Abstract
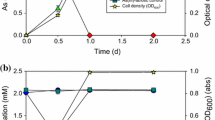
Biotransformation of arsenic (As) plays an important role in its environmental fate. However, the impact of direct microbial interspecies interactions on valence state and migration of As is rarely reported and cognized. Here, by co-cultivating two aerobic AsV-reducing bacteria (Arthrobacter sp. QXT-31 and Sphingopyxis sp. QXT-31) in a culture medium containing initial AsV (10 μM) and bivalent manganese (MnII, 175 μM), we demonstrated how the interactions between strains affect valence state and partition of As. The results showed that both the strains first reduced AsV to AsIII via a detoxification mechanism during aerobic growth, with participation of AsV-reducing gene arsC; the expression of a MnII-oxidizing gene of Arthrobacter sp. QXT-31 was then triggered in the presence of Sphingopyxis sp. QXT-31, and emerging MnII-oxidizing activity oxidized 90% of MnII to Mn oxides; the formed Mn oxides oxidized AsIII to AsV and adsorbed AsV; MnII-oxidizing activity decreased significantly in the later stage, resulting to desorption of AsV from Mn oxides and subsequent bioreduction in aqueous phase. Considering the universality of the two bacterial genera and the interspecies interactions, our study hints at the pervasive impact of direct microbial interspecies interactions on the environmental fate of As in an aquatic ecosystem containing Mn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nickson R, Mcarthur J, Burgess W, Ahmed KM, Ravenscroft P, Rahman M (1998) Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater Nature 395:338
Bai YH, Liu RP, Liang JS, Qu JH (2013) Integrated metagenomic and physiochemical analyses to evaluate the potential role of microbes in the sand filter of a drinking water treatment system PLoS One 8:e61011
Berg M, Tran HC, Nguyen TC, Pham HV, Schertenleib R, Giger W (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater and drinking water in Vietnam: a human health threat Environ Sci Technol 35:2621–2626
Zhang SY, Zhao FJ, Sun GX, Su JQ, Yang XR, Li H, Zhu YG (2015) Diversity and abundance of arsenic biotransformation genes in paddy soils from southern China Environ Sci Technol 49:4138–4146. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b00028
Cervantes C, Ji GY, Ramirez JL, Silver S (1994) Resistance to arsenic compounds in microorganisms FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:355–367. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00145.x
Chen CM, Misra TK, Silver S, Rosen BP (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the structural genes for an anion pump. The plasmid-encoded arsenical resistance operon J Biol Chem 261:15030–15038
Ji G, Silver S (1992) Reduction of arsenate to arsenite by the ArsC protein of the arsenic resistance operon of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258 Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:9474–9478. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.20.9474
Saltikov CW, Newman DK (2003) Genetic identification of a respiratory arsenate reductase Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10983–10988. doi:10.1073/pnas.1834303100
Ahmann D, Roberts AL, Krumholz LR, Morel FMM (1994) Microbe grows by reducing arsenic Nature 371:750–750. doi:10.1038/371750a0
Laverman AM, Blum JS, Schaefer JK, Phillips E, Lovley DR, Oremland RS (1995) Growth of strain SES-3 with arsenate and other diverse electron acceptors Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3556–3561
Muller D, Lièvremont D, Simeonova DD, Hubert JC, Lett MC (2003) Arsenite oxidase aox genes from a metal-resistant β-proteobacterium J Bacteriol 185:135–141
Inskeep WP, Macur RE, Hamamura N, Warelow TP, Ward SA, Santini JM (2007) Detection, diversity and expression of aerobic bacterial arsenite oxidase genes Environ Microbiol 9:934–943
Santini JM, vanden Hoven RN (2004) Molybdenum-containing arsenite oxidase of the chemolithoautotrophic arsenite oxidizer NT-26 J Bacteriol 186:1614–1619
Silver S, Phung LT (2005) Genes and enzymes involved in bacterial oxidation and reduction of inorganic arsenic Appl Environ Microbiol 71:599–608
Zhang J, Zhou W, Liu B, He J, Shen Q, Zhao F-J (2015) Anaerobic arsenite oxidation by an autotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium from an arsenic-contaminated paddy soil Environ Sci Technol 49:5956–5964. doi:10.1021/es506097c
Zargar K, Hoeft S, Oremland R, Saltikov CW (2010) Identification of a novel arsenite oxidase gene, arxA, in the haloalkaliphilic, arsenite-oxidizing bacterium Alkalilimnicola ehrlichii strain MLHE-1 J Bacteriol 192:3755–3762
Santini JM, Sly LI, Schnagl RD, Macy JM (2000) A new chemolithoautotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a gold mine: phylogenetic, physiological, and preliminary biochemical studies Appl Environ Microbiol 66:92–97
