Abstract
Objective
To describe the use of medicines and to determine the frequency of off-label use in emergency room paediatric patients.
Patients and methods
A prospective, observational and descriptive study was carried out in the setting of the paediatric emergency room of a Spanish general hospital. Medicines used by children <14 years prior to their emergency room visit were analysed based on information collected from parents/guardians and relatives for each drug prescription. Off-label use was defined as the utilization of a drug at an indication, dosage, frequency or route of administration that differed from the specifications in the Summary of Product Characteristics or by children outside the authorized age group.
Results
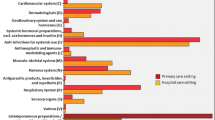
The patient cohort comprised 462 children, among whom 336 children had been prescribed 667 prescriptions. Of the medicines prescribed, 90% fell into only five 5 Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System groups. The most frequent active principles were ibuprofen and paracetamol. Of a total of 152 different formulations recorded, no paediatric information was provided for 40 formulations, and one formulation was contraindicated in children. Based on the established criteria, 338 prescriptions were off-label: no paediatric information or contraindication in children were available (82 prescriptions); the drug was used for an indication different from the authorized one (111 prescriptions); drug use was inconsistent with age recommendations (16 prescriptions); drug use was inconsistent with dose/frequency (129 prescriptions). Of the 152 formulations, 107 were occasionally used in an off-label manner.
Conclusions
Although the mean number of drugs used in children is small, off-label use is frequent. Research efforts should target paediatric studies that allow a rational drug use in children.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morales-Olivas FJ, Morales-Carpi C (2006) Clinical trials in children. Rev Recent Clin Trials 1:251–258
Pandolfini C, Impicciatore P, Provasi D, Rocchi F, Campi R, Bonati M (2002) Off-label use of drugs in Italy: a prospective, observational and multicentre study. Acta Paediatr 91:339–347
Cuzzolin L, Zaccaron A, Fanos V (2003) Unlicensed and off-label uses of drugs in paediatrics: a review of the literature. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 17:125–131
Conroy S, Choonara I, Impicciatore P, Mohn A, Arnell H, Rane A et al (2000) Survey of unlicensed and off label drug use in paediatric wards in European countries. European network for drug investigation in children. Br Med J 320:79–82
Turner S, Longworth A, Nunn AJ, Choonara I (1998) Unlicensed and off-label drug use in paediatric wards: prospective study. Br Med J 316:343–345
McIntyre J, Conroy S, Avery A, Corns H, Choonara I (2000) Unlicensed and off-label prescribing of drugs in general practice. Arch Dis Child 83:498–501
Pandolfini C, Bonati M (2005) A literature review on off-label drug use in children. Eur J Pediatr 164:552–558
Chalumeau M, Tréluyer JM, Salanave B, Assathiany R, Chéron G, Crocheton N et al (2000) Off-label and unlicensed drug used among French office based paediatricians. Arch Dis Child 83:502–505
Pandolfini C, Campi R, Clavenna A, Cazzato T, Bonati M (2005) Italian paediatricians and off-label prescriptions: loyal to regulatory or guideline standards? Acta Paediatr 94:753–757
Horen B, Montastruc JL, Lapeyre-Mestre M (2002) Adverse drug reactions and off-label drug use in paediatric outpatients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54:665–670
Lifshitz M, Gavrilov V, Grossman Z, Binsthok M, Hornik D, Rosemblum H et al (2002) Unapproved prescription practices in primary pediatric clinics in Israel: a prospective analysis. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 63:830–837
Bazzano AT, Mangione-Smith R, Schonlau M, Suttorp MJ, Brook RH (2009) Off-label prescribing to children in the United States outpatient setting. Acad Pediatr 9:81–88
Danés I, Vallano A, de la Cruz G, Juárez JC, Arnau JM (2002) Utilización de medicamentos y condiciones de uso recomendadas en pediatría. An Pediatr (Barc) 57:414–419
Cazzato T, Pandolfini C, Campi R, Bonati M (2001) Drug prescribing in out-patients children in Southern Italy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 57:611–616
Sanz E, Hernandez MA, Ratchina S, Stratchounsky L, Peiré MA, Lapeyre-Mestre M et al (2004) Drug utilisation in outpatient children. A comparison among Tenerife, Valencia, and Barcelona (Spain), Toulouse (France), Sofia (Bulgaria), Bratislava (Slovakia) and Smolensk (Russia). Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:127–134
Martínez-Mir I, García-López M, Palop V, Ferrer JM, Rubio E, Morales-Olivas FJ (1999) A prospective study of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized children. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47:681–688
Turner S, Nunn AJ, Choonara I (1997) Unlicensed drug use in children in the UK. Paediatr Perinatal Drug Ther 1:52–55
Neubert A, Wong IC, Bonifazi A, Catapano M, Felisi M, Baiardi P et al (2008) Defining off-label and unlicensed use of medicines for children: results of a Delphi survey. Pharmacol Res 58:316–322
McCarney R, Warner J, Iliffe S, van Haselen R, Griffin M, Fisher P (2007) The Hawthorne effect: a randomised, controlled trial. BMC Med Res Methodol 7:30
Ekins-Daukes S, Helms PJ, Simpson CR, Taylor MW, McLay JS (2004) Off-label prescribing to children in primary care: retrospective observational study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:349–353
Headley J, Northstone K (2007) Medication administered to children from 0 to 7.5 years in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:189–195
Hoppu K (2008) Paediatric clinical pharmacology—at the beginning of a new era. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64:201–205
Schirm E, Tobi H, de Jong–van den Berg LT (2003) Risk factors for unlicensed and off-label drug use in children outside the hospital. Pediatrics 111:291–295
Morales-Carpi C, Estañ L, Torró I, Lurbe E, Morales-Olivas FJ (2006) ¿Son los niños hipertensos españoles huérfanos terapéuticos? An Pediatr (Barc) 64:114–119
Regulation (EC) No 1901/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 December 2006 on medicinal products for paediatric use and amending Regulation (EEC) No 1768/92, Directive 2001/20/EC, Directive 2001/83/EC and Regulation (EC) No 726/2004. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/pharmaceuticals/eudralex/vol-1/reg_2006_1901/reg_2006_1901_en.pdf. Accessed 17 July 2009
Funding
None
Competing interests
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
What is already known on this topic?
• There is little information currently available on the effects of drugs in children; thus many drugs used by paediatric patients are prescribed in an off-label manner.
• No data are available on the frequency of off-label use in Spanish paediatric community setting.
What does this study add to the current body of information on this topic?
• Off-label use is a common practice in the Spanish paediatric population.
• More than half of the prescriptions received by the children in our study were off-label.
• Off-label use in self-medication was similar to that observed in prescriptions from paediatricians.
• More than three-quarters of the children of our study received at least one off-label drug.
• There are seasonal variations in the use of drugs in children
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morales-Carpi, C., Estañ, L., Rubio, E. et al. Drug utilization and off-label drug use among Spanish emergency room paediatric patients . Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66, 315–320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0747-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0747-z