Abstract
Introduction
Pilomyxoid astrocytoma (PMA) is a relatively new tumor entity which has been added to the 2007 WHO Classification of tumors of the central nervous system. The goal of this study is to utilize arterial spin labeling (ASL) perfusion imaging to differentiate PMA from pilocytic astrocytoma (PA).
Methods
Pulsed ASL and conventional MRI sequences of patients with PMA and PA in the past 5 years were retrospectively evaluated. Patients with history of radiation or treatment with anti-angiogenic drugs were excluded.
Results
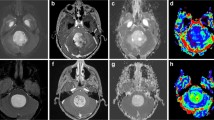
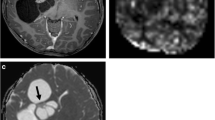
A total of 24 patients (9 PMA, 15 PA) were included. There were statistically significant differences between PMA and PA in mean tumor/gray matter (GM) cerebral blood flow (CBF) ratios (1.3 vs 0.4, p < 0.001) and maximum tumor/GM CBF ratio (2.3 vs 1, p < 0.001). Area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for differentiation of PMA from PA was 0.91 using mean tumor CBF, 0.95 using mean tumor/GM CBF ratios, and 0.89 using maximum tumor/GM CBF. Using a threshold value of 0.91, the mean tumor/GM CBF ratio was able to diagnose PMA with 77 % sensitivity, 100 % specificity, and a threshold value of 0.7, provided 88 % sensitivity and 86 % specificity. There was no statistically significant difference between the two tumors in enhancement pattern (p = 0.33), internal architecture (p = 0.15), or apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values (p = 0.07).
Conclusion
ASL imaging has high accuracy in differentiating PMA from PA. The result of this study may have important applications in prognostication and treatment planning especially in patients with less accessible tumors such as hypothalamic-chiasmatic gliomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tihan T, Fisher PG, Kepner JL et al (1999) Pediatric astrocytomas with monomorphous pilomyxoid features and a less favorable outcome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58(10):1061Y1068
Brat DJ, Scheithauer BW, Fuller GN, Tihan T (2007) Newly codified glial neoplasms of the 2007 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System: angiocentric glioma, pilomyxoid astrocytoma and pituicytoma. Brain Pathol 17(3):319–324
Lee IH, Kim JH, Suh YL et al (2011) Imaging characteristics of pilomyxoid astrocytomas in comparison with pilocytic astrocytomas. Eur J Radiol 79(2):311–316
Osborn AG, Salzman KL, Thurnher MM et al (2012) The new World Health Organization Classification of Central Nervous System Tumors: what can the neuroradiologist really say? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(5):795–802
Komotar RJ, Burger PC, Carson BS et al (2004) Pilocytic and pilomyxoid hypothalamic/chiasmatic astrocytomas. Neurosurgery 54(1):72–79
Cirak B, Horska A, Barker PB et al (2005) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in pediatric pilomyxoid astrocytoma. Childs Nerv Syst 21(5):404–409
Hamada H, Kurimoto M, Hayashi N et al (2008) Pilomyxoid astrocytoma in a patient presenting with fatal hemorrhage. Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1(3):244–246
Komotar RJ, Zacharia BE, Sughrue ME et al (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of pilomyxoid astrocytoma. Neurol Res 30(9):945–951
Linscott LL, Osborn AG, Blaser S et al (2008) Pilomyxoid astrocytoma: expanding the imaging spectrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(10):1861–1866
Komotar RJ, Zacharia BE, Sughrue ME et al (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of pilomyxoid astrocytoma. Neurol Res 30(9):945–951
Morales H, Kwock L, Castillo M (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of pilomyxoid astrocytomas: case reports and comparison with pilocytic astrocytomas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31(5):682–687
Arslanoglu A, Cirak B, Horska A et al (2003) MR imaging characteristics of pilomyxoidastrocytomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1906–1908
Leon SP, Folkerth RD, Black PM (1996) Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 77:362–372
Folkerth RD (2000) Descriptive analysis and quantification of angiogenesis in human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 50(1–2):165–172
Warmuth C, Gunther M, Zimmer C (2003) Quantification of blood flow in brain tumors: comparison of arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 228:523–532
Wolf RL, Wang J, Wang S et al (2005) Grading of CNS neoplasms using continuous arterial spin labeled perfusion MR imaging at 3 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 22(4):475–482
Noguchi T, Yshiura T, Hiwatashi A (2008) Perfusion imaging of brain tumors using arterial spin labeling: correlation with histopathologic vascular density. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:688–693
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (eds) (2007) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 4th edn. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France
Johnson MW, Eberhart CG, Perry A et al (2010) Spectrum of pilomyxoid astrocytomas: intermediate pilomyxoid tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 34:1783–1791
Yeom KW, Mitchell LA, Lober RM et al (2014) Arterial spin-labeled perfusion of pediatric brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(2):395–401
Grand SD, Kremer S, Tropres IM et al (2007) Perfusion-sensitive MRI of pilocytic astrocytomas: initial results. Neuroradiology 49(7):545–550
Bing F, Kremer S, Lamalle L et al (2009) Value of perfusion MRI in the study of pilocytic astrocytoma and hemangioblastoma: preliminary findings. J Neuroradiol 36(2):82–87
Luh WM, Wong EC, Bandettini PA et al (1999) QUIPSS II with thin-slice TI1 periodic saturation: a method for improving accuracy of quantitative perfusion imaging using pulsed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 41:1246–1254
Noguchi T, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2007) Quantitative perfusion imaging with pulsed arterial spin labeling: a phantom study. Magn Reson Med Sci 6:91–97
Parkes LM, Rashid W, Chard DT et al (2004) Normal cerebral perfusion measurements using arterial spin labeling: reproducibility, stability, and age and gender effects. Magn Reson Med 51:736–743
Donahue MJ, Lu H, Jones CK et al (2006) An account of the discrepancy between MRI and PET cerebral blood flow measures: a high-field MRI investigation. NMR Biomed 19:1043–1054
Ye FQ, Berman KF, Ellmore T et al (2000) H215O PET validation of steady-state arterial spin tagging cerebral blood flow measurements in humans. Magn Reson Med 44:450–456
Burger PC, Scheithauer BW, Paulus W et al (2000) Pilocytic astrocytoma. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee W (eds) World Health Organization Classificationof Tumours: pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France, pp 45–51
Birlik B, Canda S, Ozer E (2006) Tumour vascularity is of prognostic significance in adult, but not paediatric astrocytomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:532–538
Sie M, de Bont ES, Scherpen FJ et al (2010) Tumour vasculature and angiogenic profile of paediatric pilocytic astrocytoma; is it much different from glioblastoma? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:636–647
Binning MJ, Liu JK, Kestle JR et al (2007) Optic pathway gliomas: a review. Neurosurg Focus 23(5):E2
Komotar RJ, Mocco J, Jones JE et al (2005) Pilomyxoid astrocytoma: diagnosis, prognosis, and management. Neurosurg Focus 18(6A):E7
Yeom KW, Lober RM, Alexander A et al (2014) Hydrocephalus decreases arterial spin-labeled cerebral perfusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(7):1433–1439
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the IRB Committee of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Due to the retrospective nature of study, informed consent was waived.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabavizadeh, S.A., Assadsangabi, R., Hajmomenian, M. et al. High accuracy of arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging in differentiation of pilomyxoid from pilocytic astrocytoma. Neuroradiology 57, 527–533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1497-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1497-5