Abstract
Background
Portal hypertension, a major complication of hepatic fibrosis, can affect the stiffness of the spleen.
Objective
To suggest normal values of spleen stiffness determined by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in healthy children and to compare measurements using two different US probes.
Materials and methods
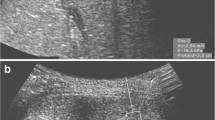
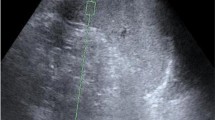
In a prospective study, 60 healthy children between 1 day and 14 years of age were assigned to four age groups with 15 children in each. Measurements were performed using two transducers (convex 4C1 and linear 9L4), and 10 measurements were obtained in each child, 5 with each probe.
Results
The mean splenic shear wave velocities were 2.17 m/s (SD 0.35, 95% CI 2.08–2.26) with the 4C1 probe and 2.15 m/s (SD 0.23, 95% CI 2.09–2.21) with the 9L4 probe (not significant).
Conclusion
We found normal values for spleen stiffness with no difference in the mean values obtained using two types of US transducers, but with higher variability using a convex compared to a linear transducer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rifai K, Cornberg J, Bahr M et al (2011) ARFI elastography of the spleen is inferior to liver elastography for detection of portal hypertension. Ultraschall Med 32:24–30
Grgurevic I, Cikara I, Horvat J et al (2011) Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis with acoustic radiation force imaging: increased liver and splenic stiffness in patients with liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Ultraschall Med 32:160–166
Sporea I, Sirli R, Bota S et al (2011) Is ARFI elastography reliable for predicting fibrosis severity in chronic HCV hepatitis? World J Radiol 3:188–193
Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M et al (2012) Performance of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat 19:212–219
Rizzo L, Calvaruso V, Cacopardo B et al (2011) Comparison of transient elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse for non-invasive staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 106:2112–2120
Noruegas MJ, Matos H, Goncalves I et al (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 42:201–204
Marginean CO, Marginean C (2012) Elastographic assessment of liver fibrosis in children: a prospective single center experience. Eur J Radiol 81:e870–e874
Li Y, Qian L, He W (2009) A study on the relationship between liver fibrosis staging and spleen volume by computed tomography in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Chin J Misdiagnostics 9:7561–7562
Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R et al (2010) Spleen assessment by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography (ARFI) for prediction of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Med Ultrason 12:213–217
Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R et al (2012) Can ARFI elastography predict the presence of significant esophageal varices in newly diagnosed cirrhotic patients? Ann Hepatol 11:519–525
Furuichi Y, Moriyasu F, Taira J et al (2012) Noninvasive diagnostic method for idiopathic portal hypertension based on measurements of liver and spleen stiffness by ARFI elastography. J Gastroenterol 48:1061–1068
Chen S, Li Y, Lai H et al (2012) Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis via spleen stiffness measurement using acoustic radiation force impulse sonoelastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B or C. J Viral Hepat 19:654–663
Ye X, Ran H, Cheng J et al (2012) Liver and spleen stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis and esophageal varices in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Ultrasound Med 31:1245–1253
Lee M-J, Kim MJ, Han KH et al (2013) Age-related changes in liver, kidney, and spleen stiffness in healthy children measured with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Eur J Radiol 82:290–294
World Health Organization (2011) WHO Anthro, version 3.2.2. http://www.who.int/childgrowth/software/en/. Accessed 27 Jan 2015
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Takahashi H, Ono N, Eguchi Y et al (2010) Evaluation of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for fibrosis staging of chronic liver disease: a pilot study. Liver Int 30:538–545
Sirli R, Bota S, Sporea I et al (2013) Liver stiffness measurements by means of supersonic shear imaging in patients without known liver pathology. Ultrasound Med Biol 8:1362–1367
Pariente D, Franchi-Abella S (2010) Paediatric chronic liver diseases: how to investigate and follow up? Role of imaging in the diagnosis of fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol 40:906–919
Ma JJ, Ding H, Mao F et al (2014) Assessment of liver fibrosis with elastography point quantification technique in chronic hepatitis B virus patients: a comparison with liver pathological results. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:814–819
Chongsrisawat V, Vejapipat P, Siripon NB (2011) Transient elastography for predicting esophageal/gastric varices in children with biliary atresia. BMC Gastroenterol 18:41
Gallotti A, D’Onofrio M, Pozzi Mucelli R (2010) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging (ARFI) technique in ultrasound with virtual touch tissue quantification of the upper abdomen. Radiol Med 115:889–897
Fontanilla T, Canas T, Macia A et al (2014) Normal values of liver shear wave velocity in healthy children assessed by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging using a convex probe and a linear probe. Ultrasound Med Biol 40:470–477
Mannelli L, Godfrey E, Joubert I et al (2010) MR elastography: spleen stiffness measurements in healthy volunteers — preliminary experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:387–392
Hanquinet S, Courvoisier D, Kanavaki A et al (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging — normal values of liver stiffness in healthy children. Pediatr Radiol 43:539–544
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cañas, T., Fontanilla, T., Miralles, M. et al. Normal values of spleen stiffness in healthy children assessed by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI): comparison between two ultrasound transducers. Pediatr Radiol 45, 1316–1322 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3306-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3306-z