Abstract
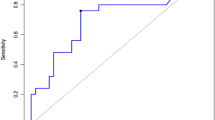
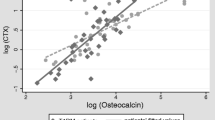
We examined whether or not BMD or bone markers were useful for assessing the risk of vertebral fractures in 248 Japanese men with type 2 diabetes. We analyzed the relationships between bone markers (osteocalcin [OC], bone-specific alkaline phosphatase [BAP], urinary N-terminal cross-linked telopeptide of type-I collagen) or BMD and HbA1c, urinary C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), parathyroid hormone, 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D, and the presence of prevalent vertebral fractures. Multiple regression analysis adjusted for age, body height, weight, duration of diabetes, and serum creatinine showed that serum OC and OC/BAP ratio were correlated negatively with HbA1c (P < 0.01) and positively with IGF-I (P < 0.01). Multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for the above parameters showed that serum OC/BAP ratio was inversely associated with the presence of vertebral fractures (odds ratio = 0.695, P < 0.05). This association was still significant after additional adjustment for lumbar or femoral neck BMD. Our results suggest that poor diabetic control and lower IGF-I level are linked to impaired bone formation and resultant reduction in OC/BAP ratio in men with type 2 diabetes. The OC/BAP ratio could be clinically useful for assessing the risk of vertebral fractures independent of BMD in diabetic men.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett-Connor E, Holbrook TL (1992) Sex differences in osteoporosis in older adults with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. JAMA 268:3333–3337
Center JR, Nguyen TV, Schneider D, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA (1999) Mortality after all major types of osteoporotic fracture in men and women: an observational study. Lancet 353:878–882
Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Ensrud KC, Scott JC, Black D (2000) Risk of mortality following clinical fractures. Osteoporos Int 11:556–561
Vestergaard P (2007) Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 18:427–444
Lipscombe LL, Jamal SA, Booth GL, Hawker GA (2007) The risk of hip fractures in older individuals with diabetes: a population-based study. Diabetes Care 30:835–841
Strotmeyer ES, Cauley JA, Schwartz AV, Nevitt MC, Resnick HE, Bauer DC, Tylavsky FA, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Newman AB (2005) Nontraumatic fracture risk with diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose in older white and black adults: the health, aging, and body composition study. Arch Intern Med 165:1612–1617
Yamamoto M, Yamaguchi T, Yamauchi M, Kaji H, Sugimoto T (2009) Diabetic patients have an increased risk of vertebral fractures independent of bone mineral density or diabetic complications. J Bone Miner Res 24:702–709
Saito M, Fujii K, Mori Y, Marumo K (2006) Role of collagen enzymatic and glycation induced cross-links as a determinant of bone quality in spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats. Osteoporos Int 17:1514–1523
Terada M, Inaba M, Yano Y, Hasuma T, Nishizawa Y, Morii H, Otani S (1998) Growth-inhibitory effect of a high glucose concentration on osteoblast-like cells. Bone 22:17–23
Botolin S, MacCabe LR (2006) Chronic hyperglycemia modulates osteoblast gene expression through osmotic and non-osmotic pathways. J Cell Biochem 99:411–424
Gopalakrishnan V, Vignesh RC, Arunakaran J, Aruldhas MM, Srinivasan N (2006) Effects of glucose and its modulation by insulin and estradiol on BMSC differentiation into osteoblastic lineages. Biochem Cell Biol 84:93–101
Verhaeghe J, Suiker AM, Nyomba BL, Visser WJ, Einhorn TA, Dequeker J, Bouillon R (1989) Bone mineral homeostasis in spontaneously diabetic BB rats. II. Impaired bone turnover and decreased osteocalcin synthesis. Endocrinology 124:573–582
Gerdhem P, Isaksson A, Akesson K, Obrant KJ (2005) Increased bone density and decreased bone turnover, but no evident alteration of fracture susceptibility in elderly women with diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos Int 16:1506–1512
Li YM, Schilling T, Benisch P, Zeck S, Meissner-Weigl J, Schneider D, Limbert C, Seufert J, Kassem M, Schutze N, Jakob F, Ebert R (2007) Effects of high glucose on mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:209–215
Alikhani M, Alikhani Z, Boyd C, MacLellan CM, Raptis M, Liu R, Pischon N, Trackman PC, Gerstenfeld L, Graves DT (2007) Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways. Bone 40:345–353
Brenner RE, Riemenschneider B, Blum W, Morike M, Teller WM, Pirsig W, Heinze E (1992) Defective stimulation of proliferation and collagen biosynthesis of human bone cells by serum from diabetic patients. Acta Endocrinol 127:509–514
Balint E, Szabo P, Marshall CF, Sprague SM (2001) Glucose-induced inhibition of in vitro bone mineralization. Bone 28:21–28
Yamamoto T, Ozono K, Miyauchi A, Kasayama S, Kojima Y, Shima M, Okada S (2001) Role of advanced glycation end products in adynamic bone disease in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 38:S161–S164
Ogawa N, Yamaguchi T, Yano S, Yamauchi M, Yamamoto M, Sugimoto T (2007) The combination of high glucose and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) inhibits the mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells through glucose-induced increase in the receptor for AGEs. Horm Metab Res 39:871–875
