Abstract.
The effect of salinity and the mode of application (oral versus aqueous) on the lead accumulation in different tissues of the fish host eel (Anguilla anguilla) and its parasites Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda) and Paratenuisentis ambiguus (Acanthocephala) was investigated. Waterborne as well as dietary lead exposure caused an increase in the metal levels of different eel tissues and the parasites. The mode of lead application had a significant influence on the distribution of lead in the fish tissues. No significant difference on the lead concentration due to water salinity was found for the fish tissues.
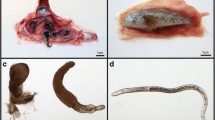
Among the analyzed tissues and helminths, the intestinal acanthocephalan P. ambiguus contained the significantly highest amounts of lead, which were affected by neither the mode of application nor the water salinity. In contrast, the lead level of the nematode A. crassus dwelling in the swim bladder of eels was even below the levels detected for host liver, intestine, and bile. Thus, depending on the mode of lead application, the resulting metal concentrations were approximately 20 to 2,000 times higher in P. ambiguus than in A. crassus. These differences may be due to the different microhabitats and nutrient uptake mechanisms of both parasite species.
This study presents important new facts for the use of intestinal fish parasites as biological indicators for water quality, not only in freshwater, but also in marine and estuarine ecosystems. The combination of the results obtained from the host and the parasites could reveal a more detailed tool to ascertain the source of an environmental contamination than a study based on a single species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 January 1999/Accepted: 3 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmermann, S., Sures, B. & Taraschewski, H. Experimental Studies on Lead Accumulation in the Eel-Specific Endoparasites Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda) and Paratenuisentis ambiguus (Acanthocephala) as Compared with Their Host, Anguilla anguilla . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 37, 190–195 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900505
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900505