Abstract
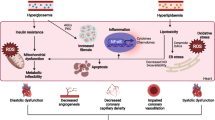
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of mortality among patients with diabetes, and heart failure exists even in the absence of coronary disease. Myocardial metabolism is altered in the diabetic heart as a result of changes in substrate availability secondary to insulin resistance. The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha (PPARα) and PPAR-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1α) play important roles in transcriptional regulation of myocardial metabolism and contribute significantly to the changes that occur in the diabetic heart. This review summarizes the role of PPARα and PGC-1α in myocardial metabolism in the normal heart and in the diabetic heart.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arany Z, He H, Lin J, Hoyer K, Handschin C, Toka O, Ahmad F, Matsui T, Chin S, Wu PH, Rybkin II, Shelton JM, Manieri M, Cinti S, Schoen FJ, Bassel-Duby R, Rosenzweig A, Ingwall JS, Spiegelman BM (2005) Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell Metab 1:259–271
Arany Z, Novikov M, Chin S, Ma Y, Rosenzweig A, Spiegelman BM (2006) Transverse aortic constriction leads to accelerated heart failure in mice lacking PPARγ coactivator 1α. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10086–10091
Barger PM, Brandt JM, Leone TC, Weinheimer CJ, Kelly DP (2000) Deactivation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α during cardiac hypertrophic growth. J Clin Invest 105:1723–1730
Belke DD, Larsen TS, Gibbs EM, Severson DL (2000) Altered metabolism causes cardiac dysfunction in perfused hearts from diabetic (db/db) mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E1104–E1113
Bernal-Mizrachi C, Weng S, Feng C, Finck BN, Knutsen RH, Leone TC, Coleman T, Mecham RP, Kelly DP, Semenkovich CF (2003) Dexamethasone induction of hypertension and diabetes is PPAR-α dependent in LDL receptor-null mice. Nat Med 9:1069–1075
Boudina S, Abel ED (2006) Mitochondrial uncoupling: a key contributor to reduced cardiac efficiency in diabetes. Physiology 21:250–258
Boudina S, Sena S, O’Neill BT, Tathireddy P, Young ME, Abel ED (2005) Reduced mitochondrial oxidative capacity and increased mitochondrial uncoupling impair myocardial energetics in obesity. Circulation 112:2686–2695
Buchanan J, Mazumder PK, Hu P, Chakrabarti G, Roberts MW, Jeong Yun U, Cooksey RC, Litwin SE, Abel ED (2005) Reduced cardiac efficiency and altered substrate metabolism precedes the onset of hyperglycemia and contractile dysfunction in two mouse models of insulin resistance and obesity. Endocrinology 146:5341–5349
Campbell FM, Kozak R, Wagner A, Altarejos JY, Dyck JR, Belke DD, Severson DL, Kelly DP, Lopaschuk GD (2002) A role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in the control of cardiac malonyl-CoA levels: reduced fatty acid oxidation rates and increased glucose oxidation rates in the hearts of mice lacking PPARalpha are associated with higher concentrations of malonyl-CoA and reduced expression of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 277:4098–4103
Chakravarthy MV, Lodhi IJ, Yin L, Malapaka RR, Xu HE, Turk J, Semenkovich CF (2009) Identification of a physiologically relevant endogenous ligand for PPARalpha in liver. Cell 138:476–488
Chiu HC, Kovacs A, Ford DA, Hsu FF, Garcia R, Herrero P, Saffitz JE, Schaffer JE (2001) A novel mouse model of lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest 107:813–822
Chiu HC, Kovacs A, Blanton RM, Han X, Courtois M, Weinheimer CJ, Yamada KA, Brunet S, Xu H, Nerbonne JM, Welch MJ, Fettig NM, Sharp TL, Sambandam N, Olson KM, Ory DS, Schaffer JE (2005) Transgenic expression of FATP1 in the heart causes lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 96:225–233
Cook WS, Yeldandi AV, Rao MS, Hashimoto T, Reddy JK (2000) Less extrahepatic induction of fatty acid beta-oxidation enzymes by PPAR alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 278:250–257
Dashti N, Ontko JA (1983) Alterations in rat serum lipids and apolipoproteins following clofibrate treatment. Atherosclerosis 49:255–266
Desvergne B, Wahli W (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20:649–688
Djouadi F, Bastin J, Kelly DP, Merlet-Benichou C (1996) Transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoids of mitochondrial oxidative enzyme genes in the developing rat kidney. Biochem J 315:555–562
Duncan JG, Fong JL, Medeiros DM, Finck BN, Kelly DP (2007) Insulin-resistant heart exhibits a mitochondrial biogenic response driven by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α/PGC-1α gene regulatory pathway. Circulation 115:909–917
