Abstract
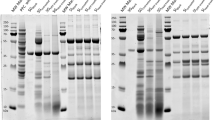
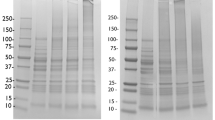
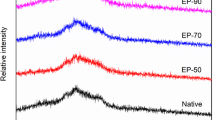
Processing-induced conformational changes may affect digestibility and antigenic potential of food proteins. In vitro gastrointestinal digestibility of gluten proteins was established after treatment at various pH (3 or 7), temperature (room temperature or 100 °C) and shear (0 or 1500 s−1). Electrophoretic patterns (SDS-PAGE) of the resulting hydrolysates and antigenicity (ELISA and immunoblotting) of gliadin fraction of the proteins were also studied. Digestibility was positively correlated with α-helix/β-sheet ratio. Lower antigenic reaction shown by digested hydrolysate of gluten samples treated at pH 3 and room temperature was ascribed to its acidic deamidation and improved digestibility. Further heating to 100 °C slightly increased antigenicity. In contrast, hydrolysate of gluten at pH 7 and room temperature exhibited highest antigenicity, attributed to partial resistance of α-/β-gliadin to digestion and appearance of some new potentially antigenic polypeptides. However, heating at 100 °C caused heat-induced protein aggregation, consequently lowered digestibility and availability of antigenic components resulting in a minimum (60 % reduction) antigenicity. Overall, shear had no effect on digestibility and antigenicity irrespective of pH and temperature. Thus, antigenic potential of gliadins can be minimized by selecting appropriate parameters during processing.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catassi C, Fabiani E, Iacono G, D’Agate C, Francavilla R, Biagi F, Volta U, Accomando S, Picarelli A, De Vitis I (2007) A prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to establish a safe gluten threshold for patients with celiac disease. Am J Clin Nutr 85(1):160–166
Moore M, Dal Bello F, Arendt E (2008) Sourdough fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FST 1.7 improves the quality and shelf life of gluten-free bread. Eur Food Res Technol 226(6):1309–1316
Susanna S, Prabhasankar P (2011) A comparative study of different bio-processing methods for reduction in wheat flour allergens. Eur Food Res Technol 233(6):999–1006. doi:10.1007/s00217-011-1589-3
Moreno FJ (2007) Gastrointestinal digestion of food allergens: effect on their allergenicity. Biomed Pharmacother 61(1):50–60. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2006.10.005
Thomas K, Herouet-Guicheney C, Ladics G, Bannon G, Cockburn A, Crevel R, Fitzpatrick J, Mills C, Privalle L, Vieths S (2007) Evaluating the effect of food processing on the potential human allergenicity of novel proteins: international workshop report. Food Chem Toxicol 45(7):1116–1122. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2006.12.016
Peram MR, Loveday SM, Ye A, Singh H (2013) In vitro gastric digestion of heat-induced aggregates of β-lactoglobulin. J Dairy Sci 96(1):63–74
Peñas E, Restani P, Ballabio C, Préstamo G, Fiocchi A, Gómez R (2006) Assessment of the residual immunoreactivity of soybean whey hydrolysates obtained by combined enzymatic proteolysis and high pressure. Eur Food Res Technol 222(3–4):286–290
Vieths S, Reindl J, Müller U, Hoffmann A, Haustein D (1999) Digestibility of peanut and hazelnut allergens investigated by a simple in vitro procedure. Eur Food Res Technol 209(6):379–388. doi:10.1007/s002170050513
Pasini G, Simonato B, Giannattasio M, Peruffo AD, Curioni A (2001) Modifications of wheat flour proteins during in vitro digestion of bread dough, crumb, and crust: an electrophoretic and immunological study. J Agric Food Chem 49(5):2254–2261
De Zorzi M, Curioni A, Simonato B, Giannattasio M, Pasini G (2007) Effect of pasta drying temperature on gastrointestinal digestibility and allergenicity of durum wheat proteins. Food Chem 104(1):353–363
Singh H, MacRitchie F (2004) Changes in proteins induced by heating gluten dispersions at high temperature. J Cereal Sci 39(2):297–301. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2003.11.004
Sun S, Song Y, Zheng Q (2008) pH-induced rheological changes for semi-dilute solutions of wheat gliadins. Food Hydrocolloids 22(6):1090–1096
Katina K, Arendt E, Liukkonen KH, Autio K, Flander L, Poutanen K (2005) Potential of sourdough for healthier cereal products. Trends Food Sci Technol 16(1–3):104–112. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2004.03.008
Morel M-H, Redl A, Guilbert S (2002) Mechanism of heat and shear mediated aggregation of wheat gluten protein upon mixing. Biomacromolecules 3(3):488–497
Rahaman T, Vasiljevic T, Ramchandran L (2016) Shear, heat and pH induced conformational changes of wheat gluten—impact on antigenicity. Food Chem 196:180–188
