Abstract
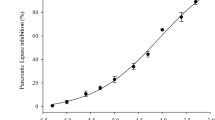
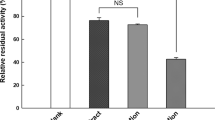
Effect of gypenosides on porcine pancreatic lipase (PL) activity was determined in vitro. Gypenosides inhibited the PL activity in a dose-dependent manner at the concentrations of 0–1.0 mg/ml. The Lineweaver–Burk plots for gypenosides indicated that the inhibition on PL by gypenosides was noncompetitive. The conformation of PL was investigated by means of circular dichroism and fluorescence. The result revealed the decrease in α-helix contents, increase in β-sheet and the decrease in fluorescence intensity after gypenosides treatment. The incorporation of cholesterol into micelles was inhibited by gypenosides. A complex was observed by transmission electron microscopy, indicating interaction between cholesterol and gypenosides which led to the decrease in cholesterol micelle solubility. The result revealed the fact that gypenosides played a role in inhibiting PL activity and reducing intestinal cholesterol absorption via inhibition of micelle formation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobson TA, Miller M, Schaefer EJ (2007) Hypertriglyceridemia and cardiovascular risk reduction. Clin Ther 29:763–777
Estadella D, Oyama LM, Dâmaso AR, Ribeiro EB, Do Nascimento CMO (2004) Effect of palatable hyperlipidic diet on lipid metabolism of sedentary and exercised rats. Nutrition 20:218–224
Mukherjee M (2003) Human digestive and metabolic lipases—a brief review. J Mol Catal B Enzym 22:369–376
Drent ML, Van der Veen EA (1993) Lipase inhibition: a novel concept in the treatment of obesity. Int J Obes 17:241–244
Yamamoto M, Shimura S, Itoh Y, Ohsaka T, Egawa M, Inoue S (2000) Anti-obesity effects of lipase inhibitor CT-II, an extract from edible herbs, Nomame Herba, on rats fed a high-fat diet. Int J Obes 24:758–764
Kawaguchi K (1997) Hesperidin as an inhibitor of lipases from porcine pancreas and pseudomonas. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:102–104
Nakai M, Fukui Y, Asami S, Toyoda-Ono Y, Iwashita T, Shibata H et al (2005) Inhibitory effects of oolong tea polyphenols on pancreatic lipase in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 53:4593–4598
Han LK (2001) Anti-obesity effects in rodents of dietary tea saponin, a lipase inhibitor. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25:1459–1464
Liu R (2010) Anti-obesity effects of protopanaxdiol types of ginsenosides isolated from the leaves of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) in mice fed with a high-fat diet. Fitoterapia 81:1079–1087
Liu W, Zheng Y, Han L, Wang H, Saito M, Ling M et al (2008) Saponins (Ginsenosides) from stems and leaves of Panax quinquefolium prevented high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Phytomedicine 15:1140–1145
Han LK (2002) Saponins from platycodi radix ameliorate high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J Nutr 132:2241–2245
Bai MS, Gao JM, Fan C, Yang SX, Zhang G, Zheng CD (2010) Bioactive dammarane-type triterpenoids derived from the acid hydrolysate of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins. Food Chem 119:306–310
Megalli S (2006) Anti-hyperlipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the Zucker fatty rat. J Pharm Pharm Sci 9:281–291
Wang S, Dong S, Zhang R, Shao H, Liu Y (2014) Effects of proanthocyanidins on porcine pancreatic lipase: conformation, activity, kinetics and thermodynamics. Process Biochem 49:237–243
Wang S, Sun Z, Dong S, Liu Y, Liu Y (2014) Molecular interactions between (–)-epigallocatechin gallate analogs and pancreatic lipase. Plos One 9:1–10
Malinow MR, Mclaughlin P, Stafford C, Livingston AL, Kohler GO, Pr C (1979) Comparative effects of alfalfa saponins and alfalfa fiber on cholesterol absorption in rats. Am J Clin Nutr 32:1810–1812
