Abstract
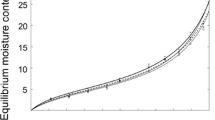
The hygroscopicity and thermodynamic properties of Pinus canariensis wood buried in volcanic ash, dating from 1100 BC, were studied and compared with recently felled juvenile and mature wood of the same species. The sorption isotherms were obtained by the saturated salt method at 35 and 50 °C. The isotherms were fitted using the Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer model. The thermodynamic parameters were determined following the Clausius–Clapeyron integration method. To understand the behaviour of each type of wood, the chemical composition, infrared spectra and X-ray diffractograms were determined for each sample. The mature wood has a higher sugar content and lower extractive content than the juvenile and the buried wood. For both temperatures, the isotherm of the mature wood is above the isotherm of the juvenile wood and this, in turn, is above the isotherm of the buried wood, primarily influenced by the higher cellulose and hemicellulose contents and lower extractives content in the mature wood, resulting in a higher number of accessible –OH groups. Degradation of the buried wood due to high temperatures explains why its isotherms are below the isotherms of the recent wood. The energy involved in the desorption process is greater than in adsorption. Similarly, more energy is involved in the mature wood than in the juvenile wood, and the energy involved in the juvenile wood is greater than in the buried wood.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson S, Serimaa R, Paakkari T, Saranpaa P, Pesonen E (2003) Crystallinity of wood and the size of cellulose crystallites in Norway spruce (Picea abies). J Wood Sci 49:531–537
Andersson S, Wikberg H, Pesonen E, Maunu SL, Serimaa R (2004) Studies of crystallinity of Scots pine and Norway spruce cellulose. Trees Struct Funct 18:346–353
Arevalo-Pinedo A, Giraldo-Zuñiga AD, Dos Santos FL, Arevalo ZDS, Arevalo RP (2004) Sorption isotherms experimental data and mathematical models for murici pulp (Byrsonima sericea). In: Proceedings of the 14th international drying symposium (IDS 2004), August 22–25, Sao Paulo, Brazil, vol A, pp 634–639
Avramidis S (1997) The basics of sorption. In: International conference on wood-water relations, June 16–17, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 1–16
Avramidis S, Dubois J (1992) Sorption energies of some Canadian species. Holzforschung 46:177–179
Balakshin MY, Capanema EA, Goldfarb B, Frampton J, Kadla JF (2005) NMR studies on Fraser fir Abies fraseri (Pursh) Poir. lignins. Holzforschung 59:488–496
Bertaud F, Holmbom B (2004) Chemical composition of earlywood and latewood in Norway spruce heartwood, sapwood and transition zone wood. Wood Sci Technol 38:245–256
Blanchette RA (2000) A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood from different environments. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 46:189–204
Bratasz L, Kozlowska A, Kozlowski R (2012) Analysis of water adsorption by wood using the Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer equation. Eur J Wood Prod 70:445–451
Chang HT, Chang ST (2002) Moisture excluding efficiency and dimensional stability of wood improved by acylation. Bioresour Technol 85:201–204
Choong ET, Achmadi SS (1991) Effect of extractives on moisture sorption and shrinkage in tropical woods. Wood Fiber Sci 23:185–196
Christensen GN, Kelsey KE (1959) The rate of sorption of water vapor by wood. Holz Roh Werkst 17:178–188
Climent JM, Gil L, Pardos JA (1993) Heartwood and sapwood development and its relationship to growth and environment in Pinus canariensis Chr.Sm ex DC. J. For Ecol Manage 59:165–174
Climent JM, Gil L, Pardos JA (1998) Xylem anatomical traits related to resinous heartwood formation in Pinus canariensis Sm. Trees 12:139–145
Climent JM, Chambel M, Pérez E, Gil L, Pardos JA (2002) Relationship between heartwood radius and early radial growth, tree age, and climate in Pinus canariensis. Can J For Res 32:103–111
