Abstract
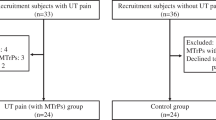
Our aim was to describe the differences in the presence of trigger points (TrPs) in the shoulder muscles and to investigate the presence of mechanical hypersensitivity in patients with unilateral shoulder impingement and healthy controls. Twelve patients with strictly unilateral shoulder impingement and 10 matched controls were recruited. TrPs in the levator scapula, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, pectoralis major, and biceps brachii muscles were explored. TrPs were considered active if the local and referred pain reproduced the pain symptoms and the patient recognized the pain as a familiar pain. Pressure pain thresholds (PPT) were assessed over the levator scapulae, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, pectoralis major, biceps brachii, and tibialis anterior muscles. Both explorations were randomly done by an assessor blinded to the subjects’ condition. Patients with shoulder impingement have a greater number of active (mean ± SD: 2.5 ± 1; P < 0.001) and latent (mean ± SD: 2 ± 1; P = 0.003) TrPs when compared to controls (only latent TrPs, mean ± SD: 1 ± 1). Active TrPs in the supraspinatus (67%), infraspinatus (42%), and subscapularis (42%) muscles were the most prevalent in the patient group. Patients showed a significant lower PPT in all muscles when compared to controls (P < 0.001). Within the patient group a significant positive correlation between the number of TrPs and pain intensity (r s = 0.578; P = 0.045) was found. Active TrPs in some muscles were associated to greater pain intensity and lower PPTs when compared to those with latent TrPs in the same muscles (P < 0.05). Significant negative correlations between pain intensity and PPT levels were found. Patients with shoulder impingement showed widespread pressure hypersensitivity and active TrPs in the shoulder muscles, which reproduce their clinical pain symptoms. Our results suggest both peripheral and central sensitisation mechanisms in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj P, Bajaj P, Graven-Nielsen T, Arendt-Nielsen L (2001) Osteoarthritis and its association with muscle hyperalgesia: an experimental controlled study. Pain 93:107–114
Bron C, Wensing M, Franssen JLM, Oostendorp RAB (2007a) Treatment of myofascial trigger points in common shoulder disorders by physical therapy: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8:107
Bron C, Franssen JL, Wensing M, Oostendorp AB (2007b) Inter-observer reliability of palpation of myofascial trigger points in shoulder muscles. J Man Manipulative Ther 15:203–215
Calandre EP, Hidalgo J, García-Leiva JM, Rico-Villademoros F (2006) Trigger point evaluation in migraine patients: an indication of peripheral sensitization linked to migraine predisposition? Eur J Neurol 13:244–249
Chesterson LS, Sim J, Wright CC, Foster NE (2007) Inter-rater reliability of algometry in measuring pressure pain thresholds in healthy humans, using multiple raters. Clin J Pain 23:760–766
Chesterton LS, Barlas P, Foster NE, Baxter GD, Wright CC (2003) Gender differences in pressure pain threshold in healthy humans. Pain 101:259–266
Fernández-Carnero J, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, De-la-Llave-Rincón AI, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L (2007) Prevalence of and referred pain from myofascial trigger points in the forearm muscles in patients with lateral epicondylalgia. Clin J Pain 23:353–360
Fernández-Carnero J, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, De-La-Llave-Rincón AI, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L (2009) Widespread mechanical pain hyper-sensitivity as sign of central sensitization in unilateral lateral epicondylalgia: a blinded, controlled study. Clin J Pain 25:555–561
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML, Pareja JA (2006) Myofascial trigger points, neck mobility and forward head posture in unilateral migraine. Cephalalgia 26:1061–1070
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Alonso-Blanco C, Miangolarra J (2007a) Myofascial trigger points in subjects presenting with mechanical neck pain: a blinded, controlled study. Man Ther 12:29–33
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML, Arendt-Nielsen L, Simons DG, Pareja JA (2007b) Myofascial trigger points and sensitisation: an updated pain model for tension type headache. Cephalalgia 27:383–393
