Abstract
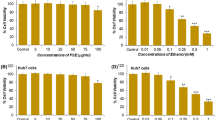
L-theanine is a natural amino acid in green tea and it has been well known for its activities of relieving depression and neuroprotection. However, cytoprotective effect and its mechanism of L-theanine on hepatocytes have not been reported. The objective of this work was to investigate the hepatoprotective effect of L-theanine as well as its mechanism by using the human hepatic L02 cells injured by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Results showed that L-theanine dose dependently decreased H2O2-induced cell viability loss and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. L-theanine pretreatment improved nuclear morphology of the cells injured by H2O2. By using flow cytometric analysis, we found that L-theanine significantly inhibited H2O2-induced cell apoptosis. Further, L-theanine attenuated H2O2-induced reduction in pro-caspase3 and cleavage of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase (PARP). H2O2-activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) was also inhibited by L-theanine. These data suggest that L-theanine could protect L02 cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis via suppression of p38 MAPK. L-theanine might potentially be useful in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano E (2008) Oxidative mechanisms in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Mol Aspects Med 29:9–16
Zhang W, Wang M, Xie HY et al (2007) Role of reactive oxygen species in mediating hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and its therapeutic applications in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 39:1332–1337
Choi J, Ou JH (2006) Mechanisms of liver injury. III. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G847–G851
Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI et al (2002) Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 65:166–176
Lieber CS (1997) Ethanol metabolism, cirrhosis and alcoholism. Clin Chim Acta 257:59–84
Kurose I, Higuchi H, Miura S et al (1997) Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis of hepatocytes exposed to acute ethanol intoxication. Hepatology 25:368–378
Medina J, Moreno-Otero R (2005) Pathophysiological basis of antioxidant therapy in chronic liver diseases. Drugs 65:2445–2461
Finger A, Kuhr S, Engelhardt UH (1992) Chromatography of tea constituents. J Chromatogr 624:293–315
Yokozawa T, Dong E (1997) Influence of green tea and its three major components upon low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Exp Toxicol Pathol 49:329–335
Nishida K, Yasuda E, Nagasawa K et al (2008) Altered levels of oxidation and phospholipase C isozyme expression in the brains of theanine-administered rats. Biol Pharm Bull 31:857–860
Kim Tae Il, Lee Yong Kyung, Park Sang Gi et al (2009) L-Theanine, an amino acid in green tea, attenuates β-amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction and neurotoxicity: reduction in oxidative damage and inactivation of ERK/p38 kinase and NF-κB pathways. Free Radical Bio Med 47:1601–1610
Cho HS, Kim S, Lee SY et al (2008) Protective effect of the green tea component, L-theanine on environmental toxins-induced neuronal cell death. Neurotoxicology 29:656–662
Sadzuka Y, Inoue C, Hirooka S et al (2005) Effects of theanine on alcohol metabolism and hepatic toxicity. Biol Pharm Bull 28:1702–1706
Wu YF, Fan YM, Xue B et al (2006) Human glutathione S-transferase P1–1 interacts with TRAF2 and regulates TRAF2-ASK1 signals. Oncogene 25:5787–5800
Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S (2001) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radical Bio Med 29:323–333
Gardner AM, Xu FH, Fady C (1997) Apoptotic vs. non apoptotic cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radical Bio Med 22:73–83
Kanno S, Ishikawa M, Takayanagi M et al (2000) Characterization of hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in mouse primary cultured hepatocytes. Biol Pharm Bull 23:37–42
Suzuki K, Kostin S, Person V (2001) Time course of the apoptotic cascade and effects of caspase inhibitors in adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:983–994
Lin R, Wang WR, Liu JT et al (2006) Protective effect of tanshinone IIA on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injured by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol 108:217–222
Maria EG, Gregory JG (2010) Apoptosis as a mechanism for liver disease progression. Semin Liver Dis 30:402–410
Chen CN, Liang CM, Lai JR et al (2003) Capillary electrophoretic determination of theanine, caffeine, and catechins in fresh tea leaves and oolong tea and their effects on rat neurosphere adhesion and migration. J Agric Food Chem 51:7495–7503
Di X, Yan J, Zhao Y et al (2010) L-theanine protects the APP (Swedish mutation) transgenic SH-SY5Y cell against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity via inhibition of the NMDA receptor pathway. Neuroscience 168(3):778–786
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA et al (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Slee EA, Adrain C, Martin SJ (2001) Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Bio Chem 276:7320–7326
Wang H, Xue Z, Wang Q et al (2008) Propofol protects hepatic L02 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases pathway. Anesth Analg 107(2):534–540
Wada T, Penninger JM (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 23:2838–2849
Chaudhary PM, Eby MT, Jasmin A et al (1999) Activation of c-Jun N terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by overexpression of caspase 8 and its homologs. J Biol Chem 274:19211–19219
Frasch SC, Nick JA, Fadok VA et al (1998) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent and independent pathways leading to apoptosis in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 273:8389–8397
Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC (2003) p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:717–726
Valerio A, Boroni F, Benarese M et al (2006) NF-kappaB pathway: a target for preventing beta amyloid (Abeta)-induced neuronal damage and Abeta42production. Eur J Neurosci 23:1711–1720
Pannaccione A, Secondo A, Scorziello A et al (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species mediates voltagegated K+ current enhancement by neurotoxic beta-amyloid peptides in nerve growth factor differentiated PC-12 cells and hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 94:572–586
Qu XJ, Xia X, Wang YS et al (2009) Protective effects of Salvia plebeia compound homoplantaginin on hepatocyte injury. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1710–1715
Yao P, Nussler A, Liu L et al (2007) Quercetin protects human hepatocytes from ethanol-derived oxidative stress by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathways. J Hepatol 47:253–261
Xu YM, Vladimir IK, Wang H et al (2009) Freeze-Dried grape powder attenuates mitochondria- and oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in liver cells. J Agric Food Chem 57:9324–9331
Schroeter H, Boyd C, Spencer JP et al (2002) MAPK signaling in neurodegeneration: influences of flavonoids and of nitric oxide. Neurobiol Aging 23:861–880
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81072433 and 31071000) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Kang, J., Yao, X. et al. The component of green tea, L-theanine protects human hepatic L02 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. Eur Food Res Technol 233, 427–435 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1534-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1534-5