Easty DB, Malcolm EW (1982) Estimation of pulping yield in continuous digesters from carbohydrate and lignin determinations. Tappi J 65:78–80
Engelund ET, Thygesen LG, Svensson S, Hill CAS (2013) A critical discussion of the physics of wood-water interactions. Wood Sci Technol 47:141–161
Esteban LG, Gasson P, Climent JM, de Palacios P, Guindeo A (2005) The wood of Pinus canariensis and its resinous heartwood. IAWA J 26:69–77
Esteban LG, Fernandez FG, Casasus AG, de Palacios PD, Gril J (2006) Comparison of the hygroscopic behaviour of 205-year-old and recently cut juvenile wood from Pinus sylvestris L. Ann For Sci 63:309–317
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Fernandez FG, Guindeo A, Cano NN (2008a) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of old and new Pinus sylvestris wood. Wood Fiber Sci 40:111–121
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Fernandez FG, Guindeo A, Conde M, Baonza V (2008b) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood after 103 years of submersion. Holzforschung 62:745–751
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Garcia Fernandez F, Martin JA, Genova M, Fernandez-Golfin JI (2009) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of buried juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood aged 1170 ± 40 BP. Wood Sci Technol 43:140–151
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Fernandez FG, Garcia-Amorena I (2010) Effects of burial of Quercus spp. wood aged 5910 ± 250 BP on sorption and thermodynamic properties. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 64:371–377
Esteban LG, Simon C, Fernandez FG, de Palacios P, Martín-Sampedro R, Eugenio ME, Hosseinpourpia R (2015) Juvenile and mature wood of Abies pinsapo Boissier: sorption and thermodynamic properties. Wood Sci Technol 49:725–738
Fengel D (1991) Aging and fossilization of wood and its components. Wood Sci Technol 25:153–177
Fengel D, Wegener G (1983) Wood chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
Fernandez FG, Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Simon C, Garcia-Iruela A, de la Fuente J (2014) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of Terminalia superba Engl. & Diels. and Triplochiton scleroxylon K. Schum. through the 15, 35 and 50°C sorption isotherms. Eur J Wood Prod 72:99–106
Freundt A (2003) Entrance of hot pyroclastic flows into the sea: experimental observations. Bull Volcanol 65:144–164
Genova M, Santana C (2006) Crecimiento y longevidad en el pino canario (Pinus canariensis Smith.). Invest Agrar Sist Recur For 15:296–307
Gurioli L, Zanella E, Gioncada A, Sbrana A (2012) The historic magmatic-hydrothermal eruption of the Breccia di Commenda, Vulcano, Italy. Bull Volcanol 74:1235–1254
Hernandez RE (2007) Moisture sorption properties of hardwoods as affected by their extraneous substances, wood density, and interlocked grain. Wood Fiber Sci 39:132–145
Hill C (2006) Wood modification. Chemical, thermal and other proccesses. Wiley, England
Hill CAS, Jones D (1996) The dimensional stabilisation of Corsican pine sapwood by reaction with carboxylic acid anhydrides. The effect of chain length. Holzforschung 50:457–462
Hill CAS, Jones D (1999) Dimensional changes in Corsican pine sapwood due to chemical modification with linear chain anhydrides. Holzforschung 53:267–271
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2009) The water vapor sorption behavior of natural fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 112:1524–1537
Hill CAS, Norton AJ, Newman G (2010) The water vapour sorption properties of Sitka spruce determined using a dynamic vapour sorption apparatus. Wood Sci Technol 44:497–514
Huo D, Fang G, Yang Q, Han S, Deng Y, Shen K, Lin Y (2013) Enhancement of eucalypt chips’ enzymolysis efficiency by a combination method of alkali impregnation and refining pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 150:73–78
Iiyama K, Kasuya N, Lam TBT, Nakano J, Sakaguchi H (1988) Chemical characterization of ancient buried wood. Holzforschung 42:5–10