Malinow MR, Mclaughlin P, Papworth L, Stafford C, Kohler GO, Livingston AL et al (1978) Effect of alfalfa saponins on intestinal cholesterol absorption in rats. Am J Clin Nutr 30:2061–2067
Woollett L, Wang Y, Buckley D, Yao L, Chin S, Granholm N et al (2006) Micellar solubilisation of cholesterol is essential for absorption in humans. Gut 55:197–204
Mel’Nikov SM, Seijen JW, Ap E (2004) Effect of phytosterols and phytostanols on the solubilization of cholesterol by dietary mixed micelles: an in vitro study. Chem Phys Lipids 127:121–141
Ikeda I, Imasato Y, Sasaki E, Nakayama M, Nagao H, Takeo T et al (1992) Tea catechins decrease micellar solubility and intestinal absorption of cholesterol in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 1127:141–146
Vermeer MA, Mulder TPJ, Molhuizen HOF (2008) Theaflavins from black tea, especially theaflavin-3-gallate, reduce the incorporation of cholesterol into mixed micelles. J Agric Food Chem 56:12031–12036
Yang TT (1999) Chinese green tea lowers cholesterol level through an increase in fecal lipid excretion. Life Sci 66:411–423
Yang YH, Yang J, Jiang QH (2013) Hypolipidemic effect of gypenosides in experimentally induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Lipids Health Dis 12:109–116
Chávez-Santoscoy RA, Gutiérrez-Uribe JA, So SS (2013) Effect of flavonoids and saponins extracted from black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seed coats as cholesterol micelle disruptors. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 68:416–423
Liu Y, Chen D, Xu L, Yan Y (2012) Evaluation of structure and hydrolysis activity of candida rugosa Lip7 in presence of sub-/super-critical CO2. Enzyme Microb Technol 51:354–358
Zhang J, Zhang W, Mamadouba B, Xia W (2012) A comparative study on hypolipidemic activities of high and low molecular weight chitosan in rats. Int J Biol Macromol 51:504–508
Yoshizumi K, Hirano K, Ando H, Hirai Y, Ida Y, Tsuji T et al (2005) Lupane-type saponins from leaves of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and their inhibitory activity on pancreatic lipase. J Agric Food Chem 54:335–341
Vol N (1999) Applications of circular dichroism in protein and peptide analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 18:236–244
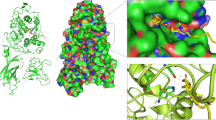
Winkler F, d’Arcy A, Hunziker W (1990) Structure of human pancreatic lipase. Nature 343:771–774
Jd S, Yg L, Wu S, Cygler M (1991) Ser-His-Glu triad forms the catalytic site of the lipase from Geotrichum candidum. Nature 351:761–764
Goncalves R, Mateus N, de Freitas V (2010) Study of the interaction of pancreatic lipase with procyanidins by optical and enzymatic methods. J Agric Food Chem 58:11901–11906
Yi J, Jiang B, Zhang Z, Liao X, Zhang Y, Hu X (2011) Effect of ultrahigh hydrostatic pressure on the activity and structure of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) polyphenoloxidase. J Agric Food Chem 60:593–599
Ikeda I, Yamahira T, Kato M, Ishikawa A (2010) Black-tea polyphenols decrease micellar solubility of cholesterol in vitro and intestinal absorption of cholesterol in rats. J Agric Food Chem 58:8591–8595
Adisakwattana S, Moonrat J, Srichairat S, Chanasit C, Tirapongporn H, Chanathong B et al (2010) Lipid-lowering mechanisms of grape seed extract (Vitis vinifera L) and its antihyperlidemic activity. J Med Plants Res 4:2113–2120
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 125 Project (2012BAD33B05), and Anhui Tongling Ruipu Peony Industry Development Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J., Wang, H., Ma, C. et al. Hypolipidemic mechanism of gypenosides via inhibition of pancreatic lipase and reduction in cholesterol micellar solubility. Eur Food Res Technol 242, 305–312 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-015-2540-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-015-2540-9