Kulp TR, Hoeft SE, Oremland RS (2004) Redox transformations of arsenic oxyanions in periphyton communities Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6428–6434. doi:10.1128/aem.70.11.6428-6434.2004
Simoes LC, Simoes M, Vieira MJ (2007) Biofilm interactions between distinct bacterial genera isolated from drinking water Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6192–6200. doi:10.1128/aem.00837-07
Sankar M, Vega M, Defoe PP, Kibria M, Ford S, Telfeyan K, Neal AW, Mohajerin T, Hettiarachchi GM, Barua S (2014) Elevated arsenic and manganese in groundwaters of Murshidabad, West Bengal, India Sci Total Environ 488:570–579
Liang JS, Bai YH, Men YJ, Qu JH (2017) Microbe-microbe interactions trigger Mn(II)-oxidizing gene expression ISME J 11:67–77. doi:10.1038/ismej.2016.106
Liang JS, Bai YH, Hu CZ, Qu JH (2016) Cooperative Mn(II) oxidation between two bacterial strains in an aquatic environment Water Res 89:252–260. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.062
Tani Y, Miyata N, Ohashi M, Ohnuki T, Seyama H, Iwahori K, Soma M (2004) Interaction of inorganic arsenic with biogenic manganese oxide produced by a Mn-oxidizing fungus, strain KR21-2 Environ Sci Technol 38:6618–6624
Fischel JS, Fischel MH, Sparks DL (2015) Advances in understanding reactivity of manganese oxides with arsenic and chromium in environmental systems. Advances in the environmental biogeochemistry of manganese oxides. Am Chem Soc, 1197 pp. 1–27
Sánchez-Rodas D, Corns WT, Chen B, Stockwell PB (2010) Atomic fluorescence spectrometry: a suitable detection technique in speciation studies for arsenic, selenium, antimony and mercury J Anal At Spectrom 25:933–946
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL (2007) Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer Bioinformatics 23:673–679. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm160
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez J, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676
Singh VK, Mangalam AK, Dwivedi S, Naik S (1998) Primer premier: program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence BioTechniques 24:318–319
Rychlik W (2007) OLIGO 7 primer analysis software Methods Mol Biol 402:35–60
Rocha DJP, Santos CS, Pacheco LGC (2015) Bacterial reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-qPCR: survey and analysis Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:685–693. doi:10.1007/s10482-015-0524-1
Elzinga EJ (2011) Reductive transformation of birnessite by aqueous Mn(II) Environ Sci Technol 45:6366–6372. doi:10.1021/es2013038
Zhao HY, Zhu MQ, Li W, Elzinga EJ, Villalobos M, Liu F, Zhang J, Feng XH, Sparks DL (2016) Redox reactions between Mn(II) and hexagonal birnessite change its layer symmetry Environ Sci Technol 50:1750–1758. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b04436
Brock SL, Sanabria M, Suib SL, Urban V, Thiyagarajan P, Potter DI (1999) Particle size control and self-assembly processes in novel colloids of nanocrystalline manganese oxide J Phys Chem B 103:7416–7428
Tu JJ, Yang ZD, Hu C, Qu JH (2014) Characterization and reactivity of biogenic manganese oxides for ciprofloxacin oxidation J Environ Sci-China 26:1154–1161
Lafferty BJ, Ginder-Vogel M, Zhu MQ, Livi KJT, Sparks DL (2010) Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide. 2. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction Environ Sci Technol 44:8467–8472. doi:10.1021/Es102016c
Lafferty BJ, Ginder-Vogel M, Sparks DL (2010) Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide 1. Stirred-flow experiments Environ Sci Technol 44:8460–8466
Sankar MS, Vega MA, Defoe PP, Kibria MG, Ford S, Telfeyan K, Neal A, Mohajerin TJ, Hettiarachchi GM, Barua S, Hobson C, Johannesson K, Datta S (2014) Elevated arsenic and manganese in groundwaters of Murshidabad, West Bengal, India Sci Total Environ 488:574–583
Jones D, Keddie R (2006) The genus Arthrobacter. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp. 945–960
Cavicchioli R, Ostrowski M, Fegatella F, Goodchild A, Guixa-Boixereu N (2003) Life under nutrient limitation in oligotrophic marine environments: an eco/physiological perspective of Sphingopyxis alaskensis (formerly Sphingomonas alaskensis) Microb Ecol 45:203–217. doi:10.1007/s00248-002-3008-6
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff at BL15U from the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for their help with data collection and analysis. This study was supported by a major program (51290282), general program (51578537), and international (regional) joint research project (51420105012) granted by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 580 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Bai, Y. & Qu, J. Microbial Interspecies Interactions Affect Arsenic Fate in the Presence of MnII . Microb Ecol 74, 788–794 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-017-1008-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-017-1008-9