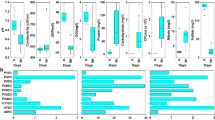
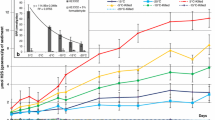
Abstract
The deep subsurface hosts diverse life, but the mechanisms that sustain this diversity remain elusive. Here, we studied microbial communities involved in carbon cycling in deep, dark biosphere and identified anaerobic microbial energy production mechanisms from groundwater of Fennoscandian crystalline bedrock sampled from a deep drill hole in Outokumpu, Finland, by using molecular biological analyses. Carbon cycling pathways, such as carbon assimilation, methane production and methane consumption, were studied with cbbM, rbcL, acsB, accC, mcrA and pmoA marker genes, respectively. Energy sources, i.e. the terminal electron accepting processes of sulphate-reducing and nitrate-reducing communities, were assessed with detection of marker genes dsrB and narG, respectively. While organic carbon is scarce in deep subsurface, the main carbon source for microbes has been hypothesized to be inorganic carbon dioxide. However, our results demonstrate that carbon assimilation is performed throughout the Outokumpu deep scientific drill hole water column by mainly heterotrophic microorganisms such as Clostridia. The source of carbon for the heterotrophic microbial metabolism is likely the Outokumpu bedrock, mainly composed of serpentinites and metasediments with black schist interlayers. In addition to organotrophic metabolism, nitrate and sulphate are other possible energy sources. Methanogenic and methanotrophic microorganisms are scarce, but our analyses suggest that the Outokumpu deep biosphere provides niches for these organisms; however, they are not very abundant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahonen L, Kietäväinen R, Kortelainen N, Kukkonen IT, Pullinen A, Toppi T, Bomberg M, Itävaara M, Nousiainen A, Nyyssönen M (2011) Hydrogeological characteristics of the Outokumpu deep drill hole. In: Kukkonen IT (ed) Outokumpu Deep Drilling Project 2003–2010, Special paper 51. Geological Survey of Finland, Espoo, pp 151–168
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403
Auclair J, Lépine F, Parent S, Villemur R (2010) Dissimilatory reduction of nitrate in seawater by a Methylophaga strain containing two highly divergent narG sequences. ISME J 4:1302
Auguet J, Borrego CM, Bañeras L, Casamayor EO (2008) Fingerprinting the genetic diversity of the biotin carboxylase gene (accC) in aquatic ecosystems as a potential marker for studies of carbon dioxide assimilation in the dark. Environ Microbiol 10:2527
Baker BJ, Moser DP, MacGregor BJ, Fishbain S, Wagner M, Fry NK, Jackson B, Speolstra N, Loos S, Takai K (2003) Related assemblages of sulphate-reducing bacteria associated with ultradeep gold mines of South Africa and deep basalt aquifers of Washington State. Environ Microbiol 5:267
Berg IA, Kockelkorn D, Ramos-Vera WH, Say RF, Zarzycki J, Hügler M, Alber BE, Fuchs G (2010) Autotrophic carbon fixation in archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:447
Berg IA (2011) Ecological aspects of the distribution of different autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1925
Boden R, Cunliffe M, Scanlan J, Moussard H, Kits KD, Klotz MG, Jetten MS, Vuilleumier S, Han J, Peters L, Mikhailova N, Teshima H, Tapia R, Kyrpides N, Ivanova N, Pagani I, Cheng JF, Goodwin L, Han C, Hauser L, Land ML, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Pitluck S, Woyke T, Stein L, Murrell JC (2011) Complete genome sequence of the aerobic marine methanotroph Methylomonas methanica MC09. J Bacteriol 193:7001
Brazelton WJ, Morrill PL, Szponar N, Schrenk MO (2013) Bacterial communities associated with subsurface geochemical processes in continental serpentinite springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3906
Casamayor EO, García-Cantizano J, Pedrós-Alió C (2008) Carbon dioxide fixation in the dark by photo-synthetic bacteria in sulfide-rich stratified lakes with oxic-anoxic interfaces. Limnol Oceanogr 53:1193
Cheng YS, Halsey JL, Fode KA, Remsen CC, Collins ML (1999) Detection of methanotrophs in groundwater by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:648
