Abstract
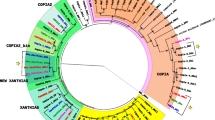
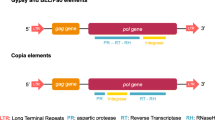
Copia is a retrotransposon that appears to be distributed widely among the Drosophilidae subfamily. Evolutionary analyses of regulatory regions have indicated that the Copia retrotransposon evolved through both positive and purifying selection, and that horizontal transfer (HT) could also explain its patchy distribution of the among the subfamilies of the melanogaster subgroup. Additionally, Copia elements could also have transferred between melanogaster subgroup and other species of Drosophilidae—D. willistoni and Z. tuberculatus. In this study, we surveyed seven species of the Zaprionus genus by sequencing the LTR–ULR and reverse transcriptase regions, and by using RT–PCR in order to understand the distribution and evolutionary history of Copia in the Zaprionus genus. The Copia element was detected, and was transcriptionally active, in all species investigated. Structural and selection analysis revealed Zaprionus elements to be closely related to the most ancient subfamily of the melanogaster subgroup, and they seem to be evolving mainly under relaxed purifying selection. Taken together, these results allowed us to classify the Zaprionus sequences as a new subfamily—ZapCopia, a member of the Copia retrotransposon family of the melanogaster subgroup. These findings indicate that the Copia retrotransposon is an ancient component of the genomes of the Zaprionus species and broaden our understanding of the diversity of retrotransposons in the Zaprionus genus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida LM, Carareto CM (2006) Sequence heterogeneity and phylogenetic relationships between the copia retrotransposon in Drosophila species of the repleta and melanogaster groups. Genet Sel Evol 38(5):535–550
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27(2):573–580
Bergsten J (2005) A review of long-branch attraction. Cladistics 21(2):163–193
Biémont C, Cizeron G (1999) Distribution of transposable elements in Drosophila species. Genetica 105(1):43–62
Bowen NJ, McDonald JF (2001) Drosophila euchromatic LTR retrotransposons are much younger than the host species in which they reside. Genome Res 11(9):1527–1540
Brunet F, Godin F, Bazin C, Capy P (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of Mos1-like transposable elements in the Drosophilidae. J Mol Evol 49(6):760–768
Cavarec L, Heidmann T (1993) The Drosophila copia retrotransposon contains binding sites for transcriptional regulation by homeoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res 21(22):5041–5049
Chassagnard M-T, Kraaijeveld AR (1991) The occurrence of Zaprionus sensu stricto in the Palearctic region (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Ann Soc Entomol Fr 27(4):495–496
Cizeron G, Lemeunier F, Loevenbruck C, Brehm A, Biémont C (1998) Distribution of the retrotransposable element 412 in Drosophila species. Mol Biol Evol 15(12):1589–1599
Costa AP, Scortecci KC, Hashimoto RY, Araujo PG, Grandbastien MA, Van Sluys MA (1999) Retrolycl-1, a member of the Tntl retrotransposon super-family in the Lycopersicon peruvianum genome. Genetica 107(1–3):65–72
Da Lage JL, Kergoat GJ, Maczkowiak F, Silvain JF, Cariou ML, Lachaise D (2007) A phylogeny of Drosophilidae using the amyrel gene: questioning the Drosophila melanogaster species group boundaries. J Zoolog Syst Evol Res 45(1):47–63
De Salle R (1992) The origin and possible time of divergence of the Hawaiian Drosophilidae: evidence from DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 9(5):905–916
De Setta N, Carareto CMA (2007) Screening for transposable elements in South America invasive species Zaprionus indianus and Drosophila malerkotliana. Drosoph Inf Serv 90(1):96–99
De Setta N, Van Sluys MA, Capy P, Carareto CM (2009) Multiple invasions of Gypsy and Micropia retroelements in genus Zaprionus and melanogaster subgroup of the genus Drosophila. BMC Evol Biol 9:279
Deprá M, Panzera Y, Ludwig A, Valente VL, Loreto EL (2010) Hosimary: a new hAT transposon group involved in horizontal transfer. Mol Genet Genomics 283(5):451–459
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791
Grabe N (2002) AliBaba2: context specific identification of transcription factor binding sites. In Silico Biol 2(1):S1–S15
