Abstract
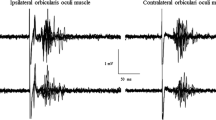
Noxious low-frequency stimulation (LFS) of presynaptic nerve fibers induces long-term depression (LTD) of synaptic transmission. In vitro studies suggest a sole homosynaptic effect. Consequently, the present study addressed the hypothesis that LTD of craniofacial nociception in man is mediated by a homosynaptic mechanism. Nociceptive supraorbital afferents were excited by electric pulses via a concentric electrode in ten healthy volunteers. The electrically evoked bilateral blink reflex (BR) was recorded from both orbicularis oculi muscles by surface electrodes. The BR was evoked in blocks of ten electric stimuli each (0.1 Hz) with an interblock interval of 8 min. Conditioning noxious LFS (1 Hz, 20 min) was applied via concentric electrode either to the same site as BR test stimuli (ipsilateral) or to the corresponding contralateral forehead area (contralateral). LFS and test stimulus intensities corresponded to about threefold the pain threshold. After three baseline stimulus blocks, either conditioning ipsilateral or contralateral LFS were applied or stimulation was interrupted for 20 min as a control task. Afterwards, test stimulation blocks were continued for 40 min. Each volunteer participated in all three sessions on different days. Noxious LFS induced LTD of the BR independently from the side of conditioning stimulation. Pain perception decreased after ipsilateral LFS but not after contralateral LFS. The bilateral effect of noxious LFS on the BR provides evidence for heterosynaptic LTD based on bilateral projections of supraorbital nerve afferents onto spinal trigeminal nuclei. The divergent effect on pain perception may be due to a preferential contralateral projection of nociceptive afferents onto reflex interneurons but not onto trigeminothalamic projection neurons.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvidsson J, Gobel S (1981) An HRP study of the central projections of primary trigeminal neurons which innervate tooth pulps in the cat. Brain Res 210:1–16
Braunewell KH, Manahan-Vaughan D (2001) Long-term depression: a cellular basis for learning? Rev Neurosci 12:121–140
Bromm B, Meier W (1984) The intracutaneous stimulus: a new pain model for algesimetric studies. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 6:405–410
Chen J, Sandkuhler J (2000) Induction of homosynaptic long-term depression at spinal synapses of sensory Adelta-fibers requires activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuroscience 98:141–148
Chia LG, Shen WC (1993) Wallenberg’s lateral medullary syndrome with loss of pain and temperature sensation on the contralateral face: clinical, MRI and electrophysiological studies [see comments]. J Neurol 240:462–467
Cruccu G, Iannetti GD, Marx JJ, Thoemke F, Truini A, Fitzek S, Galeotti F, Urban PP, Romaniello A, Stoeter P, Manfredi M, Hopf HC (2005) Brainstem reflex circuits revisited. Brain 128:386–394
Deuschl G, Eisen A (2000) Recommendations for the practice of clinical neurophysiology: guidelines of the international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Dudek SM, Bear MF (1992) Homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of hippocampus and effects of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4363–4367
Ellrich J (2002) Trigeminal nociceptive reflexes. Mov Disord 17(Suppl. 2):S41–S44
Ellrich J (2004) Electric low-frequency stimulation of the tongue induces long-term depression of the jaw-opening reflex in anesthetized mice. J Neurophysiol 92:3332–3338
Ellrich J (2005) Dopamine D2-like receptor activation antagonizes long-term depression of orofacial sensorimotor processing in anesthetized mice. Brain Res 1035:94–99
Ellrich J, Hopf HC (1996) The R3 component of the blink reflex: normative data and application in spinal lesions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 101:349–354
Ellrich J, Messlinger K (1999) Afferent input to the medullary dorsal horn from the contralateral face in rat. Brain Res 826:321–324
Ellrich J, Schorr A (2002) Long-term depression of the human masseter inhibitory reflex. Neurosci Lett 329:265–268
Ellrich J, Schorr A (2004) Low-frequency stimulation of trigeminal afferents induces long-term depression of human sensory processing. Brain Res 996:255–258
Ellrich J, Treede RD (1998) Characterization of blink reflex interneurons by activation of diffuse noxious inhibitory controls in man. Brain Res 803:161–168
Ellrich J, Bromm B, Hopf HC (1997) Pain-evoked blink reflex. Muscle Nerve 20:265–270
Ellrich J, Andersen OK, Treede RD, Arendt-Nielsen L (1998) Convergence of nociceptive and non-nociceptive input onto the medullary dorsal horn in man. Neuroreport 9:3213–3217
Ellrich J, Andersen OK, Messlinger K, Arendt-Nielsen L (1999) Convergence of meningeal and facial afferents onto trigeminal brainstem neurons: an electrophysiological study in rat and man. Pain 82:229–237
Garraway SM, Hochman S (2001) Serotonin increases the incidence of primary afferent-evoked long-term depression in rat deep dorsal horn neurons. J Neurophysiol 85:1864–1872