Daumas S, Cord-Ruwisch R, Garcia J (1988) Desulfotomaculum geothermicum sp. nov., a thermophilic, fatty acid-degrading, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated with H2 from geothermal ground water. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 54:165
Doerfert SN, Reichlen M, Iyer P, Wang M, Ferry JG (2009) Methanolobus zinderi sp. nov., a methylotrophic methanogen isolated from a deep subsurface coal seam. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1064
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792
Ettwig KF, Shima S, De Pas‐Schoonen V, Katinka T, Kahnt J, Medema MH, Op Den C, Huub JM, Jetten MS, Strous M (2008) Denitrifying bacteria anaerobically oxidize methane in the absence of Archaea. Environ Microbiol 10:3164
Fardeau ML, Ollivier B, Patel BK, Dwivedi P, Ragot M, Garcia JL (1995) Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfotomaculum thermosapovorans sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:218
Fisher E, Dawson AM, Polshyna G, Lisak J, Crable B, Perera E, Ranganathan M, Thangavelu M, Basu P, Stolz JF (2008) Transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic by Alkaliphilus oremlandii sp. nov. strain OhILAs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125:230
Gagen EJ, Denman SE, Padmanabha J, Zadbuke S, Al Jassim R, Morrison M, McSweeney CS (2010) Functional gene analysis suggests different acetogen populations in the bovine rumen and tammar wallaby forestomach. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7785
Geets J, Borremans B, Diels L, Springael D, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D, Vanbroekhoven K (2006) DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 66:194
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696
Hales BA, Edwards C, Ritchie DA, Hall G, Pickup RW, Saunders JR (1996) Isolation and identification of methanogen-specific DNA from blanket bog peat by PCR amplification and sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:668
Hallbeck L, Pedersen K (2012) Culture-dependent comparison of microbial diversity in deep granitic groundwater from two sites considered for a Swedish final repository of spent nuclear fuel. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 81:66
Hallbeck L, Pedersen K (2008) Characterization of microbial processes in deep aquifers of the Fennoscandian Shield. Appl Geochem 23:1796
Hammer Ø, Harper D, Ryan P (2001) Past: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Paleontología Electrónica 4: 1–9. URL Http://palaeo-Electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.Html
Hoehler TM, Jørgensen BB (2013) Microbial life under extreme energy limitation. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:83
Itävaara M, Nyyssönen M, Kapanen A, Nousiainen A, Ahonen L, Kukkonen I (2011) Characterization of bacterial diversity to a depth of 1500 m in the Outokumpu deep borehole, Fennoscandian Shield. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:295
Jetten MS, Strous M, Pas‐Schoonen KT, Schalk J, Dongen UG, Graaf AA, Logemann S, Muyzer G, Loosdrecht M, Kuenen JG (1998) The anaerobic oxidation of ammonium. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:421
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3059
Kietäväinen R, Ahonen L, Kukkonen IT, Hendriksson N, Nyyssönen M, Itävaara M (2013) Characterisation and isotopic evolution of saline waters of the Outokumpu Deep Drill Hole, Finland—implications for water origin and deep terrestrial biosphere. Appl Geochem 32:37
Kukkonen IT, Rath V, Kivekäs L, Šafanda J, Čermak V (2011) Geothermal studies of the Outokumpu Deep Drill Hole, Finland: vertical variation in heat flow and palaeoclimatic implications. Phys Earth Planet Inter 188:9
Lalucat J, Bennasar A, Bosch R, Garcia-Valdes E, Palleroni NJ (2006) Biology of Pseudomonas stutzeri. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:510
Lever MA (2013) Functional gene surveys from ocean drilling expeditions—a review and perspective. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 84:1
Lever MA (2012) Acetogenesis in the energy-starved deep biosphere—a paradox? Front Microbiol 2:284
Lin L, Hall J, Onstott T, Gihring T, Lollar BS, Boice E, Pratt L, Lippmann-Pipke J, Bellamy RE (2006) Planktonic microbial communities associated with fracture-derived groundwater in a deep gold mine of South Africa. Geomicrobiol J 23:475
