Abstract
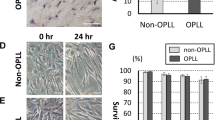
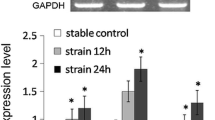
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) of the spine is characterized by progressive ectopic bone formation in the spinal ligament. To identify the genes related to ossification affected by mechanical stress during OPLL, analyses using cDNA microarray were carried out using cultured human spinal ligament cells that had been subjected to uniaxial cyclic stretching. Samples were obtained from a total of 14 patients: seven cervical or thoracic OPLL patients and seven control patients. Spinal ligament cells derived from tissues of OPLL (OPLL cells) and control (non-OPLL cells) patients were subjected to uniaxial sinusoidal cyclic stretching (0.5 Hz, 20% stretch) for various time periods (0–9 hours). cDNA microarrays revealed that ranges of distribution of both up- and downregulated genes evoked by cyclic stretching were significantly wider in OPLL cells than in non-OPLL cells. Increases in the mRNA expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) as well as various marker genes related to ossification were also observed. mRNA expression of ET-1 and alkaline phosphatase was increased by mechanical stress in a time-dependent manner, while addition of ET-1 to static cultures of OPLL cells increased mRNA expression of alkaline phosphatase in a dose-dependent manner. During 9 hours of cyclic stretching, ET-1 release increased to about sixfold the amount observed in nonstretched cells. In non-OPLL cells, neither cyclic stretching nor ET-1 induced any increase in alkaline phosphatase expression. These results suggest that mechanical stress promotes the progression of ossification in OPLL cells through autocrine and/or paracrine mechanisms of ET-1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba H, Furusawa N, Fukuda M, Maezawa Y, Imura S, Kawahara N, Nakahashi K, Tomita K (1997) Potential role of streptozotocin in enhancing ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine in the hereditary spinal hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy). Eur J Histochem 41:191–202
Numasawa T, Koga H, Ueyama K, Maeda S, Sakou T, Harata S, Leppert M, Inoue I (1999) Human retinoic X receptor beta: complete genomic sequence and mutation search for ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res 14:500–508
Wang PN, Chen SS, Liu HC, Fuh JL, Kuo BI, Wang SJ (1999) Ossi?cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. A case-control risk factor study. Spine 24:142–144
Furushima K, Shimo-Onoda K, Maeda S, Nobukuni T, Ikari K, Koga H, Komiya S, Nakajima T, Harata S, Inoue I (2002) Large-scale screening for candidate genes of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. J Bone Miner Res 17:128–137
White AA, Panjabi MM (1990) Clinical Biomechanics of the Spine, 2nd ed. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Nakamura H (1994) A radiographic study of the progression of ossification of the cervical posterior longitudinal ligament: the correlation between the ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and that of the anterior longitudinal ligament. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 68:725–730
Takatsu T, Ishida Y, Suzuki K, Inoue H (1999) Radiological study of cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Spinal Disord 12:271–273
Yamamoto Y, Furukawa K-I, Ueyama K, Nakanishi T, Takigawa M, Harata S (2002) Possible roles of CTGF/Hcs24 in the initiation and development of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine 27:1852–1857
Tanno M, Furukawa K-I, Ueyama K, Harata S, Motomura S (2003) Uniaxial cyclic stretch induces osteogenic differentiation and synthesis of bone morphogenetic proteins of spinal ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Bone 33:475–484
Ohishi H, Furukawa K-I, Iwasaki K, Ueyama K, Okada A, Motomura S, Harata S, Toh S (2003) Role of prostaglandin I2 in the gene expression induced by mechanical stress in spinal ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:818–824
Iwasaki K, Furukawa K-I, Tanno M, Kusumi T, Ueyama K, Tanaka M, Kudo H, Toh S, Harata S, Motomura S (2004) Uni-axial cyclic stretch induces Cbfa1 expression in spinal ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Calcif Tissue Int 74:448–457
Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL (2003) Role of endothelin in human hypertension. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 81:533–541
Yamazaki T, Komuro I, Kudoh S, Zou Y, Shiojima I, Hiroi Y, Mizuno T, Maemura K, Kurihara H, Akikawa R, Takano H, Yazaki Y (1996) Endothelin-1 is involved in mechanical stress-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 271:3221–3228
