Abstract
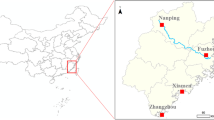
Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are of special concern due to their environmental persistence and biotoxicity. In the present study, spatial distribution of PFCs in atmosphere of the Pearl River Delta (PRD) of Southern China was investigated from November 2013 to January 2014. Forty-two air samples were collected using passive air samplers to determine the 13 target analytes, including perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs, C5–14) and perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs, C4, C6, and C8). Results showed that the total concentrations of PFCs (ΣPFCs) ranged from 53.7 to 225 pg m−3 with an average level of 122 ± 41.5 pg m−3, indicating a wide variation on ΣPFCs in atmosphere of the PRD. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) was the most abundant PFCs, followed by perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), perfluoropentanoic acid (PFPeA), and perfluoroheptanoic acid (PFHpA). PFOS, PFOA, PFPeA, and PFHpA accounted for 26%, 22%, 21%, and 19% of ΣPFCs, respectively. A general decline in ΣPFCs was observed in the atmosphere from south PRD to north PRD. It was likely related to the industrial distribution, population density, and wind direction. In addition, the same order of magnitude of PFOS and lower level of PFOA were observed in this study compared with those in atmosphere sampled in other regions. The lifetime risk indexes on the PFOS and PFOA concentrations were much less than unity, suggesting a lower nononcogenic risk to residents in the PRD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach CC, Vested A, Jorgensen KT, Bonde JP, Henriksen TB, Toft G (2016) Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and measures of human fertility: a systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol 46(9):735–755
Bai Z (1995) Research of two important issues in atmospheric pollution chemistry. Tianjin, Chinese Doctoral Dissertation of Naikai University
Barber JL, Berger U, Chaemfa C, Huber S, Jahnke A, Temme C, Jones KC (2007) Analysis of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J Environ Monit 9(6):530–541
Chaemfa C, Barber JL, Huber S, Breivik K, Jones KC (2010) Screening for PFOS and PFOA in European air using passive samplers. J Environ Monit 12(5):1100–1109
D’Eon JC, Hurley MD, Wallington TJ, Mabury SA (2006) Atmospheric chemistry of N-methyl perfluorobutane sulfonamidoethanol, C4F9SO2N(CH3)CH2CH2OH: kinetics and mechanism of reaction with OH. Environ Sci Technol 40(6):1862–1868
Dreyer A, Ebinghaus R (2009) Polyfluorinated compounds in ambient air from ship- and land-based measurements in northern Germany. Atmos Environ 43(8):1527–1535
Duan X (2012) Research methods of exposure factors and its application in environmental health risk assessment. Science Press, Beijing
Ellis DA, Martin JW, De Silva AO, Mabury SA, Hurley MD, Sulbaek Andersen MP, Wallington TJ (2004) Degradation of fluorotelomer alcohols: a likely atmospheric source of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. Environ Sci Technol 38(12):3316–3321
General Administration of Sport of China (2011) The national physique monitoring bulletin in 2010. http://www.sport.gov.cn/n16/n1077/n297454/2052709.html. Accessed 11 Nov 2011
Gouin T, Harner T, Blanchard P, Mackay D (2005) Passive and active air samplers as complementary methods for investigating persistent organic pollutants in the great lakes basin. Environ Sci Technol 39(23):9115–9122
He P, Zhang H, Li J, He L, Luo J, Liu G, Shen J, Yang B, Cui X (2016) Residue characteristics of perfluorinated compounds in the atmosphere of Shenzhen. Environ Sci 37(4):1240–1247
Hu G, Zheng H, Zhang L, Xu Z, Chen L, He D, Li H (2013) Contamination characteristics of perfluorinated compounds in soil from Pearl River Delta, South China. China Environ Sci 33(S1):37–42
Kim SK, Shoeib M, Kim KS, Park JE (2012) Indoor and outdoor poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Korea determined by passive air sampler. Environ Pollut 162(5):144–150
Kissa E (2001) Fluorinated surfactants and repellents, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Langer V, Dreyer A, Ebinghaus R (2010) Polyfluorinated compounds in residential and nonresidential indoor air. Environ Sci Technol 44(21):8075–8081
Li J, Vento SD, Schuster J, Zhang G, Chakraborty P, Kobara Y, Jones KC (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in the Asian atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 45(17):7241–7248
Liu B, Zhang H, Yao D, Li J, Xie L, Wang X, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang B (2015) Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in the atmosphere of Shenzhen, China: spatial distribution, sources and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 138:511–518
Martin JW, Ellis DA, Mabury SA, Hurley MD, Wallington TJ (2006) Atmospheric chemistry of perfluoroalkane sulfonamides: kinetic and product studies of the OH radical and Cl atom initiated oxidation of N-ethyl perfluorobutane sulfonamide. Environ Sci Technol 40(3):864–872
OECD (2002) Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Hazard assessment of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and its salts. [ENV/JM/RD (2002) 17/FINAL]
Paul AG, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2009) A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Sci Technol 43(2):386–392
Prevedouros K, Cousins IT, Buck RC, Korzeniowski SH (2006) Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ Sci Technol 40(1):32–44
Renner R (2001) Growing concern over perfluorinated surfactants under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Chemosphere 32:1563–1574
Schenker U, Scheringer M, Macleod M, Martin JW, Cousins IT, Hungerbühler K (2008) Contribution of volatile precursor substances to the flux of perfluorooctanoate to the arctic. Environ Sci Technol 42(10):3710–3716
Schultz MM, Barofsky DF, Field JA (2003) Fluorinated alkyl surfactants. Environ Eng Sci 20(5):487–501
Shoeib M, Harner T (2002) Characterization and comparison of three passive air samplers for persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 36(19):4142–4151
Shoeib M, Harner T, Ikonomou M, Kannan K (2004) Indoor and outdoor air concentrations and phase partitioning of perfluoroalkyl sulfonamides and polybrominated diphenyls ethers. Environ Sci Technol 38(5):1313–1320
Shoeib M, Harner T, Vlahos P (2006) Perfluorinated chemicals in the Arctic atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 40(24):7577–7583
Stock NL, Furdui VI, Muir DC, Mabury SA (2007) Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in the Canadian arctic: evidence of atmospheric transport and local contamination. Environ Sci Technol 41(10):3529–3536
Tian Y, Yao Y, Chang S, Zhao Z, Zhao Y, Yuan X, Wu F, Sun H (2018) Occurrence and phase distribution of neutral and ionizable per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the atmosphere and plant leaves around landfills: a case study in Tianjin, China. Environ Sci Technol 52(3):1301–1310
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2009) The toxicity of perfluorooctanic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pfoa/pubs/Final%20PFOA%20PFOS%20RfD%20memo%2010-28-09.pdf. Accessed 28 Oct 2009
Voogt DP, Sáez M (2006) Analytical chemistry of perfluoroalkylated substances. Trends Anal Chem 25(4):326–342
Yamashita N, Kannan K, Taniyasu S, Horii Y, Petrick G, Gamo T (2005) A global survey of perfluorinated acids in oceans. Mar Pollut Bull 51(8–12):658–668
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31670527), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, China (No. 20170101166JC), and the Natural Science Foundation of Changchun Normal University (No. 2015003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Xie, L., Zhang, H. et al. Spatial Distribution of Perfluorinated Compounds in Atmosphere of the Pearl River Delta, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 77, 180–187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00637-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00637-6