Kieffer R, Schurer F, Köhler P, Wieser H (2007) Effect of hydrostatic pressure and temperature on the chemical and functional properties of wheat gluten: studies on gluten, gliadin and glutenin. J Cereal Sci 45(3):285–292. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.09.008
Van Der Borght A, Goesaert H, Veraverbeke WS, Delcour JA (2005) Fractionation of wheat and wheat flour into starch and gluten: overview of the main processes and the factors involved. J Cereal Sci 41(3):221–237. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2004.09.008
Rahaman T, Vasiljevic T, Ramchandran L (2015) Conformational changes of β-lactoglobulin induced by shear, heat, and pH—effects on antigenicity. J Dairy Sci 98:4255–4265
Georget DMR, Belton PS (2006) Effects of temperature and water content on the secondary structure of wheat gluten studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 7(2):469–475. doi:10.1021/bm050667j
Yong YH, Yamaguchi S, Matsumura Y (2006) Effects of enzymatic deamidation by protein-glutaminase on structure and functional properties of wheat gluten. J Agric Food Chem 54(16):6034–6040. doi:10.1021/jf060344u
Drago SR, González RJ (2000) Foaming properties of enzymatically hydrolysed wheat gluten. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 1(4):269–273. doi:10.1016/S1466-8564(00)00034-5
Helrich K (1990) Official methods of analysis of the AOAC, vol 2, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Inc., Maryland
Wessel D, Flügge U-I (1984) A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem 138(1):141–143
Akagawa M, Handoyo T, Ishii T, Kumazawa S, Morita N, Suyama K (2007) Proteomic analysis of wheat flour allergens. J Agric Food Chem 55(17):6863–6870
J-s Wang, Z-y Wei, Li L, Bian K, M-m Zhao (2009) Characteristics of enzymatic hydrolysis of thermal-treated wheat gluten. J Cereal Sci 50(2):205–209
Qiu C, Sun W, Cui C, Zhao M (2013) Effect of citric acid deamidation on in vitro digestibility and antioxidant properties of wheat gluten. Food Chem 141(3):2772–2778
Carbonaro M, Maselli P, Nucara A (2012) Relationship between digestibility and secondary structure of raw and thermally treated legume proteins: a Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic study. Amino Acids 43(2):911–921
Dunn BM (2001) Overview of pepsin‐like aspartic peptidases. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 21.3:1–6
Simonato B, Pasini G, Giannattasio M, Peruffo AD, De Lazzari F, Curioni A (2001) Food allergy to wheat products: the effect of bread baking and in vitro digestion on wheat allergenic proteins. A study with bread dough, crumb, and crust. J Agric Food Chem 49(11):5668–5673
Liao L, Liu T-X, Zhao M-M, Cui C, Yuan B-E, Tang S, Yang F (2010) Functional, nutritional and conformational changes from deamidation of wheat gluten with succinic acid and citric acid. Food Chem 123(1):123–130. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.017
Berti C, Roncoroni L, Falini ML, Caramanico R, Dolfini E, Bardella MT, Elli L, Terrani C, Forlani F (2007) Celiac-related properties of chemically and enzymatically modified gluten proteins. J Agric Food Chem 55(6):2482–2488. doi:10.1021/jf062623n
Kumagai H, Suda A, Sakurai H, Kumagai H, Arai S, Inomata N, Ikezawa Z (2007) Improvement of digestibility, reduction in allergenicity, and induction of oral tolerance of wheat gliadin by deamidation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(4):977–985
Zhao J, Tian Z, Chen L (2010) Effects of deamidation on structure and functional properties of barley hordein. J Agric Food Chem 58(21):11448–11455. doi:10.1021/jf102307f
Lagrain B, Thewissen BG, Brijs K, Delcour JA (2008) Mechanism of gliadin–glutenin cross-linking during hydrothermal treatment. Food Chem 107(2):753–760. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.08.082
Stathopoulos CE, Tsiami AA, Dobraszczyk BJ, Schofield JD (2006) Effect of heat on rheology of gluten fractions from flours with different bread-making quality. J Cereal Sci 43(3):322–330. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2005.12.004
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Australian Government Award “Endeavour Postgraduate Scholarships” for providing financial assistance to the first author. Authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Sarah Fraser, for the technical support provided for immunoblotting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahaman, T., Vasiljevic, T. & Ramchandran, L. Effect of heat, pH and shear on digestibility and antigenic characteristics of wheat gluten. Eur Food Res Technol 242, 1829–1836 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-016-2682-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-016-2682-4