Abstract
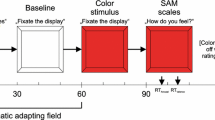
Although facial muscles are heavily involved in emotional expressions, there is still a lack of evidence about the role of face primary motor cortex (face M1) in the processing of facial recognition and expression. This work investigated the effects of the passive viewing of different facial expressions on face M1 and compared data with those obtained from the hand M1. Thirty healthy subjects were randomly assigned to two groups undergoing transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of face or hand M1. In both groups, short-latency intracortical inhibition (SICI) and intracortical facilitation (ICF) were probed in the depressor anguli oris (DAO) and first dorsal interosseous (FDI) muscles 300 ms after presentation of a picture of a face that expressed happy, sad or neutral emotions. Statistical analysis of SICI showed a non-significant effect of muscle (F1,28 = 1.903, p = 0.179), but a significant effect of emotion (F2,56 = 6.860, p = 0.004) and a significant interaction between muscle and emotion (F2,56 = 5.072, p = 0.015). Post hoc analysis showed that there was a significant reduction of SICI in the DAO muscle after presentation of a face with a happy expression compared with a neutral face (p < 0.001). In the FDI, a significant difference was observed between neutral and sad expressions (p = 0.010) No clear differences in ICF were detected. The different responses of face and hand muscles to emotional stimuli may be due to their functional roles in emotional expression versus protection of the body.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R (2002) Recognizing emotion from facial expressions: psychological and neurological mechanisms. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev 1(1):21–62
Anderson AK, Phelps EA (2001) Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events. Nature 411(6835):305–309
Baumgartner T, Willi M, Jäncke L (2007) Modulation of corticospinal activity by strong emotions evoked by pictures and classical music: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. NeuroReport 18(3):261–265
Blair RJ (2003) Facial expressions, their communicatory functions and neuro-cognitive substrates. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358(1431):561–572
Blair RJ (2004) The roles of orbital frontal cortex in the modulation of antisocial behavior. Brain Cogn 55(1):198–208 (Review)
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F, Uske A (1988) Thalamic infarcts: clinical syndromes, etiology, and prognosis. Neurology 38(6):837–848 (Erratum in: Neurology, 38(8):1335)
Bonini L, Rozzi S, Serventi FU, Simone L, Ferrari PF, Fogassi L (2010) Ventral premotor and inferior parietal cortices make distinct contribution to action organization and intention understanding. Cereb Cortex 20(6):1372–1385. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp200
Borra E, Belmalih A, Calzavara R, Gerbella M, Murata A, Rozzi S, Luppino G (2008) Cortical connections of the macaque anterior intraparietal (AIP) area. Cereb Cortex 18(5):1094–1111
Bouras T, Stranjalis G, Sakas DE (2007) Traumatic midbrain hematoma in a patient presenting with an isolated palsy of voluntary facial movements. Case report. J Neurosurg 107(1):158–160
Brainard DH (1997) The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis 10(4):433–436
Calder AJ, Young AW (2005) Understanding the recognition of facial identity and facial expression. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(8):641–651
Carlson TA, Hogendoorn H, Kanai R, Mesik J, Turret J (2011) High temporal resolution decoding of object position and category. J Vis 11(10):9. https://doi.org/10.1167/11.10.9
Carlson T, Tovar DA, Alink A, Kriegeskorte N (2013) Representational dynamics of object vision: the first 1000 ms. J Vis 13(10):1. https://doi.org/10.1167/13.10.1
Caruana F, Jezzini A, Sbriscia-Fioretti B, Rizzolatti G, Gallese V (2011) Emotional and social behaviors elicited by electrical stimulation of the insula in the macaque monkey. Curr Biol 21(3):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2010.12.042
Cattaneo L, Pavesi G (2014) The facial motor system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:135–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.11.002
Cerrato P, Imperiale D, Bergui M, Giraudo M, Baima C, Grasso M, Lentini A, Bergamasco B (2003) Emotional facial paresis in a patient with a lateral medullary infarction. Neurology 60(4):723–724
Coombes SA, Tandonnet C, Fujiyama H, Janelle CM, Cauraugh JH, Summers JJ (2009) Emotion and motor preparation: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study of corticospinal motor tract excitability. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 9(4):380–388. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.9.4.380
