AG (1996) Cytochrome c: a multidisciplinary approach. University Science Books, Sausalito, Calif., USA
Shi YG (2001) A structural view of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Nat Struct Biol 8: 394–401
Smith WE (1993) Surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol 226C:482–495
Soulimane T, Buse G (1995) Integral cytochrome c oxidase: preparation and progress towards a 3-dimensional crystallization. Eur J Biochem 227:588–595
Spooner PJR, Watts A (1991) Reversible unfolding of cytochrome c upon interaction with cardiolipin bilayers. 1. Evidence from deuterium NMR measurements. Biochemistry 30:3871–3879
Stewart JM, Blakely JA, Johnson MD (2000) The interaction of ferrocytochrome c with long-chain fatty acids and their CoA and carnitine esters. Biochem Cell Biol 78:675–681
Takeda K, Takahashi K, Batra PP (1985) Kinetic aspects of the interaction of horse heart cytochrome c with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Arch Biochem Biophys 236:411–417
Wackerbarth H, Klar U, Gunther W, Hildebrandt P (1999) Novel time-resolved surface-enhanced (resonance) Raman spectroscopic technique for studying the dynamics of interfacial processes: application to the electron transfer reaction of cytochrome c at a silver electrode. Appl Spectrosc 53:283–291
Wackerbarth H, Murgida DH, Oellerich S, Döpner S, Rivas L, Hildebrandt P (2001) Dynamics and mechanism of the electron transfer process of cytochrome c probed by resonance Raman and surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 563:51–59
Witt H, Malatesta F, Nicoletti F, Brunori M, Ludwig B (1998) Tryptophan 121 of subunit II is the electron entry site to cytochrome-c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans: involvement of a hydrophobic patch in the docking reaction. Eur J Biochem 251:367–373
Yeh SR, Takahashi S, Fan BC, Rousseau DL (1997) Ligand exchange during cytochrome c folding. Nat Struct Biol 4:51–56
Yeh SR, Han SW, Rousseau DL (1998) Cytochrome c folding and unfolding: a biphasic mechanism. Acc Chem Res 31:727–736
Yoshimura T (1988) A change in the heme stereochemistry of cytochrome c upon addition of sodium dodecylsulfate: electron paramagnetic resonance and electronic absorption spectral study. Arch Biochem Biophys 264:450–461
Yu TN, Wang XD, Purring-Koch C, Wei Y, McLendon GL (2001) A mutational epitope for cytochrome c binding to the apoptosis protease activation factor-1. J Biol Chem 276:13084–13088
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. E. Bill, Prof. N. Metzler-Nolte, and Dr. R. Schumacher for kind support in EPR, NMR, and stopped-flow experiments, respectively. Technical assistance by B. Deckers is gratefully acknowledged. The work was supported by the Volkswagen-Stiftung (I 72826).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oellerich, S., Wackerbarth, H. & Hildebrandt, P. Conformational equilibria and dynamics of cytochrome c induced by binding of sodium dodecyl sulfate monomers and micelles. Eur Biophys J 32, 599–613 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0306-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0306-y