Illic J, Northway R, Pongracic S (2003) Juvenile wood characteristics, effects and identification. Literature review. Forest and Wood Products Research and Development Corporation
Jahan MS, Mun SP (2005) Effect of tree age on the cellulose structure of Nalita wood (Trema orientalis). Wood Sci Technol 39:367–373
Jannot Y, Kanmogne A, Talla A, Monkam L (2006) Experimental determination and modelling of water desorption isotherms of tropical woods: afzelia, ebony, iroko, moabi and obeche. Holz Roh Werkst 64:121–124
Jones PD, Schimleck LR, Peter GF, Daniels RF, Clark A (2006) Nondestructive estimation of wood chemical composition of sections of radial wood strips by diffuse reflectance near infrared spectroscopy. Wood Sci Technol 40:709–720
Larson PR (1966) Changes in chemical composition of wood cell walls associated with age in Pinus resinosa. For Prod J 16:37–45
Lenth CA, Kamke FA (2001) Equilibrium moisture content of wood in high-temperature pressurized environments. Wood Fiber Sci 33:104–118
Li XJ, Cao ZY, Wei ZY, Feng QY, Wang JS (2011) Equilibrium moisture content and sorption isosteric heats of five wheat varieties in China. J Stored Prod Res 47:39–47
Lionetto F, Del Sole R, Cannoletta D, Vasapollo G, Maffezzoli A (2012) Monitoring wood degradation during weathering by cellulose crystallinity. Materials 5:1910–1922
Majka J, Olek W (2008) Sorption properties of mature and juvenile lime wood (Tilia sp.). Folia For Pol Ser B 39:65–75
Major JJ, Pierson TC, Hoblitt RP, Moreno H (2013) Pyroclastic density currents associated with the 2008-2009 eruption of Chaiten Volcano (Chile): forest disturbances, deposits, and dynamics. Andean Geol 40:324–358
Mangas J, Pérez-Torrado JF, Gimeno D, Hansen A, Paterne M, Guillou H (2002) Caracterización de los materiales volcánicos asociados a las erupciones holocenas de la Caldera de Pinos de Galdar y edificios volcánicos adyacentes (Gran Canaria) (Characterisation of the volcanic materials associated with the Holocene eruptions of Caldera de Pinos, Gáldar, and adjacent volcanic edifices (Gran Canaria)) (In Spanish). Geogaceta 32:49–52
McMinn WAM, Magee TRA (2003) Thermodynamic properties of moisture sorption of potato. J Food Eng 60:157–165
Mihranyan A, Llagostera AP, Karmhag R, Stromme M, Ek R (2004) Moisture sorption by cellulose powders of varying crystallinity. Int J Pharm 269:433–442
Militz H, Busetto D, Hapla F (2003) Investigation on natural durability and sorption properties of Italian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) from coppice stands. Holz Roh Werkst 61:133–141
Murata K, Watanabe Y, Nakano T (2013) Effect of thermal treatment on fracture properties and adsorption properties of Spruce wood. Materials 6:4186–4197
Neimsuwan T, Wang S, Taylor AM, Rials TG (2008) Statics and kinetics of water vapor sorption of small loblolly pine samples. Wood Sci Technol 42:493–506
Nogales J, Schmincke HU (1969) El Pino enterrado de la Cañada de las Arenas (Gran Canaria) (The buried pine of Cañada de las Arenas (Gran Canaria)) (In Spanish). Notebooks of Canary Islands Botany No. 5. Llano de la Piedra plant acclimatisation garden, Santa Lucia de Tirajana
Olek W, Majka J, Czaijkowski L (2013) Sorption isotherms of thermally modified wood. Holzforschung 67:183–191
Peralta PN, Bangi AP, Lee AWC (1997) Thermodynamics of moisture sorption by the giant-timber bamboo. Holzforschung 51:177–182
Peura M, Saren MP, Laukkanen J, Nygard K, Andersson S, Saranpaa P, Paakkari T, Hamalainen K, Serimaa R (2008) The elemental composition, the microfibril angle distribution and the shape of the cell cross-section in Norway spruce xylem. Trees Struct Funct 22:499–510
Popescu CM, Hill CAS (2013) The water vapour adsorption-desorption behaviour of naturally aged Tilia cordata Mill. wood. Polym Degrad Stabil 98:1804–1813
Rautkari L, Hill CAS, Curling S, Jalaludin Z, Ormondroyd G (2013) What is the role of the accessibility of wood hydroxyl groups in controlling moisture content? J Mater Sci 48:6352–6356
