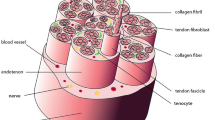
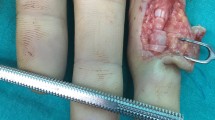
Abstract
Creation of adhesions in digital flexor tendons after repairing remains a major problem in hand surgery. The adhesions are part of the healing process and produce almost inevitably functional disability following the biological response after tendon injury. To achieve better gliding function of the digital tendons by reducing peritendinous adhesions without adversely affecting the healing process itself, several options, both surgical and pharmacological have been explored. Attempts at reducing postoperative adhesion formation have included early postoperative rehabilitation, low-friction surgical repair techniques, pharmacological antiadhesive reagents, and the use of physical barriers to adhesion formation.
Level of Evidence: Not ratable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duci SB, Ahmeti HR (2016) Partially divided flexor tendon injuries: should they repaired or not? J Surg 02(03):89–90
Khanna A, Gougoulias N, Maffulli N (2009) Modalities in prevention of flexor tendon adhesion in the hand: what have we achieved so far? Acta Orthop Belg 75(4):433–444
Amadio PC (2005) Friction of the gliding surface. Implications for tendon surgery and rehabilitation. J Hand Ther 18(2):112–119
Gelberman RH, Manske PR (1985) Factors influencing flexor tendon adhesions. Hand Clin 1(1):35–42
Wong JK, Lui YH, Kapacee Z, Kadler KE, Ferguson MW, McGrouther DA (2009) The cellular biology of flexor tendon adhesion formation: an old problem in a new paradigm. Am J Pathol 175(5):1938–1951
Caulfield RH, Maleki-Tabrizi A, Patel H, Coldham F, Mee S, Nanchahal J (2008) Comparison of zones 1 to 4 flexor tendon repairs using absorbable and unabsorbable four-strand core sutures. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 33(4):412–417
Duci SB, Arifi HM, Ahmeti HR, Manxhuka-Kerliu S, Mekaj AY, Shahini L, Kurshumliu F (2017) Histological evaluation of the effects of 5-fluorouracil on partially divided flexor tendon injuries in rabbits. Eur J Plast Surg 40(1):1–10
Khana A, Friel M, Gougoulias N, Longo UG, Maffulli N (2009) Prevention of adhesions in surgery of the flexor tendons of the hand: what is the evidence? Br Med Bull 90:85–109
Barrie KA, Tomak SL, Cholewick J et al (2001) Effect of suture locking and suture caliber on fatigue strength of flexor tendon repairs. J Hand Surg 26A:340–346
Sanders DW, Milne AD, Dobravec A et al (1997) Cyclic testing of flexor tendon repairs: an in vitro biomechanical study. J Hand Surg 22A:1004–1010
Lee H (1990) Double loop locking suture: a technique of tendon repair for early active mobilization. Part I: evolution of technique and experimental study. J Hand Surg 15A:945–953
Lim BH, Tsai TM (1996) The six-strand technique for flexor tendon repair. Atlas Hand Clin 1:65–76
Dovan TT, Ditsios KT, Boyer MI (2003) Eight-strand core suture technique for repair of intrasynovial flexor tendon lacerations. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 7(2):70–74
Savage R (1985) In vitro studies of a new method of flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg 10B:135–141
Viinikainen A, Goransson H, Huovinen K, Keijomaki M, Rokkanen P (2004) A comparative analysis of the biomechanical behavior of five flexor tendon core sutures. J Hand Surg 29B:536–543
Shaieb MD, Singer DI (1997) Tensile strengths of various suture techniques. J Hand Surg 22B:764–767
Bainbridge LC, Robertson C, Gillies D, Elliot D (1994) A comparison of post-operative mobilization of flexor tendon repairs with “ passive flexion active extension” and “controlled active motion” techniques. J Hand Surg 19B:517–521
Tang JB, Shi D, Gu YQ, Chen JC, Zhau B (1994) Double and multiple looped suture tendon repair. J Hand Surg 19B:699–703
Kusano N, Yoshizu T, Maki Y (1999) Experimental study of two new flexor tendon suture techniques for postoperative early active flexion exercises. J Hand Surg 24B:152–156
Winters SC, Gelberman RH, Woo SL, Chan SS, Grewal R, Seiler JG 3rd (1998) The effects of multiple-strand suture methods on the strength and excursion of repaired intrasynovial flexor tendons: a biomechanical study in dogs. J Hand Surg 23:97–104
Zhao C, Amadio PC, Momose T, Couvreur P, Zobitz ME, An KN (2001) The effect of suture technique on adhesion formation after flexor tendon repair for partial lacerations in a canine model. J Trauma 51(5):917–921