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L, Cuadrado ML, Pareja JA (2007c) Referred pain from trapezius muscle trigger point shares similar characteristics with chronic tension type headache. Eur J Pain 11:475–482
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L, Cuadrado ML, Pareja JA (2007d) The local and referred pain from myofascial trigger points in the temporalis muscle contributes to pain profile in chronic tension-type headache. Clin J Pain 23:786–792
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Simons DG, Cuadrado ML, Pareja JA (2007e) The role of myofascial trigger points in musculoskeletal pain syndromes of the head and neck. Curr Pain Headache Rep 11:365–372
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L, Pareja JA (2007f) Increased peri-cranial tenderness, decreased pressure pain threshold and headache clinical parameters in chronic tension type headache patients. Clin J Pain 23:346–352
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML, Arendt-Nielsen L, Pareja JA (2008) Side toside differences in pressure pain thresholds and pericranial muscle tenderness in strictly unilateral migraine. Eur J Neurol 15:162–168
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, De-la-Llave-Rincón AI, Fernández-Carnero J, Cuadrado ML, Arendt-Nielsen L, Pareja JA (2009) Bilateral widespread mechanical pain sensitivity in carpal tunnel syndrome: evidence of central processing in unilateral neuropathy. Brain 132:1472–1479
Frieman BG, Albert TJ, Fenlin JM (1994) Rotator cuff disease: a review of diagnosis, patho-physiology, and current trends in treatment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 75:604–609
Ge HY, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Madeleine P, Arendt-Nielsen L (2008) Topographical mapping and mechanical pain sensitivity of myofascial trigger points in the infraspinatus muscle. Eur J Pain 12:859–865
Gerwin RD, Shanon S, Hong CZ, Hubbard D, Gevirtz R (1997) Interrater reliability in myofascial trigger point examination. Pain 69:65–67
Greening J, Lynn B (1998) Vibration sense in the upper limb in patients with repetitive strain injury and a group of at-risk office workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 71:29–34
Hegedus EJ, Goode A, Campbell S, Morin A, Tamaddoni M, Moorman CT 3rd, Cook C (2008) Physical examination tests of the shoulder: a systematic review with meta-analysis of individual tests. Br J Sports Med 42:80–92
Herren-Gerber R, Weiss S, Arendt-Nielsen L, Petersen-Felix S, Stefano G, Radanov B, Curaloto M (2004) Modulation of central hypersensitivity by nociceptive input in chronic pain after whiplash injury. Pain Med 5:366–376
Ingber RS (2000) Shoulder impingement in tennis/racquetball players treated with subscapularis myofascial treatments. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 81:679–682
Jensen MP, Turbner JA, Romano JM, Fisher L (1999) Comparative reliability and validity of chronic pain intensity measures. Pain 83:157–162
Jones DH, Kilgour RD, Comtois AS (2007) Test–retest reliability of pressure pain threshold measurements of the upper limb and torso in young healthy women. J Pain 8:650–656
Keating JF, Waterworth P, Shaw-Dunn J, Crossan J (1993) The relative strength of the rotator cuff muscles: a cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:137–140
Li LT, Ge HY, Yue SW, Arendt-Nielsen L (2009) Nociceptive and non-nociceptive hypersensitivity at latent myofascial trigger points. Clin J Pain 25:132–137
Lucas KR, Polus BI, Rich PA (2004) Latent myofascial trigger points: their effects on muscle activation and movement efficiency. J Bodywork Mov Ther 8:160–166
Ludewig PM, Cook TM (2000) Alterations in shoulder kinematics and associated muscle activity in people with symptoms of shoulder impingement. Phys Ther 80:276–291
Luime JJ, Koes BW, Hendriksen IJ, Verhaar JA, Miedema HS, Burdorf A (2004) Prevalence and incidence of shoulder pain in the general population: a systematic review. Scand J Rheumatol 33:73–81
MacDonald PB, Clark P, Sutherland K (2000) An analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the Hawkins and Neer subacromial impingement signs. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 9:299–301
Meislin RJ, Sperling JW, Stitik TP (2005) Persistent shoulder pain: epidemiology, patho-physiology, and diagnosis. Am J Orthop 34(12 Suppl):5–9