Gescheider GA (1985) Psychophysics: method, theory and application. Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Iannetti GD, Porro CA, Pantano P, Romanelli PL, Galeotti F, Cruccu G (2003) Representation of different trigeminal divisions within the primary and secondary human somatosensory cortex. Neuroimage 19:906–912
Jacquin MF, Chiaia NL, Haring JH, Rhoades RW (1990a) Intersubnuclear connections within the rat trigeminal brainstem complex. Somatosens Mot Res 7:399–420
Jacquin MF, Chiaia NL, Rhoades RW (1990b) Trigeminal projections to contralateral dorsal horn: central extent, peripheral origins, and plasticity. Somatosens Mot Res 7:153–183
Katsarava Z, Lehnerdt G, Duda B, Ellrich J, Diener HC, Kaube H (2002) Sensitization of trigeminal nociception specific for migraine but not pain of sinusitis. Neurology 59:1450–1453
Kaube H, Katsarava Z, Kaufer T, Diener H, Ellrich J (2000) A new method to increase nociception specificity of the human blink reflex. Clin Neurophysiol 111:413–416
Kaube H, Katsarava Z, Przywara S, Drepper J, Ellrich J, Diener HC (2002) Acute migraine headache: possible sensitization of neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus? Neurology 58:1234–1238
Kimura J (1989) The blink reflex. In: Kimura J (ed) Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscle: principles and practice. Davis, Philadelphia, pp 307–331
King MA, Bradshaw S, Chang AH, Pintar JE, Pasternak GW (2001) Potentiation of opioid analgesia in dopamine2 receptor knock-out mice: evidence for a tonically active anti-opioid system. J Neurosci 21:7788–7792
Light AR (1992) The initial processing of pain and its descending control: spinal and trigeminal systems. Karger, Basel
Liu XG, Morton CR, Azkue JJ, Zimmermann M, Sandkühler J (1998) Long-term depression of C-fibre-evoked spinal field potentials by stimulation of primary afferent A delta-fibres in the adult rat. Eur J Neurosci 10:3069–3075
MacGowan DJL, Janal MN, Clark WC, Wharton RN, Lazar RM, Sacco RL, Mohr JP (1997) Central poststroke pain and Wallenberg´s lateral medullary infarction: frequency, character, and determinants in 63 patients. Neurology 49:120–125
Marfurt CF (1981) The central projections of trigeminal primary afferent neurons in the cat as determined by the transganglionic transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 203:785–798
Mulkey RM, Malenka RC (1992) Mechanisms underlying induction of homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron 9:967–975
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen C (1991) Das Zentralnervensystem des Menschen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ongerboer de Visser BW, Kuypers HGJM (1978) Late blink reflex changes in lateral medullary lesions. An electrophysiological and neuro-anatomical study of Wallenberg’s syndrome. Brain 101:285–294
Randic M, Jiang MC, Cerne R (1993) Long-term potentiation and long-term depression of primary afferent neurotransmission in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 13:5228–5241
Romaniello A, Iannetti GD, Truini A, Cruccu G (2003) Trigeminal responses to laser stimuli. Neurophysiol Clin 33:315–324
Sandkühler J, Chen JG, Cheng G, Randic M (1997) Low-frequency stimulation of afferent Adelta-fibers induces long-term depression at primary afferent synapses with substantia gelatinosa neurons in the rat. J Neurosci 17:6483–6491
Schorr A, Ellrich J (2002) Long-term depression of the human blink reflex. Exp Brain Res 147:549–553
Schouenborg J, Weng H-R, Kalliomäki J, Holmberg H (1995) A survey of spinal dorsal horn neurones encoding the spatial organization of withdrawal reflexes in the rat. Exp Brain Res 106:19–27
Sessle BJ (2000) Acute and chronic craniofacial pain: brainstem mechanisms of nociceptive transmission and neuroplasticity, and their clinical correlates. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 11:57–91
Sessle BJ, Hu JW, Amano N, Zhong G (1986) Convergence of cutaneous, tooth pulp, visceral, neck and muscle afferents onto nociceptive and non-nociceptive neurones in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn) and its implications for referred pain. Pain 27:219–235
Smith DB, Demasters BK (1981) Demyelinating disease presenting as Wallenberg’s syndrome. Report of a patient. Stroke 12:877–878
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Sakai A (1987) Topographic organization of central terminal region of different sensory branches of the rat mandibular nerve. Exp Neurol 96:540–557
Valls-Solé J, Vila N, Obach V, Alvarez R, González LE, Chamorro A (1996) Brain stem reflexes in patients with Wallenberg’s syndrome: correlation with clinical and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. Muscle Nerve 19:1093–1099
Vila N, Valls-Solé J, Obach V, Saiz A, Alday M, Chamorro A (1997) Blink reflex in patients with Wallenberg’s syndrome. J Neurol 244:30–34
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EFIC Gruenenthal Grant 2005 and by the grants from the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research BIOMAT of the RWTH Aachen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yekta, S.S., Lamp, S. & Ellrich, J. Heterosynaptic long-term depression of craniofacial nociception: divergent effects on pain perception and blink reflex in man. Exp Brain Res 170, 414–422 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0226-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0226-4