Strick MJ, Filan SL, Hile M, McKenzie C, Walsh WR, Tonkin MA (2004) Adhesion formation after flexor tendon repair: a histologic and biomechanical comparison of 2- and 4-strand repairs in a chicken model. J Hand Surg Am. 29(1):15–21
Strauch B, de Moura W, Ferder M, Hall C, Sagi A, Greenstein B (1985) The fate of tendon healing after restoration of the integrity of the tendon sheath with autogenous vein grafts. J Hand Surg [Am] 10A:790–795
Peterson WW, Manske PR, Kain CC, Lesker PA (1986) Effect of flexor sheath integrity on tendon gliding: a biomechanical and histologic study. J Orthop Res 4:458–465
Saldana MJ, Ho PK, Lichtman DM, Chow JA, Dovelle S, Thomes LJ Flexor tendon repair and rehabilitation in zone II: open sheath technique versus closed sheath technique. J Hand Surg Am 12A:1110–1114
Gelberman RH, Woo SL-Y, Amiel D, Horibe S, Lee D (1990) Influences of flexor sheath continuity and early motion on tendon healing in dogs. J Hand Surg Am 15A:69–77
Peterson WW, Manske PR, Dunlap J, Horwitz DS, Kahn B (1990) Effect of various methods of restoring flexor sheath integrity on the formation of adhesions after tendon surgery. J Hand Surg Am 15A:48–56
Tang JB, Ishii S, Usui M, Yamamura T. Flexor sheath closure during delayed primary tendon repair. J Hand Surg Am 19A:636–640.
Boyer MI, Strickland JW, Engles DR, Sachar K, Leversedge FJ (2002) Flexor tendon repair and rehabilitation, state of the art in 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84(9):1684–1706
Duci SB, Arifi HM, Ahmeti HR, Manxhuka-Kerliu S, Neziri B, Mekaj AY, Lajqi S, Shahini L (2015) Biomechanical and macroscopic evaluations of the effects of 5-fluorouracil on partially divided flexor tendon injuries in rabbits. Chin Med J 128:1655–1661
Ferguson MW, O’Kane S (2004) Scar-free healing: from embryonic mechanisms to adult therapeutic intervention. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 359:839–850
Ruan H, Liu S, Li F, Li X, Fan C (2013) Prevention of tendon adhesions by ERK2 small interfering RNAs. Int J MolSci 14(2):4361–4371
Özgenel GY (2004) The effects of a combination of hyaluronic and amniotic membrane on the formation of peritendinous adhesions after flexor tendon surgery in chickens. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(2):301–307
Menderes A, Mola F, Tayfur V, Vayvada H, Barutçu A (2004) Prevention of peritendinous adhesions following flexor tendon injury with seprafilm. Ann Plast Surg 53(6):560–564
Demirkan F, Colakoglu N, Herek O, Erkula G (2002) The use of amniotic membrane in flexor tendon repair: an experimental model. Acta Orthop Trauma Surg 122(7):396–399
Yilmaz E, Avci M, Bulut M, Kelestimur H, Karakurt L, Ozercan I (2010) The effect of seprafilm on adhesion formation and tendon healing after flexor tendon repair in chicken. Orthopedics 33(3):164–170
Diamond MP, Burns EL, Accomando B, Mian S, Holmdahl L (2012) Seprafilm adhesion barrier (1) a review of preclinical, animal, and human investigational studies. Gynecol Surg 9(3):237–245
Hanff G, Hagberg L (1998) Prevention of restrictive adhesions with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene diffusible membrane following flexor tendon repair, an experimental study in rabbits. J Hand Surg Am 23:658–664
Necas J, Bartosikova L, Brauner P, Kolar J (2008) Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): a review. Vet Med 52:397–411
Mracek A, Varhanikova J, Lehocky M, Grundelova L, Pokopcova A, Velebny V (2008) The influence of Hofmeister series jone on hyaluronan swelling and viscosity. Molecules 13:1025–1034
Mekaj AY, Morina AA, Bytyqi CI, Mekaj YH, Duci SB (2014) Application of topical pharmacological agents at the site of peripheral nerve injury and methods used for evaluating the success of the regenerative process. J Orthop Surg Res 9:94
Arifi HM, Ahmeti HR, Mekaj AY, Duci SB (2015) Effects of topical application of pharmacological agents after flexor tendon injury and methods used for evaluation of tendon healing process. SM J Orthop. 1(4):1016
Duci SB (2015) Justification of the topical use of pharmacological agents on reduce of tendon adhesion after surgical repair. SM J Orthop 1:1006
Amiel D, Ishizue K, Billings E Jr, Wiig M, Vande BJ (1989) Hyaluronan in flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg Am. 14:837–843
Tuncay I, Ozbek H, Atik B, Ozen S, Akpinar F (2002) Effects of hyaluronic acid on postoperative adhesion of tendo calcaneus surgery: an experimental study in rats. J Foot Ankle Surg 41:104–108