Gradstein F, Ogg J, Smith A (2006) A geological time scale 2004. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Graur D, Li W-H (2000) Fundamentals of molecular evolution. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Grimaldi DA (1990) A phylogenetic, revised classification of genera in the Drosophilidae (Diptera). Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 197:123–128
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52(5):696–704
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol 22(2):160–174
Heredia F, Loreto ELS, Valente VL (2004) Complex evolution of gypsy in drosophilid species. Mol Biol Evol 21(10):1831–1842
Jordan IK, McDonald JF (1998a) Evolution of the copia retrotransposon in the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. Mol Biol Evol 15(9):1160–1171
Jordan IK, McDonald JF (1998b) Interelement selection in the regulatory region of the copia retrotransposon. J Mol Evol 47(6):670–676
Jordan IK, Matyunina LV, McDonald JF (1999) Evidence for the recent horizontal transfer of long terminal repeat retrotransposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(22):12621–12625
Jowett T (1986) Preparation of nucleic acids. In: Roberts DB (ed) Drosophila: a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 275–277
Klimczak LJ, Schindler U, Cashmore AR (1992) DNA binding activity of the Arabidopsis G-box binding factor GBF1 is stimulated by phosphorylation by casein kinase II from broccoli. Plant Cell 4(1):87–98
Kwiatowski J, Ayala FJ (1999) Phylogeny of Drosophila and related genera: conflict between molecular and anatomical analyses. Mol Phylogenet Evol 13(2):319–328
Kwiatowski J, Skarecky D, Bailey K, Ayala FJ (1994) Phylogeny of Drosophila and related genera inferred from the nucleotide sequence of the Cu, Zn Sod gene. J Mol Evol 38(5):443–454
Lachaise D, Silvain JF (2004) How two Afrotropical endemics made two cosmopolitan human commensals: the Drosophila melanogaster-D. simulans palaeogeographic riddle. Genetica 120(1–3):17–39
Ludwig A, Valente VL, Loreto EL (2008) Multiple invasions of Errantivirus in the genus Drosophila. Insect Mol Biol 17(2):112–113
Maruyama K, Hartl DL (1991) Evidence for interspecific transfer of the transposable element mariner between Drosophila and Zaprionus. J Mol Evol 33(6):514–524
Matyunina LV, Jordan IK, McDonald JF (1996) Naturally occurring variation in copia expression is due to both element (cis) and host (trans) regulatory variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(14):7097–7102
McDonald JF, Matyunina LV, Wilson S, Jordan IK, Bowen NJ, Miller WJ (1997) LTR retrotransposons and the evolution of eukaryotic enhancers. Genetica 100(1–3):3–13
Montchamp-Moreau C, Ronsseray M, Jacques M, Lehmann M, Anxolabéhère D (1993) Distribution and conservation of sequences homologous to the 1731 retrotransposon in Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 10(4):791–803
Mota NR, Ludwig A, da Silva Valente VL, Loreto EL (2009) Harrow: new Drosophila hAT transposons involved in horizontal transfer. Insect Mol Biol 19(2):217–228
Mount SM, Rubin GM (1985) Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol 5(7):1630–1638
Okada T, Carson HL (1983) The genera Phorticella DUDA and Zaprionus COQUILLETT (Diptera, Drosophilidae) of the Oriental region and New Guinea. Jpn J Entomol 51(4):539–553
Pélandakis M, Solignac M (1993) Molecular phylogeny of Drosophila based on ribosomal RNA sequences. J Mol Evol 37(5):525–543
Remsen J, DeSalle R (1998) Character congruence of multiple data partitions and the origin of the Hawaiian Drosophilidae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9(2):225–235
Robe LJ, Valente VL, Budnik M, Loreto EL (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the subgenus Drosophila (Diptera, Drosophilidae) with an emphasis on neotropical species and groups: a nuclear versus mitochondrial gene approach. Mol Phylogenet Evol 36(3):623–640
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19(18):2496–2497
Russo CA, Takezaki N, Nei M (1995) Molecular phylogeny and divergence times of drosophilid species. Mol Biol Evol 12(3):391–404
Sánchez-Gracia A, Maside X, Charlesworth B (2005) High rate of horizontal transfer of transposable elements in Drosophila. Trends Genet 21(4):200–203
Swofford D (1997) PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, Version 4.0b10. Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC
Tabata T, Nakayama T, Mikami K, Iwabuchi M (1991) HBP-1a and HBP-1b: leucine zipper-type transcription factors of wheat. EMBO J 10(6):1459–1467
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004a) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(30):11030–11035
Tamura K, Subramanian S, Kumar S (2004b) Temporal patterns of fruit fly (Drosophila) evolution revealed by mutation clocks. Mol Biol Evol 21(1):36–44
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599
Tatarenkov A, Kwiatowski J, Skarecky D, Barrio E, Ayala FJ (1999) On the evolution of Dopa decarboxylase (Ddc) and Drosophila systematics. J Mol Evol 48(4):445–462
Thomas RH, Hunt JA (1993) Phylogenetic relationships in Drosophila: a conflict between molecular and morphological data. Mol Biol Evol 10(2):362–374
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Throckmorton LH (1975) The phylogeny, ecology and geography of Drosophila. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics. Plenum, New York, pp 421–469
Vidal NM, Ludwig A, Loreto EL (2009) Evolution of Tom, 297, 17.6 and rover retrotransposons in Drosophilidae species. Mol Genet Genomics 282(4):351–362
Vilela CR (1999) Is Zaprionus indianus Gupta 1970 (Diptera, Drosophilidae) currently colonizing the Neotropical region? Drosoph Inf Serv 82(1):37–39
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, Paux E, SanMiguel P, Schulman AH (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8(12):973–982
Wilson S, Matyunina LV, McDonald JF (1998) An enhancer region within the copia untranslated leader contains binding sites for Drosophila regulatory proteins. Gene 209(1–2):239–246
Xiang C, Miao Z, Lam E (1997) DNA-binding properties, genomic organization and expression pattern of TGA6, a new member of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 34(3):403–415
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1586–1591
Yassin AE, Abou-Youssef (2004) A new front for a global invasive drosophilid: the colonization of the Northern-Western desert of Egypt by Zaprionus indianus Gupta, 1970. Drosoph Inf Serv 87(1):67–68
Yassin A, Araripe LO, Capy P, Da Lage JL, Klaczko LB, Maisonhaute C, Ogereau D, David JR (2008a) Grafting the molecular phylogenetic tree with morphological branches to reconstruct the evolutionary history of the genus Zaprionus (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 47(3):903–915
Yassin A, Capy P, Madi-Ravazzi L, Ogereau D, David JR (2008b) DNA barcode discovers two cryptic species and two geographical radiations in the invasive drosophilid Zaprionus indianus. Mol Ecol Notes 8(3):491–501
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the CAPES-COFECUB International Cooperation Program (to NS, CMAC, and PC), FAPESP (MAVS-04/02851-9), CNPq (CMAC and MAVS). NS was the recipient of a CNPq fellowship. We thank J. David and A. Yassin for providing the Zaprionus strains, F. Lemeunier for technical help, and C Metcalfe for correcting the English text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
239_2011_9435_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple alignment between Copia 5’ LTR–ULR sequences illustrating the regulatory signal conservation between the Zaprionus Copia sequences and the melanogaster variants (Full-length and Double-gap). a: heat shock element; b: TATA box; c: imperfect repeat; d: transcription start; e: downstream element; f: poly-A signal; g: PBS; h: engrailed binding site; i: DmC/EBP biding site; j-i: dyad symmetric (core SV40 enhancer); k: G-box binding factor-1 (GBF-1); l: B-box binding factor-2 (BBF-2). (TIFF 28891 kb)
239_2011_9435_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationships of the Copia RT region using the first and second codon position (ML method, HKY85 distance). The elimination of the third codon positions minimizes the long-branch attraction effect in the Group D. Bootstrap analysis was computed with 1,000 replications and sequences of repleta species group were used as outgroup. (TIFF 5172 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Setta, N., Van Sluys, MA., Capy, P. et al. Copia Retrotransposon in the Zaprionus Genus: Another Case of Transposable Element Sharing with the Drosophila melanogaster Subgroup. J Mol Evol 72, 326–338 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-011-9435-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-011-9435-6