Rautkari L, Honkanen J, Hill CAS, Ridley-Ellis D, Hughes M (2014) Mechanical and physical properties of thermally modified Scots pine wood in high pressure reactor under saturated steam at 120, 150 and 180°C. Eur J Wood Prod 72:33–41
Rowell RM (1980) Distribution of reacted chemicals in southern pine modified with methyl isocyanate. Wood Sci 13:102–110
Rowell RM (2005) Wood chemistry and wood composites. Taylor & Francis, Florida
Siau JF (1995) Wood: influence of moisture on physical properties. Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA
Simon C, Esteban LG, de Palacios P, Fernandez FG, Martín-Sampedro R, Eugenio ME (2015) Thermodynamic analysis of water vapour sorption behaviour of juvenile and mature wood of Abies alba Mill. J Mater Sci 50:7282–7292
Singh AP (2012) A review of microbial decay types found in wooden objects of cultural heritage recovered from buried and waterlogged environments. J Cult Herit 13:S16–S20
Sluiter A, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2005) Determination of extractives in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP) http://www.nrel.gov/biomass/pdfs/42619.pdf Accessed 27 Mar 2015
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker S (2011) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP) http://www.nrel.gov/biomass/pdfs/42618.pdf Accessed 27 Mar 2015
Song KL, Yin YF, Salmen L, Xiao FM, Jiang XM (2014) Changes in the properties of wood cell walls during the transformation from sapwood to heartwood. J Mater Sci 49:1734–1742
Stamm AJ, Hansen LA (1937) Minimizing wood shrinkage and swelling. Effect of heating in various gases. Ind Eng Chem 29:831–833
Telis VRN, Gabas AL, Menegalli FC, Telis-Romero J (2000) Water sorption thermodynamic properties applied to persimmon skin and pulp. Thermochim Acta 343:49–56
Themelin A, Rebollo J, Thibaut A (1997) Method for defining the behaviour of lignocellulosic produces at sorption: application to tropical wood species. In: International conference on wood-water relations. June 16–17, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 17–32
Tsoumis G (1991) Science and technology of wood. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York
Vaaler D, Syverud K, Seem B, Moe ST (2005) Estimating the pulping yield by carbohydrate analysis. Tappi J 4:23–27
Viollaz PE, Rovedo CO (1999) Equilibrium sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of starch and gluten. J Food Eng 40:287–292
Voight B, Davis MJ (2000) Emplacement temperatures of the November 22, 1994 nuee ardente deposits, Merapi Volcano, Java. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 100:371–377
Wangaard FF, Granados LA (1967) The effect of extractives on water-vapor sorption by wood. Wood Sci Technol 1:253–277
Weichert L (1963) Investigations on sorption and swelling of spruce, beech and compressed beech wood between 20° and 100°. Holz Roh Werkst 21:290–300
Willems W, Mai C, Militz H (2013) Thermal wood modification chemistry analysed using van Krevelen’s representation. Int Wood Prod J 4:166–171
Yokoyama T, Kadla JF, Chang HM (2002) Microanalytical method for the characterization of fiber components and morphology of woody plants. J Agric Food Chem 50:1040–1044
Zaihan J, Hill CAS, Hashim WS, Dahlan JM, Sun DY (2011) Analysis of the water vapour sorption isotherms of oil palm trunk and rubberwood. J Trop For Sci 23:97–105
Zobel B, Matthias M, Roberds JH, Kellison RC (1968) Moisture content of southern pine trees. Technical Reports 37 School of Forest Resources NC State Univ Raleigh, NC
Acknowledgements
This study is part of the AGL2009-12801 project of the 2008–2011 Spanish National Plan for Scientific Research, Development and Technological Innovation, funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simón, C., Esteban, L.G., de Palacios, P. et al. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of wood of Pinus canariensis C. Sm. ex DC. buried in volcanic ash during eruption. Wood Sci Technol 51, 517–534 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0884-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0884-3