Abstract
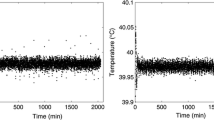
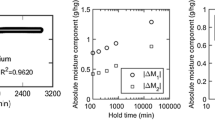
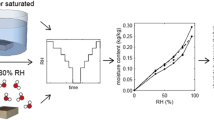
Dynamic vapor sorption (DVS) measurements are widely used to collect water vapor sorption isotherms for wood and other cellulosic materials. Equilibrium moisture content (EMC) is typically assumed to have been reached when the rate of change in moisture content with time (\({\text{d}}M/{\text{d}}t\)) drops below a certain value. However, the errors associated with determining EMC in this manner have never been characterized. Here, an operational definition of equilibrium for DVS measurements is provided, and twenty test cases over four cellulosic materials are presented where the relative humidity was stepped up or down and then held constant until equilibrium was reached. Then, both the time to reach various \({\text{d}}M/{\text{d}}t\) “stop criteria” and the errors in EMC associated with those stop criteria are quantified. The errors in the EMC from the widely used 0.002% min−1 stop criterion are found to be as large as 1.2% MC, and the average error for 20 test cases is 0.5% MC, which are much larger than the 0.1% MC error claimed in the literature. Longer data collection times are recommended, and a more stringent \({\text{d}}M/{\text{d}}t\) criterion (0.0003% min−1, using a 2-h window) for cellulosic materials is proposed. The errors with this criterion are less than 0.75% MC, and the average error is 0.3% MC. Furthermore, it is shown that the errors for a given stop criterion are systematic and can be fairly well characterized with a simple linear regression. Finally, a correction for systematic error is proposed that results in more accurate EMC values with shorter hold times.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astill D, Hall P, McConnell J (1987) An automated vacuum microbalance for measurement of adsorption isotherms. J Phys E: Sci Instrum 20:19
Benham M, Ross D (1989) Experimental determination of absorption-desorption isotherms by computer-controlled gravimetric analysis. Z Phys Chem 163:25–32
Bergren MS (1994) An automated controlled atmosphere microbalance for the measurement of moisture sorption. Int J Pharm 103:103–114
Christensen GN, Hergt HFA (1969) Effect of previous history on kinetics of sorption by wood cell walls. J Polym Sci Part A-1 Polym Chem 7:2427–2430. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1969.150070839
Engelund ET, Klamer M, Venås M (2010) Acquisition of sorption isotherms for modified woods by the use of dynamic vapour sorption instrumentation: principles and practice. In: 41st Annual meeting of the International Research Group on Wood Protection, Biarritz, France, 9–13 May 2010. IRG Secretariat
Engelund ET, Klamer M, Venås TM (2011) Adsorption boundary curve influenced by step interval of relative humidity investigated by dynamic vapour sorption equipment. In: 42nd annual meeting of the International Research Group on Wood Protection, Queenstown, New Zealand, 2011. IRG Secretariat, Paper IRG/WP 11-40547
Glass SV, Zelinka SL, Johnson JA (2014) Investigation of historic equilibrium moisture content data from the Forest Products Laboratory. Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory, General Technical Report, FPL-GTR-229, Madison, WI
Glass SV, Boardman CR, Zelinka SL (2017) Short hold times in dynamic vapor sorption measurements mischaracterize the equilibrium moisture content of wood. Wood Sci Technol 51:243–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0883-4
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2009) The water vapor sorption behavior of natural fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 112:1524–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29725
Hill C, Norton A, Newman G (2010a) The water vapour sorption properties of Sitka spruce determined using a dynamic vapour sorption apparatus. Wood Sci Technol 44:497–514
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2010b) The water vapor sorption behavior of flax fibers—analysis using the parallel exponential kinetics model and determination of the activation energies of sorption. J Appl Polym Sci 116:2166–2173. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.31819
Hill CA, Keating BA, Jalaludin Z, Mahrdt E (2012) A rheological description of the water vapour sorption kinetics behaviour of wood invoking a model using a canonical assembly of Kelvin–Voigt elements and a possible link with sorption hysteresis. Holzforschung 66:35–47
Hill CAS, Ramsay J, Laine K, Rautkari L, Hughes M (2013) Water vapour sorption behaviour of thermally modified wood. Int Wood Prod J 4:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1179/2042645313Y.0000000040