Dao HH, Essalihi R, Graillon JF, Lariviere R, De Champlain J, Moreau P (2002) Pharmacological prevention and regression of arterial remodeling in a rat model of isolated systolic hypertension. J Hypertens 20:1597–1606
Wu SY, Zhang BH, Pan CS, Jiang HF, Pang YZ, Tang CS, Qi YF (2002) Endothelin-1 is a potent regulator in vivo in vascular calcification and in vitro in calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Peptides 24:1149–1156
Sasaki T, Hong MH (1993) Endothelin-1 localization in bone cells and vascular endothelial cells in rat bone marrow. Anat Rec 237:332–337
Lodhi KM, Sakaguchi H, Hirse S, Shibabe S, Hagiwara H (1995) Perichondrial localization of ETA receptor in rat tracheal and xiphoid cartilage and in fetal rat epiphysis. Am J Physiol 268:C496-C502
Kasperk CH, Börscök I, Scairer HU, Schneider U, Nawroth PP, Niethard FU, Ziegler R (1997) Endothelin-1 is a potent regulator of human bone cell metabolism in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int 60:368–374
Kitano Y, Kurihara H, Kurihara Y, Maemura K, Ryo Y, Yazaki Y, Harii K (1998) Gene expression of bone matrix proteins and endothelin receptors in endothelin-1-deficient mice revealed by in situ hybridization. J Bone Miner Res 13:237–244
Ikeda R, Yoshida K, Tsukahara S, Sakamoto Y, Tanaka H, Furukawa K-I, Inoue I (2005) The promyelotic leukemia zinc finger promotes osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells as an upstream regulator of CBFA1. J Biol Chem 280:8523–8530
Naruse K, Yamada T, Sokabe M (1998) Involvement of SA channels in orienting response of cultured endothelial cells to cyclic stretch. Am J Physiol 274:H1532-H1538
Nicola CH, Libin J, Catherine CD, Emily MG, Clair AF (2000) A skeletal gene database. J Bone Miner Res 15:2095–2122
Sokolovsky M (1992) Structure-function relationships of endothelins, sarafotoxins, and their receptor subtypes. J Neurochem 59:809–821
Wada K, Tabuchi H, Ohba R, Satoh M, Tachibana Y, Akiyama N, Hiraoka O, Asakura A, Miyamoto C, Furuichi Y (1990) Purification of an endothelin receptor from human placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 167:251–257
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Goto K, Masaki T (1998) A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 332:411–415
Takuwa Y (1993) Endothelin in vascular and endocrine systems: biological activities and its mechanisms of action. Endocr J 40:489–506
Harter LV, Hruska KA, Duncan RL (1995) Human osteoblast-like cells respond to mechanical strain with increased bone matrix protein production independent of hormone regulation. Endocrinology 136:528–535
Koga H, Sakou T, Taketomi E, Hayashi K, Numasawa T, Harata S, Yone K, Matsunaga S, Otterud B, Inoue I (1998) Genetic mapping of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Am J Hum Genet 62:1460–1467
Tanaka T, Ikari K, Furushima K, Okada A, Tanaka H, Furukawa K-I, Yoshida K, Ikeda T, Ikegawa S, Hunt SC, Takeda J, Toh S, Harata S, Nakajima T, Inoue I (2003) Genomewide linkage and linkage disequilibrium analyses identify COL6A1, on chromosome 21, as the locus for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Am J Hum Genet 73:812–822
Beigi R, Kobatake E, Aizawa M, Dubyak GR (1999) Detection of local ATP release from activated platelets using cell surface-attached firefly luciferase. Am J Physiol 276:C267–C278
Lodhi KM, Sakaguchi H, Hirse S, Shibabe S, Hagiwara H (1995) Perichondrial localization of ETA receptor in rat tracheal and xiphoid cartilage and in fetal rat epiphysis. Am J Physiol 268:C496–C502
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Masahiko Tanno and Hirotaka Ohishi of the Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hirosaki University School of Medicine, for their technical assistance and valuable discussions. We also acknowledge Professors Hiroto Kimura and Hideki Mizunuma and Associate Professor Shinji Nishikawa (Hirosaki University School of Medicine) for their valuable suggestions. This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan and from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare. Also, we thank the Karohji-Memorial Aid of Medical Study and Hirosaki University Educational Improvement Promotional Aid for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasawa, T., Iwasaki, K., Sawada, T. et al. Pathophysiological Role of Endothelin in Ectopic Ossification of Human Spinal Ligaments Induced by Mechanical Stress. Calcif Tissue Int 79, 422–430 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0147-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0147-7