Abstract
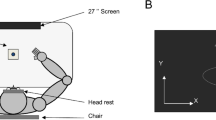
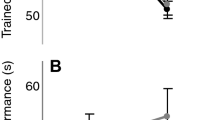
Although learning and adapting to visuo-motor tasks is critical to child development and health conditions requiring rehabilitation, the neural processes involved in learning a new visuo-motor task and adapting it to novel conditions such as execution with an untrained limb are not fully understood. Therefore, we trained 27 healthy, right-hand-dominant individuals aged 18–35 years to perform a multidirectional point-to-point visually rotated aiming task with a joystick during functional magnetic resonance imaging, with 13 participants learning the task with the dominant (D) and 14 with the non-dominant (ND) hand. All individuals performed the task with the trained and untrained hand before and after training. As expected, performance of both the trained and the untrained hand improved significantly over the course of task acquisition. Brain functional changes associated with adaptation to the demands of the task, and execution differed significantly between D and ND groups. In particular, the ND group showed greater recruitment of visual and motor regions (left middle occipital and left precentral gyri) than the D group during task acquisition. In addition, the D group exhibited greater recruitment of motor planning regions (left precuneus) that contribute to performance with the trained hand, even after bilateral transfer—switching from the trained to non-trained hand. The D group showed more persistence of activation in sensorimotor regions—greater activation when returning to the rotated task after a switching to a simpler, non-rotated aiming task for a short interval. Finally, the D group showed more activation after-effects—increases in simpler task activation after training on the visually rotated task. The findings suggest that brain functional changes associated with adaptation to a visuo-motor skill may differ substantially depending on whether the dominant or non-dominant hand is trained, with non-dominant-hand training associated with greater activation during acquisition, and dominant-hand training associated with greater activation during bilateral transfer, persistence, and after-effects.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal A, Nitsche MA, Kincses TZ, Kruse W, Hoffmann K-P, Paulus W (2004) Facilitation of visuo-motor learning by transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor and extrastriate visual areas in humans. Eur J Neurosci 19(10):2888–2892. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03367.x
Barbara E, Michele E (2016) Effects of stimulus type and strategy on mental rotation network: an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00693
Brainard DH (1997) The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis 10(4):433–436
Canizares M, MacKay C, Davis AM, Mahomed N, Badley EM (2009) A population-based study of ambulatory and surgical services provided by orthopaedic surgeons for musculoskeletal conditions. BMC Health Serv Res 9(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-9-56
Catalan MJ, Honda M, Weeks RA, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1998) The functional neuroanatomy of simple and complex sequential finger movements: a PET study. Brain 121(2):253–264
Clements AM, Rimrodt SL, Abel JR, Blankner JG, Mostofsky SH, Pekar JJ, Cutting LE (2006) Sex differences in cerebral laterality of language and visuospatial processing. Brain Lang 98(2):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2006.04.007
Gary HG, Tie-Qiang L, David R (2000) Image-based method for retrospective correction of physiological motion effects in fMRI: RETROICOR. Magn Reson Med 44(1):162
Gerloff C, Corwell B, Chen R, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1998) The role of the human motor cortex in the control of complex and simple finger movement sequences. Brain 121(9):1695–1709
Guralnik JM, Alecxih L, Branch LG, Wiener JM (2002) Medical and long-term care costs when older persons become more dependent. Am J Public Health 92(8):1244–1245. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.92.8.1244
Harrington DL, Rao SM, Haaland KY, Bobholz JA, Mayer AR, Binder JR, Cox RW (2000) Specialized neural systems underlying representations of sequential movements. J Cogn Neurosci 12(1):56–77. https://doi.org/10.1162/08989290051137602
Hikosaka O, Nakamura K, Sakai K, Nakahara H (2002) Central mechanisms of motor skill learning. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12(2):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-4388(02)00307-0
Hlustik P, Solodkin A, Gullapalli RP, Noll DC, Small SL (2002) Functional lateralization of the human premotor cortex during sequential movements. Brain Cognit 49:54–62
Hugdahl K, Thomsen T, Ersland L (2006) Sex differences in visuo-spatial processing: an fMRI study of mental rotation. Neuropsychologia 44(9):1575–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.01.026
Jansson K-Å, Granath F (2011) Health-related quality of life (EQ-5D) before and after orthopedic surgery. Acta Orthop 82(1):82–89
Kagerer FA, Contreras-Vidal JL, Stelmach GE (1997) Adaptation to gradual as compared with sudden visuo-motor distortions. Exp Brain Res 115(3):557–561
Kami A, Meyer G, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG (1995) Functional MRI evidence for adult motor cortex plasticity during motor skill learning. Nature 377(6545):155–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/377155a0
