Abstract
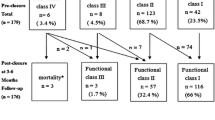
The study aimed to investigate the intermediate-term effects of transcatheter atrial septal defect (ASD) closure on cardiac remodeling in children and adult patients. Between December 2003 and February 2009, 117 patients (48 males, 50 adults) underwent transcatheter ASD closure with the Amplatzer septal occluder (ASO). The mean age of the patients was 15 years, and the mean follow-up period was 25.9 ± 12.4 months. New York Heart Association (NYHA) class, electrocardiographic parameters, and transthoracic echocardiographic (TTE) examination were evaluated before the ASD closure, then 1 day, 1 month, 6 months, 12 months, and yearly afterward. Transcatheter ASD closure was successfully performed for 112 (96%) of the 117 patients. The mean ASD diameter measured by transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) was 14.0 ± 4.2 mm, and the mean diameter stretched with a sizing balloon was 16.6 ± 4.8 mm. The mean size of the implanted device was 18.6 ± 4.9 mm. The Qp/Qs ratio was 2.2 ± 0.8. The mean systolic pulmonary artery pressure was 40 ± 10 mmHg. At the end of the mean follow-up period of 2 years, the indexed right ventricular (RV) end-diastolic diameter had decreased from 36 ± 5 to 30 ± 5 mm/m2 (p = 0.005), and the indexed left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic diameter had increased from 33 ± 5 to 37 ± 6 mm/m2 (p = 0.001), resulting in an RV/LV ratio decreased from 1.1 ± 0.2 to 0.8 ± 0.2 (p = 0.001). The New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional capacity of the patients was improved significantly 24 months after ASD closure (1.9 ± 0.5 to 1.3 ± 0.5; p = 0.001). At the 2-year follow up electrocardiographic examination, the P maximum had decreased from 128 ± 15 to 102 ± 12 ms (p = 0.001), the P dispersion had decreased from 48 ± 11 to 36 ± 9 ms (p = 0.001), and the QT dispersion had decreased from 66 ± 11 to 54 ± 8 ms (p = 0.001). Five of six patients experienced resolution of their preclosure arrhythmias, whereas the remaining patient continued to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. A new arrhythmia (supraventricular tachycardia) developed in one patient and was well controlled medically. Transcatheter ASD closure leads to a significant improvement in clinical status and heart cavity dimensions in adults and children, as shown by intermediate-term follow-up evaluation. Transcatheter ASD closure can reverse electrical and mechanical changes in atrial myocardium, resulting in a subsequent reduction in P maximum and P dispersion times.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Attenhofer Jost CH, Oechslin E, Seifert B, Maly F, Fatio R, Turina J, Jenni R (2002) Remodelling after surgical repair of atrial septal defects within the oval fossa. Cardiol Young 12:506–512
Berger F, Ewert P, Bjornstad PG, Dähnert I, Krings G, Brilla-Austenat I, Vogel M, Lange PE (1999) Transcatheter closure as standard treatment for most interatrial defects: experience in 200 patients treated with the Amplatzer septal occluder. Cardiol Young 9:468–473
Brandenburg RO Jr, Holmes DR Jr, Brandemburg RO, McGoon DC (1983) Clinical follow-up study of paroxysmal supraventricular tachyarrhythmias after operative repair of secundum type atrial septal defect in adults. Am J Cardiol 51:273–276
Brochu MC, Baril JF, Dore A, Juneau M, De Guise P, Mercier LA (2002) Improvement in exercise capacity in asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic adults after atrial septal defect percutaneous closure. Circulation 106:1821–1826
Carcagnì A, Presbitero P (2002) Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer occluder in adult patients. Ital Heart J 3:182–187
Cowley CG, Lloyd TR, Bove EL, Gaffney D, Dietrich M, Rocchini AP (2001) Comparison of results of closure of secundum atrial septal defect by surgery versus Amplatzer septal occluder. Am J Cardiol 88:589–591
Di Bernardo S, Berger F, Fasnacht M, Bauersfeld U (2005) Impact of right ventricular size on ECG after percutaneous closure of atrial septal defect with Amplatzer septal occluder. Swiss Med Wkly 135:647–651
Du ZD, Cao QL, Koenig P, Heitschmidt M, Hijazi ZM (2001) Speed of normalization of right ventricular volume overload after transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect in children and adults. Am J Cardiol 88:1450–1453
Du ZD, Hijazi ZM, Kleinman CS, Silverman NH, Larntz K, Investigators Amplatzer (2002) Comparison between transcatheter and surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect in children and adults: results of a multicenter nonrandomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:1936–1944
Fischer G, Stieh J, Uebing A, Hoffmann U, Morf G, Kramer HH (2003) Experience with transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the Amplatzer septal occluder: a single-centre study in 236 consecutive patients. Heart 89:199–204
