Abstract
Discontinuous dewetting is an attractive technique that can produce droplet array of specific volume, geometry and at predefined location on a substrate. Droplet array has great potential in bioanalysis such as high-throughput live cell screening, digital PCR, and drug candidates. Here, we propose a self-dispersing droplet array generation method, which has advantages of low cost, simple operation, and easy large-area production ability. Droplet array of specific volumes was generated on a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) substrate using a simple reusable polyimide (PI) adhesive mask. Experiment shows that the generated droplet array can be used to successfully capture single particles which obeys Poisson distribution in a high-throughput manner. Furthermore, a droplet-array sandwiching chip was created based on the self-dispersion method for rapid detection of human serum albumin (HSA) at wide range of 183–11,712 μg/mL with low reagent consumption of 2.2 μL, demonstrating its potential applications in convenient high-throughput bioanalysis and bioassays.
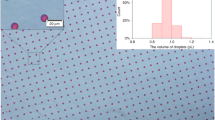
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Fan JZ, Villarreal F, Weyers B, Ding YF, Tseng KH, Li JN, Li BQ, Tan CM, Pan TR. Multi-dimensional studies of synthetic genetic promoters enabled by microfluidic impact printing. Lab Chip. 2017;17(13):2198–207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7lc00382j.
Kim SH, Iino R, Iwai S, Araki S, Sakakihara S, Noji H. Large-scale femtoliter droplet array for digital counting of single biomolecules (vol 12, pg 4986, 2012). Lab Chip. 2012;12(24):5284–5284.
Li X, Hu J, Easley CJ. Automated microfluidic droplet sampling with integrated, mix-and-read immunoassays to resolve endocrine tissue secretion dynamics. Lab Chip. 2018;18(19):2926–35. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc00616d.
Hong JW, Quake SR. Integrated nanoliter systems. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(10):1179–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt871.
Thorsen T, Maerkl SJ, Quake SR. Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science. 2002;298(5593):580–4. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1076996.
Plog J, Lowe JM, Jiang Y, Pan Y, Yarin AL. Control of direct written ink droplets using electrowetting. Langmuir. 2019;35(34):11023–36. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01061.
Ruvalcaba-Cardenas AD, Thurgood P, Chen S, Khoshmanesh K, Tovar-Lopez FJ. Droplet on soft shuttle: electrowetting-on-dielectric actuation of small droplets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(42):39283–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b10796.
Ueda E, Geyer FL, Nedashkivska V, Levkin PA. Droplet microarray: facile formation of arrays of microdroplets and hydrogel micropads for cell screening applications. Lab Chip. 2012;12(24):5218–24. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40921f.
Ueda E, Levkin PA. Emerging applications of superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic micropatterns. Adv Mater. 2013;25(9):1234–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204120.
Sakakihara S, Araki S, Iino R, Noji H. A single-molecule enzymatic assay in a directly accessible femtoliter droplet array. Lab Chip. 2010;10(24):3355–62. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0lc00062k.
Kobaku SPR, Kota AK, Lee DH, Mabry JM, Tuteja A. Patterned superomniphobic-superomniphilic surfaces: templates for site-selective self-assembly. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2012;51(40):10109–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201202823.
Feng WQ, Li LX, Du X, Welle A, Levkin PA. Single-step fabrication of high-density microdroplet arrays of low-surface-tension liquids. Adv Mater. 2016;28(16):3202–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201505972.
Biebuyck HA, Whitesides GM. Self-organization of organic liquids on patterned self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on gold. Langmuir. 1994;10(8):2790–3. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00020a047.
Feng WQ, Li LX, Yang CW, Welle A, Trapp O, Levkin PA. UV-induced tetrazole-thiol reaction for polymer conjugation and surface functionalization. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2015;54(30):8732–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201502954.
Ishizaki T, Saito N, Takai O. Correlation of cell adhesive behaviors on superhydrophobic, superhydrophilic, and micropatterned superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic surfaces to their surface chemistry. Langmuir. 2010;26(11):8147–54. https://doi.org/10.1021/la904447c.
Geyer FL, Ueda E, Liebel U, Grau N, Levkin PA. Superhydrophobic-superhydrophilic micropatterning: towards genome-on-a-chip cell microarrays. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2011;50(36):8424–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201102545.
Li JS, Li LX, Du X, Feng WQ, Welle A, Trapp O, Grunze M, Hirtz M, Levkin PA. Reactive superhydrophobic surface and its photoinduced disulfideene and thiol-ene (bio)functionalization. Nano Lett. 2015;15(1):675–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5041836.
Popova AA, Schillo SM, Demir K, Ueda E, Nesterov-Mueller A, Levkin PA. Droplet-array (DA) sandwich chip: a versatile platform for high-throughput cell screening based on superhydrophobic-superhydrophilic micropatterning. Adv Mater. 2015;27(35):5217–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502115.
Ueda E, Feng WQ, Levkin PA. Superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic patterned surfaces as high-density cell microarrays: optimization of reverse transfection. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(20):2646–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201600518.
Xia Y, Chen H, Li J, Hu H, Qian Q, He RX, Ding Z, Guo SS. Acoustic droplet-assisted superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic microarray platform for high-throughput screening of patient-derived tumor spheroids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(20):23489–501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c06655.
