Abstract
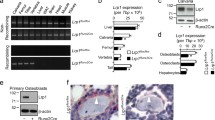
The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (Lrp)-5 regulates osteoblast proliferation and bone formation through its expression in duodenum by modifying the gut serotonin–bone endocrine axis. However, its direct role, if any, in osteoblast progenitor cells has not been studied thus far. Here, we show that mice with a Dermo1-Cre-mediated disruption of Lrp5 in osteoblast progenitor cells have normal embryonic skeletogenesis and normal skeletal growth and development postnatally. Histomorphometric analysis of 3-month-old adult mice revealed normal osteoblast numbers, bone formation rate, and bone mass in Lrp5 −/− Dermo mice. In addition, analysis of two osteoporosis pseudoglioma (OPPG) patients revealed a three- to fivefold increase in their serum serotonin levels compared to age-matched controls. These results rule out a direct function of Lrp5 in osteoblast progenitor cells and add further support to the notion that dysregulation of serotonin synthesis is involved in bone mass abnormalities observed in OPPG patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glass DA II, Karsenty G (2007) In vivo analysis of Wnt signaling in bone. Endocrinology 148:2630–2634
Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, Zacharin M, Oexle K, Marcelino J, Suwairi W, Heeger S, Sabatakos G, Apte S, Adkins WN, Allgrove J, Arslan-Kirchner M, Batch JA, Beighton P, Black GC, Boles RG, Boon LM, Borrone C, Brunner HG, Carle GF, Dallapiccola B, De Paepe A, Floege B, Halfhide ML, Hall B, Hennekam RC, Hirose T, Jans A, Juppner H, Kim CA, Keppler-Noreuil K, Kohlschuetter A, LaCombe D, Lambert M, Lemyre E, Letteboer T, Peltonen L, Ramesar RS, Romanengo M, Somer H, Steichen-Gersdorf E, Steinmann B, Sullivan B, Superti-Furga A, Swoboda W, van den Boogaard MJ, Van Hul W, Vikkula M, Votruba M, Zabel B, Garcia T, Baron R, Olsen BR, Warman ML (2001) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107:513–523
Johnson ML, Gong G, Kimberling W, Recker SM, Kimmel DB, Recker RR (1997) Linkage of a gene causing high bone mass to human chromosome 11(11q12–13). Am J Hum Genet 60:1326–1332
Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L, Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K, Lifton RP (2002) High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl J Med 346:1513–1521
Kato M, Patel MS, Levasseur R, Lobov I, Chang BH, Glass DA II, Hartmann C, Li L, Hwang TH, Brayton CF, Lang RA, Karsenty G, Chan L (2002) Cbfa1-independent decrease in osteoblast proliferation, osteopenia, and persistent embryonic eye vascularization in mice deficient in Lrp5, a Wnt coreceptor. J Cell Biol 157:303–314
Lobov IB, Rao S, Carroll TJ, Vallance JE, Ito M, Ondr JK, Kurup S, Glass DA, Patel MS, Shu W, Morrisey EE, McMahon AP, Karsenty G, Lang RA (2005) WNT7b mediates macrophage-induced programmed cell death in patterning of the vasculature. Nature 437:417–421
Junge HJ, Yang S, Burton JB, Paes K, Shu X, French DM, Costa M, Rice DS, Ye W (2009) TSPAN12 regulates retinal vascular development by promoting Norrin—but not Wnt-induced FZD4/beta-catenin signaling. Cell 139:299–311
Ye X, Wang Y, Cahill H, Yu M, Badea TC, Smallwood PM, Peachey NS, Nathans J (2009) Norrin, frizzled-4, and Lrp5 signaling in endothelial cells controls a genetic program for retinal vascularization. Cell 139:285–298
Glass DA II, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G (2005) Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell 8:751–764
Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, Sigler RE, Faugere MC, Bouxsein ML, Deng L, Clemens TL, Williams BO (2005) Essential role of beta-catenin in postnatal bone acquisition. J Biol Chem 280:21162–21168
Yadav VK, Ryu JH, Suda N, Tanaka KF, Gingrich JA, Schutz G, Glorieux FH, Chiang CY, Zajac JD, Insogna KL, Mann JJ, Hen R, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2008) Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum. Cell 135:825–837
Williams BO, Insogna KL (2009) Where Wnts went: the exploding field of Lrp5 and Lrp6 signaling in bone. J Bone Miner Res 24:171–178
Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y (2005) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell 8:739–750
Yu K, Xu J, Liu Z, Sosic D, Shao J, Olson EN, Towler DA, Ornitz DM (2003) Conditional inactivation of FGF receptor 2 reveals an essential role for FGF signaling in the regulation of osteoblast function and bone growth. Development 130:3063–3074
Settembre C, Arteaga-Solis E, McKee MD, de Pablo R, Al Awqati Q, Ballabio A, Karsenty G (2008) Proteoglycan desulfation determines the efficiency of chondrocyte autophagy and the extent of FGF signaling during endochondral ossification. Genes Dev 22:2645–2650