Okazaki R, Totsuka Y, Hamano K, Ajima M, Miura M, Hirota Y, Hata K, Fukumoto S, Matsumoto T (1997) Metabolic improvement of poorly controlled noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus decreases bone turnover. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2915–2920
Stein GS, Lian JB (1993) Molecular mechanisms mediating proliferation/differentiation interrelationships during progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocr Rev 14:424–442
Reid IR, Evans MC, Cooper GJ, Ames RW, Stapleton J (1993) Circulating insulin levels are related to bone density in normal postmenopausal women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 265:E655–E659
Abrahamsen B, Rohold A, Henriksen JE, Beck-Nielsen H (2000) Correlations between insulin sensitivity and bone mineral density in non-diabetic men. Diabet Med 17:124–129
Ravn P, Cizza G, Bjarnason NH, Thompson D, Daley M, Wasnich RD, McClung M, Hosking D, Yates AJ, Christiansen C (1999) Low body mass index is an important risk factor for low bone mass and increased bone loss in early postmenopausal women. Early Postmenopausal Intervention Cohort (EPIC) study group. J Bone Miner Res 14:1622–1627
Sugimoto T, Ritter C, Morrissey J, Hayes C, Slatopolsky E (1990) Effects of high concentrations of glucose on PTH secretion in parathyroid cells. Kidney Int 37:1522–1527
Hanaire-Broutin H, Sallerin-Caute B, Poncet MF, Tauber M, Bastide R, Rosenfeld R, Tauber JP (1996) Insulin therapy and GH-IGF-I axis disorders in diabetes: impact of glycemic control and hepatic insulization. Diabetes Metab 22:245–250
Flyvbjerg A (1990) Growth factors and diabetic complications. Diabet Med 7:387–399
Genant HK, Jergas M, Palermo L, Nevitt M, Valentin RS, Black D, Cummings SR (1996) Comparison of semiquantitative visual and quantitative morphometric assessment of prevalent and incident vertebral fractures in osteoporosis. The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res 11:984–996
Kanazawa I, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto M, Yamauchi M, Yano S, Sugimoto T (2007) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I is associated with the presence of vertebral fractures in postmonopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos Int 18:1675–1681
Kanazawa I, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto M, Yamauchi M, Yano S, Sugimoto T (2008) Combination of obesity with hyperglycemia is a risk factor for the presence of vertebral fractures in type 2 diabetic men. Calcif Tissue Int 83:324–331
Yamamoto M, Yamaguchi T, Yamauchi M, Kaji H, Sugimoto T (2007) Bone mineral density is not sensitive enough to assess the risk of vertebral fractures in type 2 diabetic women. Calcif Tissue Int 80:353–358
Yamamoto M, Yamaguchi T, Yamauchi M, Yano S, Sugimoto T (2008) Serum pentosidine levels are positively associated with the presence of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1013–1019
Thrailkill KM (2000) Insulin-like growth factor-I in diabetes mellitus: its physiology, metabolic effects, and potential clinical utility. Diabetes Technol Ther 2:69–80
McCarthy TL, Centrella M, Canalis E (1989) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and bone. Connect Tissue Res 20:277–282
Sugimoto T, Nishiyama K, Kuribayashi F, Chihara K (1997) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in osteoporotic patients with and without spinal fractures. J Bone Miner Res 12:1272–1279
Yamaguchi T, Kanatani M, Yamauchi M, Kaji H, Sugishita T, Baylink DJ, Mohan S, Chihara K, Sugimoto T (2006) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF); IGF-binding protein-3, -4, and -5; and their relationships to bone mineral density and the risk of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int 78:18–24
Raskin P, Stevenson MR, Barilla DE, Pak CY (1978) The hypercalciuria of diabetes mellitus: its amelioration with insulin. Clin Endocrinol 9:329–335
Kawagishi T, Morii H, Nakatsuka K, Sasao K, Kawasaki K, Miki T, Nishizawa Y (1991) Parathyroid hormone secretion in diabetes mellitus. Contrib Nephrol 90:217–222
Reid IR (2002) Relationships among body mass, its components, and bone. Bone 31:547–555
Fujimoto WY (1996) Overview of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in different population groups. Diabet Med 13:S7–S10
Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E, Ferron M, Ahn JD, Confavreux C, Dacquin R, Mee PJ, McKee MD, Jung DY, Zhang Z, Kim JK, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2007) Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell 130:456–469
Ferron M, Hinoi E, Karsenty G, Ducy P (2008) Osteocalcin differentially regulates beta cell and adipocyte gene expression and affects the development of metabolic diseases in wild-type mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5266–5270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanazawa, I., Yamaguchi, T., Yamamoto, M. et al. Serum Osteocalcin/Bone-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase Ratio Is a Predictor for the Presence of Vertebral Fractures in Men with Type 2 Diabetes. Calcif Tissue Int 85, 228–234 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-009-9272-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-009-9272-4