Cruccu G, Berardelli A, Inghilleri M, Manfredi M (1990) Corticobulbar projections to upper and lower facial motoneurons. A study by magnetic transcranial stimulation in man. Neurosci Lett 117(1–2):68–73
Cuthbert BN, Schupp HT, Bradley MM, Birbaumer N, Lang PJ (2000) Brain potentials in affective picture processing: covariation with autonomic arousal and affective report. Biol Psychol 52(2):95–111
Dalgleish T (2004) The emotional brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(7):583–589
Engell AD, Haxby JV (2007) Facial expression and gaze-direction in human superior temporal sulcus. Neuropsychologia 45(14):3234–3241
Ferrari PF, Gerbella M, Coudé G, Rozzi S (2017) Two different mirror neuron networks: the sensorimotor (hand) and limbic (face) pathways. Neuroscience 358:300–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.052
Gallese V (2005) Embodied simulation: from neurons to phenomenal experience. Phenomenol Cogn Sci 4(1):23–48
Gerbella M, Belmalih A, Borra E, Rozzi S, Luppino G (2010) Cortical connections of the macaque caudal ventrolateral prefrontal areas 45A and 45B. Cereb Cortex 20(1):141–168. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp087
Gerbella M, Belmalih A, Borra E, Rozzi S, Luppino G (2011) Cortical connections of the anterior (F5a) subdivision of the macaque ventral premotor area F5. Brain Struct Funct 216(1):43–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0293-6
Ginatempo F, Manzo N, Rothwell JC, Deriu F (2019) Lack of evidence for interhemispheric inhibition in the lower face primary motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2019.07.027
Hajcak G, Molnar C, George MS, Bolger K, Koola J, Nahas Z (2007) Emotion facilitates action: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study of motor cortex excitability during picture viewing. Psychophysiology 44(1):91–97
Haxby JV, Hoffman EA, Gobbini MI (2000) The distributed human neural system for face perception. Trends Cogn Sci 4(6):223–233
Holstege G (1992) The emotional motor system. Eur J Morphol 30(1):67–79
Holstege G, Bandler R, Saper CB (1996) The emotional motor system. Prog Brain Res 107:3–6
Hopf HC, Müller-Forell W, Hopf NJ (1992) Localization of emotional and volitional facial paresis. Neurology 42(10):1918–1923
Hortensius R, de Gelder B, Schutter DJ (2016) When anger dominates the mind: increased motor corticospinal excitability in the face of threat. Psychophysiology 53(9):1307–1316. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12685
Jezzini A, Caruana F, Stoianov I, Gallese V, Rizzolatti G (2012) Functional organization of the insula and inner perisylvian regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(25):10077–10082. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200143109
Khurana D, Sreekanth VR, Prabhakar S (2002) A case of emotional facial palsy with ipsilateral anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory infarction. Neurol India 50(1):102–104
Lundqvist A, Flykt A, Olhman A (1998) The Karolinska directed emotional faces. Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm
Meyer BU, Werhahn K, Rothwell JC, Roericht S, Fauth C (1994) Functional organization of corticonuclear pathways to motoneurones of lower facial muscles in man. Exp Brain Res 101(3):465–472
Morecraft RJ, Louie JL, Herrick JL, Stilwell-Morecraft KS (2001) Cortical innervation of the facial nucleus in the non-human primate: a new interpretation of the effects of stroke and related subtotal brain trauma on the muscles of facial expression. Brain 124(Pt 1):176–208
Morris JS, Ohman A, Dolan RJ (1999) A subcortical pathway to the right amygdala mediating "unseen" fear. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(4):1680–1685
Müri RM (2016) Cortical control of facial expression. J Comp Neurol 524(8):1578–1585. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23908.Review
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Oliveri M, Babiloni C, Filippi MM, Caltagirone C, Babiloni F, Cicinelli P, Traversa R, Palmieri MG, Rossini PM (2003) Influence of the supplementary motor area on primary motor cortex excitability during movements triggered by neutral or emotionally unpleasant visual cues. Exp Brain Res 149(2):214–221
Paradiso GO, Cunic DI, Gunraj CA, Chen R (2005) Representation of facial muscles in human motor cortex. J Physiol 567(Pt 1):323–336
Petrides M, Pandya DN (2002) Association pathways of the prefrontal cortex and functional observations. Oxford University Press, London