Gatzoulis MA, Redington AN, Somerville JS, Shore DF (1996) Should atrial septal defects be closed in adults. Ann Thorac Surg 61:657–659
Gatzoulis MA, Freeman MA, Siu SC, Webb GD, Harris L (1999) Atrial arrhythmia after surgical closure of atrial septal defects in adults. N Engl J Med 340:839–846
Guray U, Guray Y, Yilmaz MB, Mecit B, Sasmaz H, Korknaz S, Kutuk E (2003) Evaluation of P-wave duration and P-wave dispersion in adult patients with secundum atrial septal defect during normal sinus rhythm. Int J Cardiol 91:75–79
Guray U, Guray Y, Mecit B, Yilmaz MB, Sasmaz H, Korkmaz S (2004) Maximum P-wave duration and P-wave dispersion in adult patients with secundum atrial septal defect: the impact of surgical repair. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 9:136–141
Ho TF, Chia EL, Yip WC, Chan KY (2001) Analysis of P-wave and P-wave dispersion in children with secundum atrial septal defect. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 6:305–309
Kaya MG, Ozdogru I, Baykan A, Inanç T, Dogan A, Dogdu O, Topsakal R, Uzum K, Narin N, Oguzhan A, Ergin A, Eryol NK (2008) Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defect using Amplatzer device in adult patients: our first clinical experiences. Arch Turk Soc Cardiol 36:287–293
Masura J, Gavora P, Formanek A, Hijazi ZM (1997) Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the new self-centering Amplatzer septal occluder: initial human experience. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 42:388–393
Ning SB, Fazal H, Cook D, Wood MM, Duncan WJ, Rowe RD (1984) Right ventricular size and ventricular septal motion after repair of atrial septal defect in children. Can J Surg 27:395–398
Omeish A, Hijazi ZM (2001) Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect in children and adults using the Amplatzer septal occluder. J Interv Cardiol 14:37–44
Pascotto M, Santoro G, Cerrato F, Caputo S, Bigazzi MC, Iacono C, Carrozza M, Russo MG, Caianiello G, Calabrò R (2006) Time course of cardiac remodeling following transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect. Int J Cardiol 112:348–352
Patel A, Lopez K, Banerjee A, Joseph A, Cao QL, Hijazi ZM (2007) Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in adults ≥40 years of age: immediate and follow-up results. J Interv Cardiol 20:82–88
Pearlman AS, Borer JS, Clark CE (1978) Abnormal right ventricular size and ventricular septal motion after atrial septal defect closure: etiology and functional significance. Am J Cardiol 41:295–301
Santoro G, Pascotto M, Sarubbi B, Bigazzi MC, Calvanese R, Iacono C, Pisacane C, Palladino MT, Pacileo G, Russo MG, Calabro R (2004) Early electrical and geometric changes after percutaneous closure of large atrial septal defect. Am J Cardiol 93:876–880
Silversides CK, Haberer K, Siu SC, Webb GD, Benson LN, McLaughlin PR, Harris D (2008) Predictors of atrial arrhythmias after device closure of secundum type atrial septal defects in adults. Am J Cardiol 101:683–687
Spargias KS, Lindsay SJ, Kawar GI, Greenwood DC, Cowan JC, Ball SG, Hall AS (1999) QT dispersion as a predictor of long-term mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction and clinical evidence of heart failure. Eur Heart J 20:1158–1165
Therien J, Webb GD (2001) Congenital heart diseases in adults. In: Braunwald E, Zipes DP, Libby P (eds) Heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 6th edn. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1592–1621
Tsikouris JP, Klugger J, Song J, White CM (2001) Changes in P-wave dispersion and P-wave duration after open heart surgery are associated with peak incidence of atrial fibrillation. Heart Lung 30:466–471
Veldtman GR, Razack V, Siu S, El-Hajj H, Walker F, Webb GD, Benson LN, McLaughlin PR (2001) Right ventricular form and function after percutaneous atrial septal defect device closure. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:2108–2113
Wilson NJ, Smith J, Prommete B, Donnell CO, Gentles TL, Ruygrok PN (2008) Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder in adults and children: follow-up closure rates, degree of mitral regurgitation, and evolution of arrhythmias. Heart Lung Circ 17:318–324
Yew G, Wilson NJ (2005) Transcatheter atrial septal defect closure with the Amplatzer septal occluder: five-year follow-up. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 64:193–196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, M.G., Baykan, A., Dogan, A. et al. Intermediate-Term Effects of Transcatheter Secundum Atrial Septal Defect Closure on Cardiac Remodeling in Children and Adults. Pediatr Cardiol 31, 474–482 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-009-9623-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-009-9623-y