Abstract
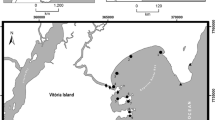
The temporal changes in the frequency and degree of imposex and tributyltin (TBT) levels in gastropod (Reishia clavigera) were evaluated in Jinhae Bay, 5 and 10 years after the total ban on TBT usage in South Korea. The frequency and degree of imposex decreased significantly after the ban, accompanied by an increase in the female-to-male ratio. The TBT concentrations in R. clavigera also decreased significantly after the ban. There were good correlations between the TBT concentration in rock shell and both the degree of imposex and the female-to-male ratio. The total TBT ban effectively reduced the TBT levels and the frequency and degree of imposex in R. clavigera. However, the current low exposure level in the study area is still sufficient to cause imposex in R. clavigera. More time is needed to reduce the TBT levels to levels that do not have adverse biological effects on R. clavigera.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidli S, Santos MM, Lahbib Y, Castro LFC, Reis-Henriques MA, Menif NTE (2012) Tributyltin (TBT) effects on Hexaplex trunculus and Bolinus brandaris (Gastropoda: Muricidae): imposex induction and sex hormone levels insights. Ecol Ind 13:13–21
Barroso CM, Moreira MH (2002) Spatial and temporal changes of TBT pollution along the Portuguese coast: inefficacy of the EEC directive 89/677. Mar Pollut Bull 44:480–486
Berto D, Giani M, Boscolo R, Covelli S, Giovanardi O, Massironi M et al (2007) Organotins (TBT and DBT) in water, sediments, and gastropods of the southern Venice lagoon (Italy). Mar Pollut Bull 55:425–435
Blackmore G (2000) Imposex in Thais clavigera (Neogastropoda) as an indicator of TBT (Tributyltin) bioavailability in coastal waters of Hong Kong. J Molluscan Stud 66:1–8
Champ MA (2000) A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. Sci Total Environ 258:21–71
Chan KM, Leung KMY, Cheung KC, Wong MH, Qiu JW (2008) Seasonal changes in imposex and tissue burden of butyltin compounds in Thais clavigera populations along the coastal area of Mirs Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 57:645–651
Choi M, Choi H-G, Moon H-B, Kim G-Y (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of tributyltin (TBT) in seawater, sediments and bivalves from coastal areas of Korea during 2001–2005. Environ Monit Assess 151:301–310
Choi M, Moon H-B, Yu J, Cho H, Choi HG (2013) Temporal trends (2004–2009) of imposex in rock shells Thais clavigera collected along the Korean coast associated with tributyltin regulation in 2003 and 2008. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64:448–455
Diez S, Abalos M, Bayona JM (2002) Oganotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Res 36:905–918
Evans SM, Leksono T, Mckinnell PD (1995) Tributyltin pollution: a diminishing problem flowing legislation limiting the use of TBT-based anti-fouling paints. Mar Pollut Bull 30:14–21
Furdek M, Vahcic M, Scancar J, Milacic R, Kniewald G, Mikac N (2012) Organotin compounds in seawater and Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels along the Croatian Adriatic coast. Mar Pollut Bull 64:189–199
Galante-Oliveira S, Oliveira I, Ferreira N, Santos JA, Pacheco M, Barroso C (2011) Nucella lapillus L. imposex levels after legislation prohibiting TBT antifoulants: temporal trends from 2003 to 2008 along the Portuguese coast. J Environ Monit 13:304–312
Gibson CP, Wilson SP (2003) Imposex still evident in eastern Australia 10 years after tributyltin restrictions. Mar Environ Res 55:101–112
Guomundsdottir LO, Ho KKY, Lam JCW, Svavarsson J (2011) Long-term temporal trends (1992–2008) of imposex status associated with organotin contamination in the dogwhelk Nucella lapillus along the Icelandic coast. Mar Pollut Bull 63:500–507
Horiguchi T, Cho H-S, Shiraishi H, Shibata Y, Soma M, Morita M et al (1998) Field studies on imposex and organotin accumulation in the rock shell, Thais clavigera, from the Seto Inland Sea and the Sanriku region, Japan. Sci Total Environ 214:65–70
Hsia M-P, Liu S-M (2003) Accumulation of organotin compounds in Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas, collected from aquaculture sites in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313:41–48
Hung T-C, Lee T-Y, Liao T-F (1998) Determination of butyltins and phenyltins in oysters and fishes from Taiwan coastal waters. Environ Pollut 102:197–203
IMO, International Maritime Organization (2008) International convention on the control of harmful anti-fouling systems on ships. http://www.imo.org/conventions. Accessed 17 Sept 2009. IMO 17-9-2008
Kim NS, Shim WJ, Yim UH, Ha SY, Park PS (2008) Assessment of tributyltin contamination in a shipyard area using a mussel transplantation approach. Mar Pollut Bull 57:883–888
Kim NS, Hong SH, Yim UH, Shin K-H, Shim WJ (2014) Temporal changes in TBT pollution in water, sediment, and oyster from Jinhae Bay after the total ban in South Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 86:547–554
Koyama J, Takenouchi A, Nigaya S, Kokushi E, Uno S (2012) Organotin residues in rock shell, Thais clavigera, and their sources in Kagoshima Bay, Japan. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 15:260–266