Pilurzi G, Hasan A, Saifee TA, Tolu E, Rothwell JC, Deriu F (2013) Intracortical circuits, sensorimotor integration and plasticity in human motor cortical projections to muscles of the lower face. J Physiol 591(7):1889–1906. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.245746
Pilurzi G, Ginatempo F, Mercante B, Cattaneo L, Pavesi G, Rothwell JC, Deriu F (2020) Role of cutaneous and proprioceptive inputs in sensorimotor integration and plasticity occurring in the facial primary motor cortex. J Physio 598(4):839–851. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP278877
Pitcher D, Garrido L, Walsh V, Duchaine BC (2008) Transcranial magnetic stimulation disrupts the perception and embodiment of facial expressions. J Neurosci 28(36):8929–8933. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1450-08.2008
Rinn WE (1984) The neuropsychology of facial expression: a review of the neurological and psychological mechanisms for producing facial expressions. Psychol Bull 95(1):52–77
Rochas V, Gelmini L, Krolak-Salmon P, Poulet E, Saoud M, Brunelin J, Bediou B (2013) Disrupting pre-SMA activity impairs facial happiness recognition: an event-related TMS study. Cereb Cortex 23(7):1517–1525. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhs133
Ross RT, Mathiesen R (1998) Images in clinical medicine. Volitional and emotional supranuclear facial weakness. N Engl J Med 338(21):1515
Rossini PM, Burke D, Chen R, Cohen LG, Daskalakis Z, Di Iorio R, Di Lazzaro V, Ferreri F, Fitzgerald PB, George MS, Hallett M, Lefaucheur JP, Langguth B, Matsumoto H, Miniussi C, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Paulus W, Rossi S, Rothwell JC, Siebner HR, Ugawa Y, Walsh V, Ziemann U (2015) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol 126(6):1071–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.001
Rossion B, Caldara R, Seghier M, Schuller AM, Lazeyras F, Mayer E (2003) A network of occipito-temporal face-sensitive areas besides the right middle fusiform gyrus is necessary for normal face processing. Brain 126(Pt 11):2381–2395
Rozzi S, Calzavara R, Belmalih A, Borra E, Gregoriou GG, Matelli M, Luppino G (2006) Cortical connections of the inferior parietal cortical convexity of the macaque monkey. Cereb Cortex 16(10):1389–1417
Scalaidhe SPÒ, Wilson FA, Goldman-Rakic PS (1997) Areal segregation of face-processing neurons in prefrontal cortex. Science 278(5340):1135–1138
Scalaidhe SPÒ, Wilson FA, Goldman-Rakic PS (1999) Face-selective neurons during passive viewing and working memory performance of rhesus monkeys: evidence for intrinsic specialization of neuronal coding. Cereb Cortex 9(5):459–475
Schutter DJ, Hofman D, Van Honk J (2008) Fearful faces selectively increase corticospinal motor tract excitability: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Psychophysiology 45(3):345–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2007.00635.x
Smith FW, Smith ML (2019) Decoding the dynamic representation of facial expressions of emotion in explicit and incidental tasks. Neuroimage 195:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.065
Trepel M, Weller M, Dichgans J, Petersen D (1996) Voluntary facial palsy with a pontine lesion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61(5):531–533
Triggs WJ, Ghacibeh G, Springer U, Bowers D (2005) Lateralized asymmetry of facial motor evoked potentials. Neurology 65(4):541–544
Trosch RM, Sze G, Brass LM, Waxman SG (1990) Emotional facial paresis with striatocapsular infarction. J Neurol Sci 98(2–3):195–201
Urban PP, Beer S, Hopf HC (1997) Cortico-bulbar fibers to orofacial muscles: recordings with enoral surface electrodes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 105(1):8–14
Vuilleumier P, Pourtois G (2007) Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychologia 45(1):174–194
Wood A, Lupyan G, Sherrin S, Niedenthal P (2016a) Altering sensorimotor feedback disrupts visual discrimination of facial expressions. Psychon Bull Rev 23(4):1150–1156
Wood A, Rychlowska M, Korb S, Niedenthal P (2016b) Fashioning the face: sensorimotor simulation contributes to facial expression recognition. Trends Cogn Sci 20(3):227–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2015.12.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Winston D. Byblow.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginatempo, F., Manzo, N., Ibanez-Pereda, J. et al. Happy faces selectively increase the excitability of cortical neurons innervating frowning muscles of the mouth. Exp Brain Res 238, 1043–1049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05777-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05777-z