Barros ER, Dias da Silva MR, Kunii IS, Hauache OM, Lazaretti-Castro M (2007) A novel mutation in the LRP5 gene is associated with osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome. Osteoporos Int 18:1017–1018
Saarinen A, Saukkonen T, Kivela T, Lahtinen U, Laine C, Somer M, Toiviainen-Salo S, Cole WG, Lehesjoki AE, Makitie O (2009) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) mutations and osteoporosis, impaired glucose metabolism and hypercholesterolaemia. Clin Endocrinol 72:481–488
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H, Kishida S (2007) Multiplicity of the interactions of Wnt proteins and their receptors. Cell Signal 19:659–671
Sawakami K, Robling AG, Ai M, Pitner ND, Liu D, Warden SJ, Li J, Maye P, Rowe DW, Duncan RL, Warman ML, Turner CH (2006) The Wnt coreceptor LRP5 is essential for skeletal mechanotransduction but not for the anabolic bone response to parathyroid hormone treatment. J Biol Chem 281:23698–23711
Robinson JA, Chatterjee-Kishore M, Yaworsky PJ, Cullen DM, Zhao W, Li C, Kharode Y, Sauter L, Babij P, Brown EL, Hill AA, Akhter MP, Johnson ML, Recker RR, Komm BS, Bex FJ (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is a normal physiological response to mechanical loading in bone. J Biol Chem 281:31720–31728
Hill TP, Spater D, Taketo MM, Birchmeier W, Hartmann C (2005) Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Dev Cell 8:727–738
Semenov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kuhl M, Sokol S, He X (2001) Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol 12:951–961
Morvan F, Boulukos K, Clement-Lacroix P, Roman Roman S, Suc-Royer I, Vayssiere B, Ammann P, Martin P, Pinho S, Pognonec P, Mollat P, Niehrs C, Baron R, Rawadi G (2006) Deletion of a single allele of the Dkk1 gene leads to an increase in bone formation and bone mass. J Bone Miner Res 21:934–945
Li J, Sarosi I, Cattley RC, Pretorius J, Asuncion F, Grisanti M, Morony S, Adamu S, Geng Z, Qiu W, Kostenuik P, Lacey DL, Simonet WS, Bolon B, Qian X, Shalhoub V, Ominsky MS, Zhu KH, Li X, Richards WG (2006) Dkk1-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling in bone results in osteopenia. Bone 39:754–766
Richards JB, Kavvoura FK, Rivadeneira F, Styrkarsdottir U, Estrada K, Halldorsson BV, Hsu YH, Zillikens MC, Wilson SG, Mullin BH, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra BA, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Soranzo N, Williams FM, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, Thorleifsson G, van Duijn CM, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ioannidis JP, Spector TD (2009) Collaborative meta-analysis: associations of 150 candidate genes with osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture. Ann Intern Med 151:528–537
Rivadeneira F, Styrkarsdottir U, Estrada K, Halldorsson BV, Hsu YH, Richards JB, Zillikens MC, Kavvoura FK, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Grundberg E, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra B, Pastinen T, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Soranzo N, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Williams FM, Wilson SG, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, van Duijn CM, Spector T, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Ioannidis JP, Uitterlinden AG (2009) Twenty bone-mineral-density loci identified by large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 41:1199–1206
Choi HY, Dieckmann M, Herz J, Niemeier A (2009) Lrp4, a novel receptor for Dickkopf 1 and sclerostin, is expressed by osteoblasts and regulates bone growth and turnover in vivo. PLoS One 4:e7930
Bonewald LF, Johnson ML (2008) Osteocytes, mechanosensing and Wnt signaling. Bone 42:606–615
Frost M, Anderson T, Yadav V, Brixen K, Karsenty G, Kassem M (2010) Patients with high bone mass phenotype due to Lrp5-T253I mutation have low plasma levels of serotonin. J Bone Miner Res doi:10.1002/jbmr.44
Modder UI, Achenbach SJ, Amin S, Riggs BL, Melton LJ, Khosla S (2009) Relation of serum serotonin levels to bone density and structural parameters in women. J Bone Miner Res doi:10.1359/jbmr.090721
Yadav VK, Oury F, Suda N, Liu ZW, Gao XB, Confavreux C, Klemenhagen KC, Tanaka KF, Gingrich JA, Guo XE, Tecott LH, Mann JJ, Hen R, Horvath TL, Karsenty G (2009) A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell 138:976–989
Acknowledgements
We thank M.-T. Rached and N. Suda for help with experiments. These studies were supported by grants from the NIH (V. K. Y. and P. D.) and a Gideon and Sevgi Rodan fellowship from IBMS (V. K. Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, V.K., Arantes, H.P., Barros, E.R. et al. Genetic Analysis of Lrp5 Function in Osteoblast Progenitors. Calcif Tissue Int 86, 382–388 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-010-9350-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-010-9350-7