Duncan JG, Bharadwaj KG, Fong JL, Mitra R, Sambandam N, Courtois MR, Lavine KJ, Goldberg IJ, Kelly DP (2010) Rescue of cardiomyopathy in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha transgenic mice by deletion of lipoprotein lipase identifies sources of cardiac lipids and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activators. Circulation 121:426–435
Fein FS, Sonnenblick EH (1985) Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 4:255–270
Finck BN, Kelly DP (2006) PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest 116:615–622
Finck BN, Lehman JJ, Leone TC, Welch MJ, Bennett MJ, Kovacs A, Han X, Gross RW, Kozak R, Lopaschuk GD, Kelly DP (2002) The cardiac phenotype induced by PPARα overexpression mimics that caused by diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 109:121–130
Finck BN, Han X, Courtois M, Aimond F, Nerbonne JM, Kovacs A, Gross RW, Kelly DP (2003) A critical role for PPARalpha-mediated lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy: modulation by dietary fat content. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1226–1231
Gamble J, Lopaschuk GD (1994) Glycolysis and glucose oxidation during reperfusion of ischemic hearts from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 1225:191–199
Gilde AJ, van der Lee KAJM, Willemsen PHM, Chinetti G, van der Leij FR, van der Vusse GJ, Staels B, van Bilsen M (2003) PPARα and PPARβ/δ, but not PPARγ, modulate the expression of genes involved in cardiac lipid metabolism. Circ Res 92:518–524
Handschin C, Spiegelman BM (2006) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr Rev 27:728–735
Herrero P, Peterson LR, McGill JB, Matthew S, Lesniak D, Dence C, Gropler RJ (2006) Increased myocardial fatty acid metabolism in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:598–604
Ide T, Oku H, Sugano M (1982) Reciprocal responses to clofibrate in ketogenesis and triglyceride and cholesterol secretion in isolated rat liver. Metabolism 31:1065–1072
Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP (1974) Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham Study. Am J Cardiol 34:29–34
Kelly DP, Scarpulla RC (2004) Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes Dev 18:357–368
Lai L, Leone TC, Zechner C, Schaeffer PJ, Kelly SM, Flanagan DP, Medeiros DM, Kovacs A, Kelly DP (2008) Transcriptional coactivators PGC-1alpha and PGC-1beta control overlapping programs required for perinatal maturation of the heart. Genes Dev 22:1948–1961
Lehman JJ, Barger PM, Kovacs A, Saffitz JE, Medeiros D, Kelly DP (2000) PPARγ coactivator-1 (PGC-1) promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis. J Clin Invest 106:847–856
Leone TC, Weinheimer CJ, Kelly DP (1999) A critical role for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) in the cellular fasting response: the PPARα-null mouse as a model of fatty acid oxidation disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7473–7478
Leone TC, Lehman JJ, Finck BN, Schaeffer PJ, Wende AR, Boudina S, Courtois M, Wozniak DF, Sambandam N, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Chen Z, Holloszy JO, Medeiros DM, Schmidt RE, Saffitz JE, Abel ED, Semenkovich CF, Kelly DP (2005) PGC-1α-deficient mice exhibit multisystem energy metabolic derangements: muscle dysfunction, abnormal weight control, and hepatic steatosis. PLoS Biol 3:672–687
Lorch SM, Sharkey A (2007) Myocardial velocity, strain, and strain rate abnormalities in healthy obese children. J Cardiometab Syndr 2:30–34
Mokdad AH, Bowman BA, Ford ES, Vinicor F, Marks JS, Koplan JP (2001) The continuing epidemics of obesity and diabetes in the United States. JAMA 286:1195–1200
Molnar D (2004) The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28:70–74
Monsalve M, Wu Z, Adelmant G, Puigserver P, Fan M, Spiegelman BM (2000) Direct coupling of transcription and mRNA processing through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Mol Cell 6:307–316
Murthy VK, Shipp JC (1977) Accumulation of myocardial triacylglycerols in ketotic diabetes. Diabetes 26:222–229
Neely JR, Rovetto MJ, Oram JF (1972) Myocardial utilization of carbohydrate and lipids. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 15:289–329
Panagia M, Gibbons GF, Radda GK, Clarke K (2005) PPAR-α activation required for decreased glucose uptake and increased susceptibility to injury during ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H2677–H2683
Park SY, Cho YR, Finck BN, Kim HJ, Higashimori T, Hong EG, Lee MK, Danton C, Deshmukh S, Cline GW, Wu JJ, Bennett AM, Rothermel B, Kalinowski A, Russell KS, Kim YB, Kelly DP, Kim JK (2005) Cardiac-specific overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha causes insulin resistance in heart and liver. Diabetes 54:2514–2524