Llirós M, Alonso‐Sáez L, Gich F, Plasencia A, Auguet O, Casamayor EO, Borrego CM (2011) Active bacteria and archaea cells fixing bicarbonate in the dark along the water column of a stratified eutrophic lagoon. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:370
López-Gutiérrez JC, Henry S, Hallet S, Martin-Laurent F, Catroux G, Philippot L (2004) Quantification of a novel group of nitrate-reducing bacteria in the environment by real-time PCR. J Microbiol Methods 57:399
Nakatsu CH, Hristova K, Hanada S, Meng XY, Hanson JR, Scow KM, Kamagata Y (2006) Methylibium petroleiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel methyl tert-butyl ether-degrading methylotroph of the Betaproteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:983
Nanba K, King GM, Dunfield K (2004) Analysis of facultative lithotroph distribution and diversity on volcanic deposits by use of the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2245
Nealson KH, Inagaki F, Takai K (2005) Hydrogen-driven subsurface lithoautotrophic microbial ecosystems (SLiMEs): do they exist and why should we care? Trends Microbiol 13:405
Nicolaisen MH, Ramsing NB (2002) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) approaches to study the diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 50:189
Nurmi PA, Kukkonen IT (1986) A new technique for sampling water and gas from deep drill holes. Can J Earth Sci 23:1450
Nyyssönen M, Hultman J, Ahonen L, Kukkonen I, Paulin L, Laine P, Itävaara M, Auvinen P (2014) Taxonomically and functionally diverse microbial communities in deep crystalline rocks of the Fennoscandian shield. ISME J 8:126–138
Nyyssönen M, Bomberg M, Kapanen A, Nousiainen A, Pitkänen P, Itävaara M (2012) Methanogenic and sulphate-reducing microbial communities in deep groundwater of crystalline rock fractures in Olkiluoto, Finland. Geomicrobiol J 29:863
Okland I, Huang S, Dahle H, Thorseth IH, Pedersen RB (2012) Low temperature alteration of serpentinized ultramafic rock and implications for microbial life. Chem Geol 318:75
Orsi WD, Edgcomb VP, Christman GD, Biddle JF (2013) Gene expression in the deep biosphere. Nature 499:205
Osaka T, Yoshie S, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, Iwami N, Inamori Y (2006) Identification of acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria under nitrate-reducing conditions by stable-isotope probing. Microb Ecol 52:253
Pedersen K, Arlinger J, Eriksson S, Hallbeck A, Hallbeck L, Johansson J (2008) Numbers, biomass and cultivable diversity of microbial populations relate to depth and borehole-specific conditions in groundwater from depths of 4–450 m in Olkiluoto, Finland. ISME J 2:760
Pedersen K (2000) Exploration of deep intraterrestrial microbial life: current perspectives. FEMS Microbiol Lett 185:9
Pedersen K (1997) Microbial life in deep granitic rock. FEMS Microbiol Rev 20:399
Pedersen K, Ekendahl S (1992) Assimilation of CO2 and introduced organic compounds by bacterial communities in groundwater from southeastern Sweden deep crystalline bedrock. Microb Ecol 23:1
Petsch S, Edwards K, Eglinton T (2005) Microbial transformations of organic matter in black shales and implications for global biogeochemical cycles. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 219:157
Petsch ST, Eglington TI, Edwards KJ (2001) 14C-dead living biomass: evidence for microbial assimilation of ancient organic carbon during shale weathering. Science 292:1127
Proskurowski G, Lilley MD, Seewald JS, Fruh-Green GL, Olson EJ, Lupton JE, Sylva SP, Kelley DS (2008) Abiogenic hydrocarbon production at lost city hydrothermal field. Science 319:604
Purkamo L, Bomberg M, Nyyssönen M, Kukkonen I, Ahonen L, Kietäväinen R, Itävaara M (2013) Dissecting the deep biosphere: retrieving authentic microbial communities from packer-isolated deep crystalline bedrock fracture zones. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85:324
Rosewarne CP, Greenfield P, Li D, Tran-Dinh N, Midgley DJ, Hendry P (2013) Draft genome sequence of Methanobacterium sp. Maddingley, reconstructed from metagenomic sequencing of a methanogenic microbial consortium enriched from coal-seam gas formation water. Genome Announc 1:e00081–12. doi:10.1128/genomeA.00081-12