Lahbib Y, Abidli S, Gonzalez PR, Alonso JIG, Menif NTE (2011) Monitoring of organotin pollution in Bizerta channel (Northern Tunisia): temporal trend from 2002 to 2010. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:531–534
Laranjeiro F, Sánchez-Marín P, Galante-Oliveira S, Barroso C (2015) Tributyltin pollution biomonitoring under the Water Framework Directive: proposal of a multi-species tool to assess the ecological quality status of EU water bodies. Ecol Indic 57:525–535
Leung KMY, Kwong RPY, Ng WC, Horiguchi T, Qiu JW, Yang R et al (2006) Ecological risk assessments of endocrine disrupting organotin compounds using marine neogastropods in Hong Kong. Chemosphere 65:922–938
Omae I (2003) Organotin antifouling paints and their alternatives. Appl Organomet Chem 17:81–105
Pavoni B, Centanni E, Valcanover S, Fasolato M, Ceccato S, Tagliapietra D (2007) Imposex levels and concentrations of organotin compounds (TBT and its metabolites) in Nassarius nitidus from the Lagoon of Venice. Mar Pollut Bull 55:505–511
Paz-Villarraga CA, Castro ÍB, Miloslavich P, Fillmann G (2015) Venezuelan Caribbean Sea under the threat of TBT. Chemosphere 119:704–710
Qiu J-W, Chan KM, Leung KMY (2011) Seasonal variations of imposex indices and butyltin concentrations in the rock shell Thais clavigera collected from Hong Kong waters. Mar Pollut Bull 63:482–488
Rodriguez JG, Borja A, Franco J, Alonso JIG, Garmendia JM, Muxika I et al (2009) Imposex and butyltin body burden in Nassarius nitidus (Jeffereys, 1867), in coastal waters within the Basque country (northern Spain). Sci Total Environ 407:4333–4339
Ruiz JM, Barreiro R, Couceiro L, Quintela M (2008) Decreased TBT pollution and changing bioaccumulation pattern in gastropods imply butyltin desorption from sediments. Chemosphere 73:1253–1257
Shim WJ, Kahng SH, Hong SH, Kim NS, Kim SK, Shim JH (2000) Imposex in the rock shell, Thais clavigera, as evidence of organotin contamination in the marine environment of Korea. Mar Environ Res 49:435–451
Shim WJ, Hong SH, Kim NS, Yim UH, Li D, Oh JR (2005) Assessment of butyl- and phenyltin pollution in the coastal environment of Korea using mussels and oysters. Mar Pollut Bull 51:922–931
Shim WJ, Kim NS, Jeon JK, Hong SH (2009) Accumulation of tributyltin and triphenyltin compounds in laboratory exposure and their induction of imposex in rock shell (Thais clavigera). Toxicol Environ Health Sci 13:182–187
Sonak S, Pangam P, Giriyan A, Hawaldar K (2009) Implications of the ban on organotins for protection of global coastal and marine ecology. J Environ Manag 90:96–108
Sousa A, Mendo S, Barroso C (2005) Imposex and organotin contamination in Nassarius reticulatus (L.) along the Portuguese coast. Appl Organomet Chem 19:315–323
Sousa A, Matsudaira C, Takahashi S, Tanabe S, Barroso C (2007) Integrative assessment of organotin contamination in a southern European estuarine system (Ria de Aveiro, NW Portugal): tracking temporal trends in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the EU ban. Mar Pollut Bull 54:1645–1653
Sousa A, Laranjeiro F, Takahashi S, Tanabe S, Barroso CM (2009) Imposex and organotin prevalence in a European post-legislative scenario: temporal trends from 2003 to 2008. Chemosphere 77:566–573
Terlizzi A, Delos AL, Garaventa F, Faimali M, Geraci S (2004) Limited effectiveness of marine protected areas: imposex in Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda, Muricidae) populations from Italian marine reserves. Mar Pollut Bull 48:188–192
Toste R, Pessoa IA, Dore MP, Parahyba MA, Fernandez MA (2013) Is aphallic vas deferens development in females related to the distance from organotin sources? A study with Stramonita haemastoma. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 91:162–170
Verhaegen Y, Monteyne E, Neudecker T, Tulp I, Smagghe G, Cooreman K et al (2012) Organotins in North Sea brown shrimp (Crangon crangon L.) after implementation of the TBT ban. Chemosphere 86:979–984
Waite ME, Waldock MJ, Thain JE, Smith DJ, Milton SM (1991) Reductions in TBT concentrations in UK estuaries following legislation in 1986 and 1987. Mar Environ Res 32:89–111
Waldock MJ, Thain JE, Smith D, Milton S (1990) The degradation of TBT in estuarine sediments. In: 3rd international organotin symposium proceedings, Monaco, 17–20 April 1990. IAEA, pp 46–48
Wilson JG, Minchin D, McHugh B, McGovern E, Tanner CJ, Giltrap M (2015) Declines in TBT contamination in Irish coastal waters 1987–2011, using the dogwhelk (Nucella lapillus) as a biological indicator. Mar Pollut Bull 100:289–296
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by research projects titled “Development of Techniques for Assessment and Management of Hazardous Chemicals in the Marine Environment.” Funding was provided by Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, N.S., Hong, S.H., Shin, KH. et al. Imposex in Reishia clavigera as an Indicator to Assess Recovery of TBT Pollution After a Total Ban in South Korea. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73, 301–309 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0369-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0369-x