Abstract
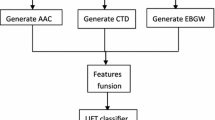
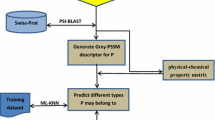
Membrane proteins were found to be involved in various cellular processes performing various important functions, which are mainly associated to their type. Given a membrane protein sequence, how can we identify its type(s)? Particularly, how can we deal with the multi-type problem since one membrane protein may simultaneously belong to two or more different types? To address these problems, which are obviously very important to both basic research and drug development, a new multi-label classifier was developed based on pseudo amino acid composition with multi-label k-nearest neighbor algorithm. The success rate achieved by the new predictor on the benchmark dataset by jackknife test is 73.94 %, indicating that the method is promising and the predictor may become a very useful high-throughput tool, or at least play a complementary role to the existing predictors in identifying functional types of membrane proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutet E, Lieberherr D, Tognolli M, Schneider M, Bairoch A (2007) Uniprotkb/swiss-prot. Springer, Plant Bioinformatics, pp 89–112
Chen Y-L, Li Q-Z (2007) Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins. J Theor Biol 245:775–783
Chou KC (1995) A novel approach to predicting protein structural classes in a (20-1)-D amino acid composition space. Proteins 21:319–344
Chou KC (2001) Prediction of protein cellular attributes using pseudo-amino acid composition. Proteins 43:246–255
Chou K-C (2011) Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 273:236–247
Chou KC, Elrod DW (1999) Prediction of membrane protein types and subcellular locations. Proteins 34:137–153
Chou K-C, Elrod DW (2003) Prediction of enzyme family classes. J Proteome Res 2:183–190
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2007) MemType-2L: a web server for predicting membrane proteins and their types by incorporating evolution information through Pse-PSSM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:339–345
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2009) Review: recent advances in developing web-servers for predicting protein attributes. Nat Sci 1:63
Chou C-H, Shen H-B (2010) Cell-PLoc 2.0: an improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Eng, 2
Chou K-C, Wu Z-C, Xiao X (2011) iLoc-Euk: a multi-label classifier for predicting the subcellular localization of singleplex and multiplex eukaryotic proteins. PLoS One 6:e18258
Chou K-C, Wu Z-C, Xiao X (2012) iLoc-Hum: using the accumulation-label scale to predict subcellular locations of human proteins with both single and multiple sites. Mol BioSyst 8:629–641
Ding C, Yuan L-F, Guo S-H, Lin H, Chen W (2012) Identification of mycobacterial membrane proteins and their types using over-represented tripeptide compositions. J Proteomics 77:321–328
Glory E, Murphy RF (2007) Automated subcellular location determination and high-throughput microscopy. Dev Cell 12:7–16
Huang C, Yuan J-Q (2013a) A multilabel model based on Chou’s pseudo-amino acid composition for identifying membrane proteins with both single and multiple functional types. J Membr Biol 246:327–334
Huang C, Yuan J-Q (2013b) Predicting protein subchloroplast locations with both single and multiple sites via three different modes of Chou’s pseudo amino acid compositions. J Theor Biol 335:205–212
Jian X, Wei R, Zhan T, Gu Q (2008) Using the concept of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition to predict apoptosis proteins subcellular location: an approach by approximate entropy. Protein Pept Lett 15:392–396
Khosravian M, Kazemi Faramarzi F, Mohammad Beigi M, Behbahani M, Mohabatkar H (2013) Predicting antibacterial peptides by the concept of Chou’s pseudo-amino acid composition and machine learning methods. Protein Pept Lett 20:180–186
Li F-M, Li Q-Z (2008) Predicting protein subcellular location using Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition and improved hybrid approach. Protein Pept Lett 15:612–616
Lin H, Wang H, Ding H, Chen Y-L, Li Q-Z (2009) Prediction of subcellular localization of apoptosis protein using Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition. Acta Biotheor 57:321–330
Lin W-Z, Fang J-A, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2013) iLoc-Animal: a multi-label learning classifier for predicting subcellular localization of animal proteins. Mol BioSyst 9:634–644
Nakashima H, Nishikawa K, Tatsuo O (1986) The folding type of a protein is relevant to the amino acid composition. J Biochem 99:153–162
Park K-J, Kanehisa M (2003) Prediction of protein subcellular locations by support vector machines using compositions of amino acids and amino acid pairs. Bioinformatics 19:1656–1663
Pu X, Guo J, Leung H, Lin Y (2007) Prediction of membrane protein types from sequences and position-specific scoring matrices. J Theor Biol 247:259–265
Saravanan V, Lakshmi P (2013) APSLAP: an adaptive boosting technique for predicting subcellular localization of apoptosis protein. Acta Biotheor 61:481–497
Schäffer AA, Aravind L, Madden TL, Shavirin S, Spouge JL, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Altschul SF (2001) Improving the accuracy of PSI-BLAST protein database searches with composition-based statistics and other refinements. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2994–3005
Shen H-B, Chou K-C (2007) Hum-mPLoc: an ensemble classifier for large-scale human protein subcellular location prediction by incorporating samples with multiple sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355:1006–1011
Shen H-B, Chou K-C (2008) PseAAC: a flexible web server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Anal Biochem 373:386–388
Shen H-B, Yang J, Chou K-C (2006) Fuzzy KNN for predicting membrane protein types from pseudo-amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 240:9–13
Smith C (2008) Subcellular targeting of proteins and drugs. http://www.biocompare.com/Articles/TechnologySpotlight/976/Subcellular-Target-ing-Of-Proteins-An
UniProt Consortium (2008) The universal protein resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res 36:D190–D195
Wang X, Li G-Z (2012) A multi-label predictor for identifying the subcellular locations of singleplex and multiplex eukaryotic proteins. PLoS One 7:e36317
Wang M, Yang J, Xu Z-J, Chou K-C (2005) SLLE for predicting membrane protein types. J Theor Biol 232:7–15
Wootton JC, Federhen S (1993) Statistics of local complexity in amino acid sequences and sequence databases. Comput Chem 17:149–163
Wu Z-C, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2012) iLoc-Gpos: a multi-layer classifier for predicting the subcellular localization of singleplex and multiplex gram-positive bacterial proteins. Protein Pept Lett 19:4–14
Xiao X, Shao S, Ding Y, Huang Z, Huang Y, Chou K-C (2005) Using complexity measure factor to predict protein subcellular location. Amino Acids 28:57–61
Xiao X, Wang P, Lin W-Z, Jia J-H, Chou K-C (2013) iAMP-2L: a two-level multi-label classifier for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Anal Biochem 436:168–177
Zhang M-L, Zhou Z-H (2007) ML-KNN: a lazy learning approach to multi-label learning. Pattern Recogn 40:2038–2048
Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:17
Zhou X-B, Chen C, Li Z-C, Zou X-Y (2007) Using Chou’s amphiphilic pseudo-amino acid composition and support vector machine for prediction of enzyme subfamily classes. J Theor Biol 248:546–551
Zou Q, Wang Z, Guan X, Liu B, Wu Y, Lin Z (2013) An Approach for identifying cytokines based on a novel ensemble classifier. BioMed Res Int 2013
Zou Q, Chen W, Huang Y, Liu X, Jiang Y (2013b) Identifying multi-functional enzyme by hierarchical multi-label classifier. J Comput Theor Nanosci 10:1038–1043
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, HL., Xiao, X. A New Multi-label Classifier in Identifying the Functional Types of Human Membrane Proteins. J Membrane Biol 248, 179–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9755-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9755-8