Abstract
Introduction
Our study aimed to elucidate the diagnostic performance of dual-energy CT (DECT) in the detection of contrast enhancement in intracranial haematomas (ICrH) with early phase dual-energy computed tomography angiography (CTA) and compare the results with those obtained by delayed CT enhancement.
Methods
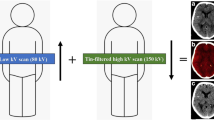
Thirty-six patients with ICrH were retrospectively included in this study. All patients had undergone single-energy non-contrast CT and contrast-enhanced dual-source DECT. DECT images were post-processed with commercial software, followed by obtaining iodine images and virtual non-contrast images and generating combined images that created the impression of 120-kVp images. Two neuroradiologists, blinded to the patients’ data, reviewed two reading sessions: session A (non-contrast CT and combined CT) and session B (non-contrast CT, combined CT, and iodine images) for detection of contrast enhancement in the haematomas.
Results
Contrast leakage or enhancement was detected in 23 (57.5 %) out of 40 haemorrhagic lesions in 36 patients on delayed CT. Three enhanced lesions were depicted only in the DECT iodine images. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of session A were 82.6, 94.1, 95.0, and 80.0 %, respectively, and those of session B were 95.7, 94.1, 95.7, and 94.1 %, respectively.
Conclusion
DECT emphasised the iodine enhancement and facilitated the detection of contrast enhancement or leakage.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICrH:
-
Intracranial haematoma
- ICeH:
-
Intracerebral haematoma
- DECT:
-
Dual-energy CT
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- HU:
-
Hounsfield units
References
Thompson AL, Kosior JC, Gladstone DJ et al (2009) Defining the CT angiography 'spot sign' in primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Can J Neurol Sci 36:456–461
Ederies A, Demchuk A, Chia T et al (2009) Postcontrast CT extravasation is associated with hematoma expansion in CTA spot negative patients. Stroke 40:1672–1676
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M et al (2007) Material differentiation by dual energy CT: initial experience. Eur Radiol 17:1510–1517
Kim SJ, Lim HK, Lee HY et al (2012) Dual-energy CT in the evaluation of intracerebral hemorrhage of unknown origin: differentiation between tumor bleeding and pure hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:865–872
Phan CM, Yoo AJ, Hirsch JA, Nogueira RG, Gupta R (2012) Differentiation of hemorrhage from iodinated contrast in different intracranial compartments using dual-energy head CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1088–1094
New PF, Aronow S (1976) Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography. Radiology 121:635–640
Flors L, Leiva-Salinas C, Norton PT, Patrie JT, Hagspiel KD (2013) Endoleak detection after endovascular repair of thoracic aortic aneurysm using dual-source dual-energy CT: suitable scanning protocols and potential radiation dose reduction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200:451–460
Gupta R, Phan CM, Leidecker C et al (2010) Evaluation of dual-energy CT for differentiating intracerebral hemorrhage from iodinated contrast material staining. Radiology 257:205–211
Huynh TJ, Demchuk AM, Dowlatshahi D et al (2013) Spot sign number is the most important spot sign characteristic for predicting hematoma expansion using first-pass computed tomography angiography: analysis from the PREDICT study. Stroke 44:972–977
Demchuk AM, Dowlatshahi D, Rodriguez-Luna D et al (2012) Prediction of haematoma growth and outcome in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage using the CT-angiography spot sign (PREDICT): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol 11:307–314
Park SY, Kong MH, Kim JH, Kang DS, Song KY, Huh SK (2010) Role of 'spot sign' on CT angiography to predict hematoma expansion in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 48:399–405
Dalfino JC, Boulos AS (2010) Visualization of an actively bleeding cortical vessel into the subdural space by CT angiography. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112:737–739
Romero JM, Kelly HR, Delgado Almandoz JE et al (2013) Contrast extravasation on CT Angiography predicts hematoma expansion and mortality in acute traumatic subdural hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:1528–1534
Letourneau-Guillon L, Huynh T, Jakobovic R, Milwid R, Symons SP, Aviv RI (2013) Traumatic intracranial hematomas: prognostic value of contrast extravasation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:773–779
Hallevi H, Abraham AT, Barreto AD, Grotta JC, Savitz SI (2010) The spot sign in intracerebral hemorrhage: the importance of looking for contrast extravasation. Cerebrovasc Dis 29:217–220
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, Y., Tsukabe, A., Kunitomi, Y. et al. Dual-energy CT for detection of contrast enhancement or leakage within high-density haematomas in patients with intracranial haemorrhage. Neuroradiology 56, 291–295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1333-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1333-3