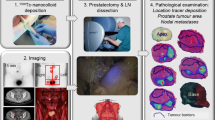
Abstract
At present there are neither clinical nor experimental data available on the influence of technical details on the quality and reproducibility of prostate lymphoscintigraphy. Six adult fox hounds received repeated transrectal ultrasound guided intraprostatic injections of a technetium 99m labeled nanocolloid to prove the influence of different techniques of injection (one central injection in both prostate lobes vs two peripheral injections in both lobes) on tracer accumulation in sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) and other organs. The reproducibility of the favored technique was examined and in a last step it was subject to scrutiny following a reduction of the injected volume to 1% of the prostate volume. The number of scintigraphically visualized SLN varied between four and seven. They were located in the region of the internal and external iliac vessels, presacrally, paravesically, and directly paraprostatically. In five of six cases, the localization was reproducible both with the central application of an identical volume as well as with the volume reduced central injection. Tracer accumulation of SLNs and other organs varied enormously. We expect that with the combination of both injection techniques, even with the reduced injection volume, an optimized prostate lymphoscintigraphy will be the outcome.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aumüller G (1983) Morphologie der normalen Prostata und experimentelle Modelle der Prostataforschung. In: Helpap B, Senge T, Vahlensieck W (eds) Die Prostata. pmi, Frankfurt, p 15
Aumüller G (2000) Anatomie. In: Höfner K, Stief CG, Jonas U (eds) Benigne Prostatahyperplasie: Ein Leitfaden für die Praxis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, p 43
Chang SC, Anthony S, Koder PC, Brown SG (1997) Transrectal ultrasound guided manipulation of the canine prostate with minimum intervention. Lab Anim 31: 219
Fukuda H, Yamada T, Kamata S, Saitoh H (2000) Anatomic distribution of intraprostatic lymphatics: implications for the lymphatic spread of prostate cancer—a preliminary study. Prostate 44: 322
Gallowitsch HJ (2001) Lymphoscintigraphy and dosimetry. In: Munz DL (ed) The sentinel lymph node concept in oncology. Facts and fiction. W. Zuckschwerdt, München p 57
Horenblas S, Jansen L, Meinhardt W, Hoefnagel CA, De Jong D, Nieweg OE (2000) Detection of occult metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the penis using a dynamic sentinel node procedure. J Urol 163: 100
Kaplan WD, Whitmore WF, Gittes RF (1980) Visualization of canine and human prostatic lymph nodes following intraprostatic injection of technetium 99m antimony sulfide colloid. Invest Radiol 15: 34
McMasters KM, Reintgen DS, Ross MI, Wong SL, Gershenwald JE, Krag DN, Noyes RD, Viar V, Cerrito PB, Edwards MJ (2001) Sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma: how many radioactive nodes should be removed? Ann Surg Oncol 8: 192
Menon M, Menon S, Strauss HW, Catalona WJ (1977) Demonstration of the existence of canine prostatic lymphatics by radioisotope technique. J Urol 118: 274
Miltenburg DM, Miller C, Karamlou TB, Brunicardi FC (1999) Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. J Surg Res 84: 138
Morton DL, Wen DR, Cochran AJ (1990) Management of early stage melanoma by intraoperative lymphatic mapping and selective lymphadenectomy. An alternative to routine elective lymphadenectomy or watch and wait. Surg Oncol Clin North Am 1: 247
Suzuki T, Kurokawa K, Yamanaka H, Jimbo H (1992) Lymphatic drainage of the prostate gland in canines. Prostate 21: 279
Uren RF, Howman-Giles RB, Thompson JF, Malouf D, Ramsey-Stewart G, Niesche FW, Rennwick SB (1995) Mammary lymphoscintigraphy in breast cancer. J Nucl Med 36: 1775
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Bachter D, Weckermann D, Hamm M, Harzmann R (2000) First experience of gamma probe guided sentinel lymph node surgery in penile cancer. Urol Res 28: 246
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Weckermann D, Wagner T, Hamm M, Harzmann R (2001) Radioisotope guided pelvic lymph node dissection for prostate cancer. J Urol 166: 1715
Wengenmair H, Kopp J, Vogt H, Wawroschek F, Gröber S, Dorn R, Heidenreich P (2002)Sentinel lymph node diagnostic in prostate carcinoma. Part II: Biokinetics and dosimetry of 99mTc-nanocolloid after intraprostatic injection. Nuklearmedizin 41: 102
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr. Keil for his assistance in translation, Mrs. Grahneis and Mr. Finke for their assistance in prostate lymphoscintigraphy imaging, and Mr. Henning from the Institute of Medical Statistics, Technische Universität München, who designed the study. The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Wa 1533/1-1, Bonn, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wawroschek, F., Wengenmair, H., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R. et al. Prostate lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel lymph node identification in canines: reproducibility, uptake, and biokinetics depending on different injection strategies. Urol Res 31, 152–158 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-003-0307-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-003-0307-4