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudson AJ (2013) Principles of neural science, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kelly AMC, Garavan H (2005) Human functional neuroimaging of brain changes associated with practice. Cereb Cortex 15:1089–1102
Kleiner M, Brainard DH, Pelli D, Ingling A, Murray R, Broussard C (2007) What's new in Psychtoolbox-3. Perception 36:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1068/v070821
Kosse NM, Dutmer AL, Dasenbrock L, Bauer JM, Lamoth CJC (2013) Effectiveness and feasibility of early physical rehabilitation programs for geriatric hospitalized patients: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr 13(1):107
Kremers HM, Larson DR, Crowson CS, Kremers WK, Washington RE, Steiner CA, Berry DJ (2015) Prevalence of total hip and knee replacement in the United States. J Bone Jt Surg 97A:1386–1397
Kumar S, Mandal M (2005) Bilateral transfer of skill in left- and right-handers. Laterality 10(4):337–344
Levin SL, Feroze BM, Steven MP (2005) Common ground for spatial cognition? A behavioral and fMRI study of sex differences in mental rotation and spatial working memory. Evol Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1177/147470490500300116
Lisberger SG (1988) The neural basis for learning of simple motor skills. Science 242(4879):728
Luppa M, Luck T, Weyerer S, König H-H, Brähler E, Riedel-Heller SG (2010) Prediction of institutionalization in the elderly. A systematic review. Age Ageing 39(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afp202
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB; American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee (2016). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 133(4):e38–e360.
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Opara JA, Jaracz K, Brola W (2010) Quality of life in multiple sclerosis. J Med Life 3(4):352
Pan Z, van Gemmert AWA (2013) The direction of bilateral transfer depends on the performance parameter. Hum Mov Sci 32(5):1070–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2012.02.013
Pelli DG (1997) The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: transforming numbers into movies. Spat Vis 10(4):437–442
Poston B, Van Gemmert AWA, Barduson B, Stelmach GE (2009) Movement structure in young and elderly adults during goal-directed movements of the left and right arm. Brain Cogn 69:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2008.05.002
Romero DH, Van Gemmert AWA, Adler CH, Bekkering H, Stelmach GE (2003a) Altered aiming movements in Parkinson’s disease patients and elderly adults as a function of delays in movement onset. Exp Brain Res 151(2):249–261
Romero DH, Van Gemmert AWA, Adler CH, Bekkering H, Stelmach GE (2003b) Time delays prior to movement alter the drawing kinematics of elderly adults. Hum Mov Sci 22:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9457(02)00160-4
Sainburg RL (2014) Convergent models of handedness and brain lateralization. Front Psychol 5:1092
Sainburg RL, Wang J (2002) Interlimb transfer of visuomotor rotations: independence of direction and final position information. Exp Brain Res 145(4):437–447
Schmidt RA, Lee TD (2014) Motor learning and performance: from principles to application, 5th edn. Human Kinetics, Champaign
Seidler RD, Noll DC (2008) Neuroanatomical correlates of motor acquisition and motor transfer. J Neurophysiol 99(4):1836–1845. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01187.2007
Seidler RD, Noll DC, Chintalapati P (2006) Bilateral basal ganglia activation associated with sensorimotor adaptation. Exp Brain Res 175(3):544–555
Stevens JA, Burns E (eds) (2015) A CDC compendium of effective fall interventions: what works for community-dwelling older adults, 3rd edn
Teixeira LA (2000) Timing and force components in bilateral transfer of learning. Brain Cognit 44:455–469
Uggetti C, Ausenda CD, Squarza S, Cadioli M, Grimoldi L, Cerri C, Cariati M (2016) Bilateral transfer phenomenon: a functional magnetic resonance imaging pilot study of healthy subjects. Neuroradiol J 29(4):250–253. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400916631992
Van Gemmert AW, Van Galen GP (1997) Stress, neuromotor noise, and human performance: a theoretical perspective. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 23(5):1299–1313
Wenderoth N, Debaere F, Sunaert S, Swinnen SP (2005) The role of anterior cingulate cortex and precuneus in the coordination of motor behaviour. Eur J Neurosci 22(1):235–246
Willingham DB (1999) The neural basis of motor-skill learning. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 8(6):178. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.00042
Xiao-Wei S, Zhang-Ye D, Xiang-Yu L, Su-Fang L, Xi-Nian Z, Chao-Zhe Z, Yu-Feng Z (2011) REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One 6(9):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025031
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Louisiana State University Biomedical Collaborative Research Program and the Pennington Biomedical Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirby, K.M., Pillai, S.R., Carmichael, O.T. et al. Brain functional differences in visuo-motor task adaptation between dominant and non-dominant hand training. Exp Brain Res 237, 3109–3121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05653-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05653-5