Mendell LM, Wall PD (1965) Responses of single dorsal cord cells to peripheral cutaneous unmyelinated fibres. Nature 206:97–99
Mitchell C, Adebajo A, Hay E, Carr A (2005) Shoulder pain: diagnosis and management in primary care. BMJ 331:1124–1128
Moraes GF, Faria CD, Teixeira-Salmela LF (2008) Scapular muscle recruitment patterns and isokinetic strength ratios of the shoulder rotator muscles in individuals with and without impingement syndrome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17(1 Suppl):48S–53S
Neer CS II (1983) Impingement lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:70–77
O’Neill S, Manniche C, Graven-Nielsen T, Arendt-Nielsen L (2007) Generalized deep-tissue hyperalgesia in patients with chronic low-back pain. Eur J Pain 11:415–420
Perez-Palomares S, Olivan-Blazquez B, Arnal-Burro AMA, Mayoral-del-Moral O, Gaspar-Calvo E, De la Torre-Beldarraín ML, López-Lapeña E, Pérez-Benito M, Ana-Loriente V, Romo-Calvo L (2009) Contributions of myofascial pain in diagnosis and treatment of shoulder pain: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 10:92
Pope DP, Croft PR, Pritchard CM, Silman AJ (1997) Prevalence of shoulder pain in the community: the influence of case definition. Ann Rheum Dis 56:308–312
Pribicevic M, Pollard H, Bonello R (2009) An epidemiologic survey of shoulder pain in chiropractic practice in Australia. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 32:107–117
Rolke R, Andrews Campbell K, Magerl W, Treede RD (2005) Deep pain thresholds in the distal limbs of healthy human subjects. Eur J Pain 9:39–48
Shah JP, Phillips TM, Danoff JV, Gerber LH (2005) An in vitro microanalytical technique for measuring the local biochemical milieu of human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 99:1977–1984
Shah JP, Danoff JV, Desai MJ, Parikh S, Nakamura LY, Phillips TM, Gerber LH (2008) Biochemical associated with pain and inflammations are elevated in sites near to and remote from active myofascial trigger points. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 89:16–23
Simons DG (2004) Review of enigmatic MTrPs as a common cause of enigmatic musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 14:95–107
Simons DG, Travell J, Simons LS (1999) Travell and Simons’ Myofascial pain and dysfunction: the trigger point manual. Volume 1, 2nd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Sterling M (2008) Testing for sensory hypersensitivity or central hyperexcitability associated with cervical spine pain. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 31:534–539
Sterling M, Jull G, Vicenzino B, Kenardy J (2003) Sensory hypersensitivity occurs soon after whiplash injury and associated with poor recovery. Pain 104:509–517
Tyler TF, Nahow R, Nicholas S, McHugh M (2005) Quantifying shoulder rotation weakness in patients with shoulder impingement. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14:570–574
Van der Windt DA, Koes BW, de Jong BA, Bouter LM (1995) Shoulder disorders in general practice: incidence, patient characteristics, and management. Ann Rheum Dis 54:959–964
Vanderweeen L, Oostendorp RB, Vaes P, Duquet W (1996) Pressure algometry in manual therapy. Man Ther 1:258–265
Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, Tugwell P, Campbell SM, Abeles M, Clark P et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for classification of fibromyalgia: report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum 33:160–170
Ylinen J, Nykanen M, Kautainen H, Hakkinen A (2007) Evaluation of repeatability of pressure algometry on the neck muscles for clinical use. Man Ther 12:192–197
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by a research project grant from the High Altitude Sports Centre Sierra Nevada (Spanish High Council for Sports).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared by the authors.
Funding
No research funds were received by authors for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidalgo-Lozano, A., Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C., Alonso-Blanco, C. et al. Muscle trigger points and pressure pain hyperalgesia in the shoulder muscles in patients with unilateral shoulder impingement: a blinded, controlled study. Exp Brain Res 202, 915–925 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2196-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2196-4