Ozgenel GY, Etoz A (2012) Effects of repetitive injections of hyaluronic acid on peritendinous adhesions after flexor tendon repair, a preliminary randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 18:11–17
Su JL, Schumacher BL, Lindley KM, Soloveychik V, Burkhart W (2001) Detection of superficial zone protein in human and animal body fluids by cross-species monoclonal antibodies specific to superficial zone protein. Hybridoma 20:149–157
Rees SG, Davies JR, Tudor D, Flannery CR, Hughes CE (2002) Immunolocalisation and expression of proteoglycan 4 (cartilage superficial zone proteoglycan) in tendon. Matrix Biol 21:593–602
Zhao C, Sun YL, Kirk RL, Thoreson AR, Jay GD (2010) Effects of a lubricin-containing compound on the results of flexor tendon repair in a canine model in vivo. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:1453–1461
Chang J, Thunder R, Most D, Longaker MT, Lineaweaver WC (2000) Studies in flexor tendon wound healing: neutralizing antibody to TGF-ß1 increase postoperative range of motion. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:148–155
Occleston NL, Daniels JT, Tarnuzzer RW, Sethi KK, Alexander RA, Bhattacharya SS, Schultz GS, Khaw PT (1997) Single exposures to antiproliferatives. Long-term effects on ocular fibroblasts wound-healing behaviour. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38(10):1998–2007
Silfverskiöld KL, May EJ, Törnvall AH (1993) Tendon excursions after flexor tendon repair in zone. II: results with a new controlled-motion program. J Hand Surg Am. 18(3):403–410
Zhao C, Amadio PC, Momose T, Couvreur P, Zobitz ME, An KN (2002) Effect of synergistic wrist motion on adhesion formation after repair of partial flexor digitorum profundus tendon lacerations in a canine model in vivo. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A(1):78–84
Klein L (2003) Early active motion flexor tendon protocol using one splint. J Hand Ther 16(3):199–206
Frykman E, Jacobsson S, Widenfalk B (1993) Fibrin sealant in prevention of flexor tendon adhesions: an experimental study in the rabbit. J Hand Surg Am. 18(1):68–75
Burns JW, Skinner K, Colt MJ, Burgess L, Rose R, Diamond MP (1996) A hyaluronate based gel for the prevention of postsurgical adhesions: evaluation in two animal species. Fertil Steril 66(5):814–821
Shih HN, Fang JF, Chen JH, Yang CL, Chen YH, Sung TH, Shih LY (2004) Reduction in experimental peridural adhesion with the use of a crosslinked hyaluronate/collagen membrane. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 71(2):421–428
Hagberg L (1992) Exogenous hyaluronate as an adjunct in the prevention of adhesions after flexor tendon surgery: a controlled clinical trial. J Hand Surg Am. 17(1):132–136
Hills BA (2000) Boundary lubrication in vivo. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 214(1):83–94
Zhao C, Sun YL, Amadio PC, Tanaka T, Ettema AM, An KN (2006) Surface treatment of flexor tendon autograft with carbodiimide-derivatized hyaluronic acid. An in vivo canine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(10):2181–2191
Akali A, Khan U, Khaw PT, McGrouther AD (1999) Decrease in adhesion formation by a single application of 5-fluorouracil after flexor tendon injury. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(1):151–158
Moran SL, Ryan CK, Orlando GS, Pratt CE, Michalko KB (2000) Effects of 5-fluorouracil on flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg Am 25(2):242–251
Karaaltin MV, Ozalp B, Dadaci M, Kayicioglu A, Kecik A, Oner F (2013) The effects of 5-fluorouracil on flexor tendon healing by using a biodegradable gelatin, slow releasing system: experimental study in a hen model. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 38(6):651–657
Greenfield DS, Liebmann JM, Jee J et al (1998) Late-onset bleb leaks after glaucoma filtering surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 116:443–447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
For this kind of article formal consent from a local ethics committee is not required.
Conflict of interest
Shkelzen Duci declares that he have no conflict of interest
Funding
This study was not funded by a grant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duci, S.B. Modalities for prevention of adhesion formation after tendon surgery: a review of the literature. Eur J Plast Surg 40, 393–400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-017-1307-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-017-1307-x