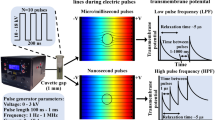
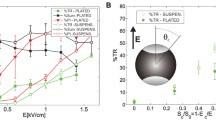
Abstract
Gene transfer and expression can be obtained by delivering calibrated electric pulses on cells in the presence of plasmids coding for the activity of interest. The electric treatment affects the plasma membrane and induces the formation of a transient complex between nucleic acids and the plasma membrane. It results in a delivery of the plasmid in the cytoplasm. Expression is only obtained if the plasmid is translocated inside the nucleus. This is a key limit in the process. We previously showed that delivery of a high-field short-duration electric pulse was inducing a structural alteration of the nuclear envelope. This study investigates if the double-pulse approach (first pulse to transfer the plasmid to the cytoplasm, and second pulse to induce the structural alteration of the envelope) was a way to enhance the protein expression using the green fluorescent protein as a reporter. We observed that not only the double-pulse approach induced the transfection of a lower number of cells but moreover, these transfected cells were less fluorescent than the cells treated only with the first pulse.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badding MA et al (2013) Proteomic and functional analyses of protein-DNA complexes during gene transfer. Mol Ther 21:775–785
Batista Napotnik T et al (2012) Nanosecond electric pulses cause mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in Jurkat cells. Bioelectromagnetics 33:257–264
Beebe SJ et al (2003) Diverse effects of nanosecond pulsed electric fields on cells and tissues. DNA Cell Biol 22:785–796
Bellard E, Teissie J (2009a) Double-pulse approach of electrogenotherapy: an analysis at the single cell level. IEEE T Plasma Sci 37:538–544
Bellard E, Teissie J (2009b) Double pulse approach of electropulsation: a fluorescence analysis of the nucleus perturbation at the single cell level. IEEE T Dielect El In 16:1267–1272
Cadossi R et al (2014) Locally enhanced chemotherapy by electroporation: clinical experiences and perspective of use of electrochemotherapy. Future Oncol 10:877–890
Cepurniene K et al (2010) Influence of plasmid concentration on DNA electrotransfer in vitro using high-voltage and low-voltage pulses. J Membr Biol 236:81–85
Chopinet L et al (2013) Nanosecond electric pulse effects on gene expression. J Membr Biol 246:851–859
Cohen RN et al (2009) Quantification of plasmid DNA copies in the nucleus after lipoplex and polyplex transfection. J Control Release 135:166–174
Escoffre JM et al (2010) Gene transfer: how can the biological barriers be overcome? J Membr Biol 236:61–74
Esser AT et al (2010) Mechanisms for the intracellular manipulation of organelles by conventional electroporation. Biophys J 98:2506–2514
Gabriel B, Teissie J (1995) Spatial compartmentation and time resolution of photooxidation of a cell membrane probe in electropermeabilized Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Biochem 228:710–718
Golzio M et al (1998) Control by osmotic pressure of voltage-induced permeabilization and gene transfer in mammalian cells. Biophys J 74:3015–3022
Golzio M et al (2002a) Cell synchronization effect on mammalian cell permeabilization and gene delivery by electric field. Biochim Biophys Acta 1563:23–28
Golzio M et al (2002b) Direct visualization at the single-cell level of electrically mediated gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1292–1297
Golzio M et al (2004) In vitro and in vivo electric field-mediated permeabilization, gene transfer, and expression. Methods 33:126–135
Hofmann F et al (1999) Electric field pulses can induce apoptosis. J Membr Biol 169:103–109
Huynh C et al (2004) Defective lysosomal exocytosis and plasma membrane repair in Chediak-Higashi/beige cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:16795–16800
Kanduser M et al (2009) Mechanisms involved in gene electrotransfer using high- and low-voltage pulses—an in vitro study. Bioelectrochemistry 74:265–271
Kotnik T et al (2012) Cell membrane electroporation—Part 1: the phenomenon. IEEE Electr Insul M 28(5):14–23
Li LH et al (1999) Apoptosis induced by DNA uptake limits transfection efficiency. Exp Cell Res 253:541–550
Miklavčič D et al (2012) Electrochemotherapy: technological advancements for efficient electroporation-based treatment of internal tumors. Med Biol Eng Comput 50:1213–1225
Mir LM et al (1996) Bleomycin: revival of an old drug. Gen Pharmacol 27:745–748
Napotnik TB et al (2010) Electropermeabilization of endocytotic vesicles in B16 F1 mouse melanoma cells. Med Biol Eng Comput 48:407–413
Neumann E, Rosenheck K (1972) Permeability changes induced by electric impulses in vesicular membranes. J Membr Biol 10:279–290
Neumann E et al (1982) Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J 1:841–845
Pavlin M et al (2012) The role of electrically stimulated endocytosis in gene electrotransfer. Bioelectrochemistry 83:38–45
Rols MP et al (1998) Control by ATP and ADP of voltage-induced mammalian-cell-membrane permeabilization, gene transfer and resulting expression. Eur J Biochem 254:382–388
Rosazza C et al (2012) Cholesterol implications in plasmid DNA electrotransfer: evidence for the involvement of endocytotic pathways. Int J Pharm 423:134–143
Satkauskas S et al (2012) Towards the mechanisms for efficient gene transfer into cells and tissues by means of cell electroporation. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12:275–286
Schoenbach KH et al (2001) Intracellular effect of ultrashort electrical pulses. Bioelectromagnetics 22:440–448
Sukhorukov VL et al (2005) Surviving high-intensity field pulses: strategies for improving robustness and performance of electrotransfection and electrofusion. J Membr Biol 206:187–201
Utvik JK et al (1999) DNA injection into single cells of intact mice. Hum Gene Ther 10:291–300
Weaver JC et al (2012) A brief overview of electroporation pulse strength-duration space: a region where additional intracellular effects are expected. Bioelectrochemistry 87:236–243
Young JL et al (2003) Effect of a DNA nuclear targeting sequence on gene transfer and expression of plasmids in the intact vasculature. Gene Ther 10:1465–1470
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to S. Daniel for her help in the preliminary study. This work was performed with the “Toulouse Réseau Imagerie” core IPBS facility support (Génotoul, Toulouse, France) which was supported by the Association Recherche Cancer (n°5585), Region Midi Pyrenees (CPER) and Grand Toulouse cluster. The Midi-Pyrénées Region has financially supported this work (Grant 11052700). Research was conducted in the scope of the EBAM European Associated Laboratory (LEA) and resulted from the networking efforts of the COST Action TD1104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasquet, L., Bellard, E., Golzio, M. et al. A Double-Pulse Approach For Electrotransfection. J Membrane Biol 247, 1253–1258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9720-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9720-6