Roslev P, Larsen MB, Jørgensen D, Hesselsoe M (2004) Use of heterotrophic CO2 assimilation as a measure of metabolic activity in planktonic and sessile bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 59:381
Russell MJ, Martin W (2004) The rocky roots of the acetyl-CoA pathway. Trends Biochem Sci 29:358
Sahl JW, Schmidt R, Swanner ED, Mandernack KW, Templeton AS, Kieft TL, Smith RL, Sanford WE, Callaghan RL, Mitton JB, Spear JR (2008) Subsurface microbial diversity in deep-granitic-fracture water in Colorado. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:143
Schrenk MO, Brazelton WJ, Lang SQ (2013) Serpentinization, carbon, and deep life. Rev Mineral Geochem 75:575
Shlimon AG, Friedrich MW, Niemann H, Ramsing NB, Finster K (2004) Methanobacterium aarhusense sp. nov., a novel methanogen isolated from a marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:759
Spiridonova E, Berg I, Kolganova T, Ivanovsky R, Kuznetsov B, Tourova T (2004) An oligonucleotide primer system for amplification of the ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase genes of bacteria of various taxonomic groups. Microbiology 73:316
Swanner E, Templeton A (2011) Potential for nitrogen fixation and nitrification in the granite-hosted subsurface at Henderson Mine, CO. Front Microbiol 2:254
Takai K, Campbell BJ, Cary SC, Suzuki M, Oida H, Nunoura T, Hirayama H, Nakagawa S, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F, Horikoshi K (2005) Enzymatic and genetic characterization of carbon and energy metabolisms by deep-sea hydrothermal chemolithoautotrophic isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7310
Taran LN, Onoshko MP, Mikhailov ND (2011) Structure and composition of organic matter and isotope geochemistry of the Palaeoproterozoic graphite and sulphide-rich metasedimentary rocks from the Outokumpu deep drill hole, eastern Finland. In: Kukkonen IT (ed) Outokumpu Deep Drilling Project 2003–2010, Special paper 51. Geological Survey of Finland, Espoo, pp 219–228
Teske A, Biddle JF (2008) Analysis of deep subsurface microbial communities by functional genes and genomics. In Dilek et al. (ed) Links between geological processes, microbial activities & evolution of life, Springer, pp 159–176
Tiago I, Veríssimo A (2013) Microbial and functional diversity of a subterrestrial high pH groundwater associated to serpentinization. Environ Microbiol 15:1687
Västi K (2011) Petrology of the drill hole R2500 at Outokumpu, eastern Finland—the deepest drill hole ever drilled in Finland. In: Kukkonen IT (ed) Outokumpu Deep Drilling Project 2003-2010, Special paper 51. Geological Survey of Finland, Espoo, pp 17–46
Wagner M, Roger AJ, Flax JL, Brusseau GA, Stahl DA (1998) Phylogeny of dissimilatory sulfite reductases supports an early origin of sulfate respiration. J Bacteriol 180:2975
Welander PV, Metcalf WW (2005) Loss of the mtr operon in Methanosarcina blocks growth on methanol, but not methanogenesis, and reveals an unknown methanogenic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10664
Whelan S, Goldman N (2001) A general empirical model of protein evolution derived from multiple protein families using a maximum-likelihood approach. Mol Biol Evol 18:691
Zhu J, Liu X, Dong X (2011) Methanobacterium movens sp. nov. and Methanobacterium flexile sp. nov., isolated from lake sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2974
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Academy of Finland, The Kone Foundation and Finnish Research Program on Nuclear Waste Management (KYT). Mirva Pyrhönen, Aura Nousiainen and Marjo Öster are acknowledged for their work with sampling at Outokumpu drill hole as well as in laboratory. Riikka Kietäväinen is thanked for commenting on the manuscript and Dr. David Thomas for critical language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Purkamo, L., Bomberg, M., Nyyssönen, M. et al. Heterotrophic Communities Supplied by Ancient Organic Carbon Predominate in Deep Fennoscandian Bedrock Fluids. Microb Ecol 69, 319–332 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0490-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0490-6