Jalaludin Z, Hill CA, Samsi HW, Husain H, Xie Y (2010a) Analysis of water vapour sorption of oleo-thermal modified wood of Acacia mangium and Endospermum malaccense by a parallel exponential kinetics model and according to the Hailwood–Horrobin model. Holzforschung 64:763–770
Jalaludin Z, Hill CAS, Xie Y, Samsi HW, Husain H, Awang K, Curling SF (2010b) Analysis of the water vapour sorption isotherms of thermally modified acacia and sesendok. Wood Mat Sci Eng 5:194–203
Keating BA, Hill CAS, Sun D, English R, Davies P, McCue C (2013) The water vapor sorption behavior of a galactomannan cellulose nanocomposite film analyzed using parallel exponential kinetics and the Kelvin-Voigt viscoelastic model. J Appl Polym Sci 129:2352–2359. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.39132
Marshall PV, Cook PA, Williams DR (1994) A new analytical technique for characterising the water vapour sorption properties of powders. Paper presented at the international symposium on solid oral dosage forms, Stockholm, Sweden
Popescu C-M, Hill CAS, Curling S, Ormondroyd G, Xie Y (2013) The water vapour sorption behaviour of acetylated birch wood: how acetylation affects the sorption isotherm and accessible hydroxyl content. J Mater Sci 49:2362–2371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7937-x
Rasmussen M, Akinc M (1983) Microcomputer-controlled gravimetric adsorption apparatus. Rev Sci Instrum 54:1558–1564
Sharratt V, Hill CAS, Zaihan J, Kint DPR (2010) Photodegradation and weathering effects on timber surface moisture profiles as studied using dynamic vapour sorption. Polym Degrad Stab 95:2659–2662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.07.011
Spalt H (1957) The sorption of water vapor by domestic and tropical woods. Forest Prod J 7:331
Spalt H (1958) The fundamentals of water vapor sorption by wood. Forest Prod J 8:288–295
Stamm AJ, Loughborough WK (1935) Thermodynamics of the swelling of wood. The Journal of Physical Chemistry 39:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150361a009
Strømdahl K (2000) Water sorption in wood and plant fibres. Technical University of Denmark. Danmarks Tekniske Universitet, Department of Structural Engineering and Materials Institut for Bærende Konstruktioner og Materialer
Thybring EE, Kymäläinen M, Rautkari L (2018) Experimental techniques for characterising water in wood covering the range from dry to fully water-saturated. Wood Sci Technol 52(2):297–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-017-0977-7
Williams D (1995) The characterisation of powders by gravimetric water vapour sorption. Int Labmate 20:40–42
Xie Y, Hill CA, Xiao Z, Jalaludin Z, Militz H, Mai C (2010) Water vapor sorption kinetics of wood modified with glutaraldehyde. J Appl Polym Sci 117:1674–1682
Xie Y, Hill CA, Jalaludin Z, Sun D (2011) The water vapour sorption behaviour of three celluloses: analysis using parallel exponential kinetics and interpretation using the Kelvin–Voigt viscoelastic model. Cellulose 18:517–530
Yelle DJ, Ralph J, Frihart CR (2008) Characterization of nonderivatized plant cell walls using high-resolution solution-state NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Chem 46:508–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.2201
Zaihan J, Hill CAS, Curling S, Hashim WS, Hamdan H (2009) Moisture adsorption isotherms of Acacia mangium and Endospermum malaccense using dynamic vapour sorption. J Trop Forest Sci 21:277–285
Zaihan J, Hill C, Curling S, Hashim W, Hamdan H (2010) The kinetics of water vapour sorption: analysis using parallel exponential kinetics model on six Malaysian hardwoods. J Trop Forest Sci 22:107–117
Zelinka SL, Glass SV (2010) Water vapor sorption isotherms for southern pine treated with several waterborne preservatives ASTM. J Test Eval 38:80–88
Zelinka SL, Lambrecht MJ, Glass SV, Wiedenhoeft AC, Yelle DJ (2012) Examination of water phase transitions in Loblolly pine and cell wall components by differential scanning calorimetry. Thermochim Acta 533:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2012.01.015
Funding
Funding was provided by US Forest Service. VILLUM FONDEN postdoc program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glass, S.V., Boardman, C.R., Thybring, E.E. et al. Quantifying and reducing errors in equilibrium moisture content measurements with dynamic vapor sorption (DVS) experiments. Wood Sci Technol 52, 909–927 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-018-1007-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-018-1007-0