Abstract
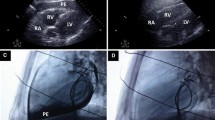
Although transcatheter arrhythmia ablation (TCA) has been performed in children for over two decades, guidelines for routine use of post-ablation transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) are absent. We sought to determine the efficacy of TTE after apparently uneventful TCA procedures in detecting adverse findings and identify predisposing factors. A retrospective review of clinical and procedural data on patients who underwent TCA for supraventricular arrhythmias from 2000 to 2015 was performed. Pre- and post-ablation TTE data were reviewed. All patients were followed at 1 week, 6 and 12 months post-TCA. A repeat TTE was performed at 12 months on patients in whom post-TCA abnormalities were found. Patients were divided into two groups: those with and without adverse TTE findings and comparative analysis between variables was performed. Data on 252 patients, 52% males, mean age 14 ± 3 years were analyzed. New onset or worsening atrioventricular valve regurgitation occurred in 17 (6.7%), a small pericardial effusion in 3 (1.2%) and worsened ventricular function in 2 patients (0.8%). Patients in the complication group had higher mean number of ablations (22.6 ± 15.3 vs. 16.8 ± 9.2, p 0.001) and required longer duration of ablation (sec) (254.6 ± 256.4 vs. 180.9 ± 158.9, p < 0.001). TCA location (including coronary sinus), energy source, arrhythmia substrate, and a trans-septal approach were noncontributory to any adverse findings. Routine post-ablation TTE uncovers asymptomatic self-resolving abnormalities that typically do not require any intervention.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Hare GF, Javitz H, Carmelli D, Saul JP, Tanel RE, Fischbach PS et al (2004) Prospective assessment after pediatric cardiac ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15(7):759–770
Kugler JD, Danford DA, Deal BJ, Gillette PC, Perry JC, Silka MJ, Van Hare GF, Walsh EP (1994) Radiofrequency catheter ablation for tachyarrhythmias in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med 330(21):1481–1487
Nielsen JC, Kottkamp H, Piorkowski C, Gerds-Li JH, Tanner H, Hindricks G (2006) Radiofrequency ablation in children and adolescents: results in 154 consecutive patients. Europace 8(5):323–329
Kammeraad JA, Sreeram N, Van Driel V, Oliver R, Balaji S (2004) Is routine echocardiography valuable after uncomplicated catheter ablation in children? Cardiol Young 14(04):386–388
Schneider HE, Kriebel T, Gravenhorst VD, Paul T (2009) Incidence of coronary artery injury immediately after catheter ablation for supraventricular tachycardias in infants and children. Heart Rhythm 6(4):461–467
Schaffer MS, Gow RM, Moak JP, Saul JP (2000) Participating members of the pediatric electrophysiology society. mortality following radiofrequency catheter ablation (from the pediatric radiofrequency ablation registry). Am J Cardiol 86(6):639–643
Blaufox AD, Felix GL, Saul JP (2001) Radiofrequency catheter ablation in infants ≤ 18 months old when is it done and how do they fare?: short-term data from the pediatric ablation registry. Circulation 104(23):2803–2808
Co-Chairs TF (2016) PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the use of catheter ablation in children and patients with congenital heart disease. Heart Rhythm 13(6):e252
Van Hare GF, Colan SD, Javitz H, Carmelli D, Knilans T, Schaffer M, Kugler J, Byrum CJ, Saul JP (2007) participating members of the pediatric electrophysiology society. prospective assessment after pediatric cardiac ablation: fate of intracardiac structure and function, as assessed by serial echocardiography. Am Heart J 153(5):815–820
Ceresnak SR, Dubin AM, Kim JJ, Valdes SO, Fishberger SB, Shetty I et al (2015) Success rates in pediatric WPW ablation are improved with 3-dimensional mapping systems compared with fluoroscopy alone: a multicenter study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 26(4):412–416
Haissaguerre M, Gaita F, Fischer B, Egloff P, Lemetayer P, Warin JF (1992) Radiofrequency catheter ablation of left lateral accessory pathways via the coronary sinus. Circulation 86(5):1464–1468
Langberg JJ, Man KC, Vorperian VR, Williamson B, Kalbfleisch SJ, Strickberger SA, Hummel JD, Morady F (1993) Recognition and catheter ablation of subepicardial accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol 22(4):1100–1104
Giorgberidze I, Saksena S, Krol RB, Mathew P (1995) Efficacy and safely of radiofrequency catheter ablation of left-sided accessory pathways through the coronary sinus. Am J Cardiol 76(5):359–365
Karpawich PP (2007) Catheter-delivered cryoablation in the pediatric coronary sinus: assessing newer arrhythmia therapies. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 18(6):598–600
Klein AL, Abbara S, Agler DA, Appleton CP, Asher CR, Hoit B et al (2013) American Society of Echocardiography clinical recommendations for multimodality cardiovascular imaging of patients with pericardial disease: endorsed by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 26(9):965–1012
Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ (2003) Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16(7):777–802
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J et al (2005) Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation 111(9):1100–1105
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J et al (2009) Prevalence and causes of fatal outcome in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(19):1798–1803
Minich LL, Snider AR, Dick M (1992) Doppler detection of valvular regurgitation after radiofrequency ablation of accessory connections. Am J Cardiol 70(1):116–117
Frias PA, Taylor MB, Kavanaugh-McHugh A, Fish FA (1999) Low incidence of significant valvar insufficiency following retrograde aortic radiofrequency catheter ablation in young patients. J Interv Cardiac Electrophysiol 3(2):181–185
Walsh EP (2007) Interventional electrophysiology in patients with congenital heart disease. Circulation 115(25):3224–3234
Buddhe S, Singh H, Du W, Karpawich PP (2012) Radiofrequency and cryoablation therapies for supraventricular arrhythmias in the young: five - year review of efficacies. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 35(6):711–717
Author Contributions
Dr. Shahnawaz Amdani and Dr. Sanjeev Aggarwal conceptualized and designed the study, carried out the analysis, drafted the initial manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. Dr. Salaam Sallaam carried out the initial analyses, reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. Dr. Peter Karpawich drafted the initial manuscript, reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amdani, S.M., Sallaam, S., Karpawich, P.P. et al. Utility of Echocardiography in Detecting Silent Complications After Pediatric Catheter Ablations. Pediatr Cardiol 38, 1426–1433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1680-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1680-z