Baghdoyan S, Roupioz Y, Pitaval A, Castel D, Khomyakova E, Papine A, Soussaline F, Gidrol X. Quantitative analysis of highly parallel transfection in cell microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(9):e77. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gnh074.
Erfle H, Neumann B, Liebel U, Rogers P, Held M, Walter T, Ellenberg J, Pepperkok R. Reverse transfection on cell arrays for high content screening microscopy. Nat Protoc. 2007;2(2):392–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.483.
Rantala JK, Makela R, Aaltola AR, Laasola P, Mpindi JP, Nees M, Saviranta P, Kallioniemi O. A cell spot microarray method for production of high density siRNA transfection microarrays. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:162. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-162.
Roguev A, Talbot D, Negri GL, Shales M, Cagney G, Bandyopadhyay S, Panning B, Krogan NJ. Quantitative genetic-interaction mapping in mammalian cells. Nat Methods. 2013;10(5):432–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2398.
Lei WX, Demir K, Overhage J, Grunze M, Schwartz T, Levkin PA. Droplet-microarray: miniaturized platform for high-throughput screening of antimicrobial compounds. Adv Biosyst. 2020; ARTN 2000073.https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202000073
Feng WQ, Ueda E, Levkin PA. Droplet microarrays: from surface patterning to high-throughput applications. Adv Mater. 2018;30(20):1706111. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706111.
Wang JX, Zhang YZ, Wang ST, Song YL, Jiang L. Bioinspired colloidal photonic crystals with controllable wettability. Accounts Chem Res. 2011;44(6):405–15. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar1001236.
Wu L, Dong ZC, Kuang MX, Li YA, Li FY, Jiang L, Song YL. Printing patterned fine 3D structures by manipulating the three phase contact line. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25(15):2237–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201404559.
Tian W, Zhou HP, Li L. Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite photodetectors. Small. 2017;13(41):1702107. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702107.
Arrabito G, Pignataro B. Solution processed micro- and nano-bioarrays for multiplexed biosensing. Anal Chem. 2012;84(13):5450–62. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300621z.
Burchak ON, Mugherli L, Ostuni M, Lacapere JJ, Balakirev MY. Combinatorial discovery of fluorescent pharmacophores by multicomponent reactions in droplet arrays. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(26):10058–61. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204016e.
Gharibi M, Haroun S, Choy JC, Li PCH. A microfluidic antibody bioarray for fast detection of human interleukins in low sample volumes. Can J Chem. 2019;97(10):737–44. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2018-0506.
Zhang Y, Minagawa Y, Kizoe H, Miyazaki K, Iino R, Ueno H, Tabata KV, Shimane Y, Noji H. Accurate high-throughput screening based on digital protein synthesis in a massively parallel femtoliter droplet array. Sci Adv. 2019;5(8):8185. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav8185.
Kane RS, Takayama S, Ostuni E, Ingber DE, Whitesides GM. Patterning proteins and cells using soft lithography. Biomaterials. 1999;20(23–24):2363–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(99)00165-9.
Li HZ, Yang Q, Li GN, Li MZ, Wang ST, Song YL. Splitting a droplet for femtoliter liquid patterns and single cell isolation. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2015;7(17):9060–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/am509177s.
Xu KR, Wang XP, Ford RM, Landers JP. Self-partitioned droplet array on laser-patterned superhydrophilic glass surface for wall-less cell arrays. Anal Chem. 2016;88(5):2652–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03764.
Wu H, Chen X, Gao X, Zhang M, Wu J, Wen W. High-throughput generation of durable droplet arrays for single-cell encapsulation, culture, and monitoring. Anal Chem. 2018;90(7):4303–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00048.
Tessari P. Protein metabolism in liver cirrhosis: from albumin to muscle myofibrils. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2003;6(1):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/00075197-200301000-00012.
Wang W, Huang Y, Zhao S, Shao T, Cheng Y. Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with intermolecular disulfide bonds. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013;49(22):2234–6. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc38397k.
Leblanc Y, Bihoreau N, Chevreux G. Characterization of human serum albumin isoforms by ion exchange chromatography coupled on-line to native mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018;1095:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.07.014.
Mao Y, Pan Y, Li X, Li B, Chu J, Pan T. High-precision digital droplet pipetting enabled by a plug-and-play microfluidic pipetting chip. Lab Chip. 2018;18(18):2720–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc00505b.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the USTC Experimental Center of Engineering and Material Sciences and the USTC center for Micro-and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication for technical support in microfabrication.
Funding
This research work has been supported in part by the Strategic Priority Research Program (C) of the CAS (No. XDC07040200), Joint Research Fund for Overseas Chinese Scholars and Scholars in Hong Kong and Macao (No. 51929501), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. WK5290000001), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51675505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kai Liu and Yang Pan designed the research and wrote the manuscript. Xiaojie Wang and Tuo Ma provided help for the establishment of the microfluidic nanoliter dispenser. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All listed co-authors and institutions agreed with the submission of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Statement on animal welfare
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (WMV 13608 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Pan, Y., Wang, X. et al. A low-cost self-dispersing method of droplet array generation enabled by a simple reusable mask for bioanalysis and bioassays. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 1141–1149 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03739-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03739-0