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P (2005) The global spread of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 146:693–700
Puigserver P, Adelmant G, Wu Z, Fan M, Xu J, O’Malley B, Spiegelman BM (1999) Activation of PPARγ coactivator-1 through transcription factor docking. Science 286:1368–1371
Regan TJ (1983) Congestive heart failure in the diabetic. Ann Rev Med 34:161–168
Regan TJ, Lyons MM, Ahmed SS, Levinson GE, Oldewurtel HA, Ahmed MR, Haider B (1977) Evidence for cardiomyopathy in familial diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 60:885–899
Rodrigues B, Cam MC, McNeill JH (1995) Myocardial substrate metabolism: implications for diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27:169–179
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A (1972) New type of cardiomyopathy associated with glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 30:595–602
Russell LK, Mansfield CM, Lehman JJ, Kovacs A, Courtois M, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Valencik ML, McDonald JA, Kelly DP (2004) Cardiac-specific induction of the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and reversible cardiomyopathy in a developmental stage-dependent manner. Circ Res 94:525–533
Sano M, Izumi Y, Helenius K, Asakura M, Rossi DJ, Xie M, Taffet G, Hu L, Pautler RG, Wilson CR, Boudina S, Abel ED, Taegtmeyer H, Scaglia F, Graham BH, Kralli A, Shimizu N, Tanaka H, MÑkelÑ TP, Schneider MD (2007) MÇnage-Ö-Trois 1 is critical for the transcriptional function of PPARγ coactivator 1. Cell Metab 5:129–142
Sharma S, Adrogue JV, Golfman L, Uray I, Lemm J, Youker K, Noon GP, Frazier OH, Taegtmeyer H (2004) Intramyocardial lipid accumulation in the failing human heart resembles the lipotoxic rat heart. FASEB J 18:1692–1700
Shen X, Zheng S, Thongboonkerd V, Xu M, Pierce WM Jr, Klein JB, Epstein PN (2004) Cardiac mitochondrial damage and biogenesis in a chronic model of type I diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:E896–E905
Spiegelman BM, Heinrich R (2004) Biological control through regulated transcriptional coactivators. Cell 119:157–167
Stanley WC, Lopaschuk GD, McCormack JG (1997) Regulation of energy substrate metabolism in the diabetic heart. Cardiovasc Res 34:25–33
Szczepaniak LS, Victor RG, Orci L, Unger RH (2007) Forgotten but not gone: the rediscovery of fatty heart, the most common unrecognized disease in America. Circ Res 101:759–767
van Bilsen M, Smeets PJH, Gilde AJ, van der Vusse GJ (2004) Metabolic remodelling of the failing heart: the cardiac burnout syndrome? Cardiovasc Res 61:218–226
Vega RB, Huss JM, Kelly DP (2000) The coactivator PGC-1 cooperates with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α in transcriptional control of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Mol Cell Biol 20:1868–1876
Wallberg AE, Yamamura S, Malik S, Spiegelman BM, Roeder RG (2003) Coordination of p300-mediated chromatin remodeling and TRAP/mediator function through coactivator PGC-1α. Mol Cell 12:1137–1149
Watanabe K, Fujii H, Takahashi T, Kodama M, Aizawa Y, Ohta Y, Ono T, Hasegawa G, Naito M, Nakajima T, Kamijo Y, Gonzalez FJ, Aoyama T (2000) Constitutive regulation of cardiac fatty acid metabolism through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α associated with age-dependent cardiac toxicity. J Biol Chem 275:22293–22299
Yagyu H, Chen G, Yokoyama M, Hirata K, Augustus A, Kako Y, Seo T, Hu Y, Lutz EP, Merkel M, Bensadoun A, Homma S, Goldberg IJ (2003) Lipoprotein lipase (LpL) on the surface of cardiomyocytes increases lipid uptake and produces a cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest 111:419–426
Yang J, Sambandam N, Han X, Gross RW, Courtois M, Kovacs A, Febbraio M, Finck BN, Kelly DP (2007) CD36 deficiency rescues lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 100:1208–1217
Zhou YT, Grayburn P, Karim A, Shimabukuro M, Higa M, Baetens D, Orci L, Unger RH (2000) Lipotoxic heart disease in obese rats: implications for human disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1784–1789
Acknowledgments
Jennifer G. Duncan, a Faculty Scholar of the Children’s Discovery Institute at Washington University School of Medicine, is supported by an NHLBI K08 award (HL084093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duncan, J.G. Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-Alpha (PPARα) and PPAR Gamma Coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1α) Regulation of Cardiac Metabolism in Diabetes. Pediatr Cardiol 32, 323–328 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9889-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9889-8