Abstract
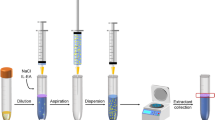
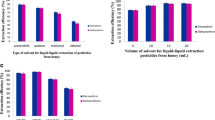
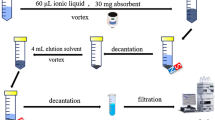
A simple, highly efficient, batch, and centrifuge-less dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on a magnetic ionic liquid (MIL-DLLME) and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS) detection was developed for ultra-trace Cd determination in honey. Initially, Cd(II) was chelated with ammonium diethyldithiophosphate (DDTP) at pH 0.5 followed by its extraction with the MIL trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrachloroferrate(III) ([P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) and acetonitrile as dispersant. The MIL phase containing the analyte was separated from the aqueous phase using only a magnet. A back-extraction procedure was applied to recover Cd from the MIL phase using diluted HNO3 and this solution was directly injected into the graphite furnace of ETAAS instrument. An extraction efficiency of 93% and a sensitivity enhancement factor of 112 were obtained under optimal experimental conditions. The detection limit (LOD) was 0.4 ng L−1 Cd, while the relative standard deviation (RSD) was 3.8% (at 2 μg L−1 Cd and n = 10), calculated from the peak height of absorbance signals. This work reports the first application of the MIL [P6,6,6,14]FeCl4 along with the DLLME technique for the successful determination of Cd at trace levels in different honey samples.

Preconcentration of ultratraces of Cd in honey using a magnetic ionic liquid and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu C, Ling Q, Yan S, Lia J, Chen Z, Peng Z. Cadmium contamination in various environmental materials in an industrial area, Hangzhou, China. Chem Spec Bioavailab. 2010;22(1):35–42.
Szkup-Jablonska M, Karakiewicz B, Grochans E, Jurczak A, Nowak-Starz G, Rotter I, et al. Effects of blood lead and cadmium levels on the functioning of children with behaviour disorders in the family environment. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012;19(2):241–6.
Ramos JC, Curtius AJ, Borges DL. Diethyldithiophosphate (DDTP): a review on properties, general applications, and use in analytical spectrometry. Appl Spectrosc Rev. 2012;47(8):583–619.
Rodrı́guez Garcı́a JC, Barciela Garcı́a J, Herrero Latorre C, Freire Rodrı́guez M, Garcı́a Martı́n S, Peña Crecente RM. Comparison of palladium–magnesium nitrate and ammonium dihydrogenphosphate modifiers for cadmium determination in honey samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta. 2003;61(4):509–17.
Ministerio de Salud de Argentina, Brasil, Paraguay y Uruguay. Reglamento Técnico Mercosur sobre límites máximos de contaminantes inorgánicos en alimentos (Res N° 12/11). 2011:10–1.
Mendil D. Determination of Cd (II), Cu (II), and Pb (II) in some foods by FAAS after preconcentration on modified silica gels with thiourea. J Food Sci. 2012;77(9):T181–6.
Stecka H, Jedryczko D, Pohl P, Welna M. Pre-concentration of traces of cadmium, cobalt, nickel and lead in natural honeys by solid phase extraction followed by their determination using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Braz Chem Soc. 2014;25:331–9.
Khammas ZAA, Ghali AA, Kadhim KH. Combined cloud-point extraction and spectrophotometric detection of lead and cadmium in honey samples using a new ligand. Int J Chem Sci. 2012;10(3):1185–204.
Rosa FC, Duarte FA, Paniz JNG, Heidrich GM, Nunes MAG, Flores EMM, et al. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction: an efficient approach for the extraction of Cd and Pb from honey and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J. 2015;123(Supplement C):211–7.
Koel M. Ionic liquids in chemical analysis. CRC Press; 2008.
Chen H, Han J, Wang Y, Hu Y, Ni L, Liu Y, et al. Hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction of cadmium(II) using an ionic liquid as the extractant. Microchim Acta. 2014;181(11–12):1455–61.
Khan S, Kazi TG, Soylak M. Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction of cadmium in biological samples: optimization by a multivariate approach. Anal Lett. 2015;48(11):1751–66.
Wang Y, Sun Y, Xu B, Li X, Wang X, Zhang H, et al. Matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in oilseeds. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;888:67–74.
Clark KD, Nacham O, Yu H, Li T, Yamsek MM, Ronning DR, et al. Extraction of DNA by magnetic ionic liquids: tunable solvents for rapid and selective DNA analysis. Anal Chem. 2015;87(3):1552–9.
Yu H, Merib J, Anderson JL. Faster dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction methods using magnetic ionic liquids as solvents. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1463:11–9.
Beiraghi A, Shokri M, Seidi S, Godajdar BM. Magnetomotive room temperature dicationic ionic liquid: a new concept toward centrifuge-less dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1376:1–8.
Del Sesto RE, McCleskey TM, Burrell AK, Baker GA, Thompson JD, Scott BL, et al. Structure and magnetic behavior of transition metal based ionic liquids. Chem Commun. 2008;(4):447–9.
Wang J, Yao H, Nie Y, Zhang X, Li J. Synthesis and characterization of the iron-containing magnetic ionic liquids. J Mol Liq. 2012;169:152–5.
Welz B, Sperling M. Atomic absorption spectrometry. Wiley; 2008.
Martinis EM, Berton P, Monasterio RP, Wuilloud RG. Emerging ionic liquid-based techniques for total-metal and metal-speciation analysis. Trends Anal Chem. 2010;29(10):1184–201.
Martí FB. Química analítica cualitativa. Editorial Paraninfo; 2008.
Rayner-Canham GG, Luis R, Escalona y Garcia, HJ, Barán EJ, Rodgers GE. Química inorgánica descriptiva. Pearson Educación; 2000.
Di Bella G, Turco VL, Potortì AG, Bua GD, Fede MR, Dugo G. Geographical discrimination of Italian honey by multi-element analysis with a chemometric approach. J Food Compost Anal. 2015;44:25–35.
Miller JN, Miller JC. Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry. Pearson Education; 2005.
WHO Technical Report. FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives, No 505 1972 p 32–33.
Berton P, Martinis EM, Martinez LD, Wuilloud RG. Selective determination of inorganic cobalt in nutritional supplements by ultrasound-assisted temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid phase microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;713:56–62.
Li S, Cai S, Hu W, Chen H, Liu H. Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for a sensitive determination of cadmium in water samples. Spectrochim Acta Part, B. 2009;64(7):666–71.
Zhang C, Wang Y, Cheng X, Xia H, Liang P. Determination of cadmium and lead in human teeth samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Chin Chem Soc. 2011;58(7):919–24.
Jahromi EZ, Bidari A, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM, Jamali MR. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: ultra trace determination of cadmium in water samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2007;585(2):305–11.
Pohl P. Determination of metal content in honey by atomic absorption and emission spectrometries. Trends Anal Chem. 2009;28(1):117–28.
Matin G, Kargar N, Buyukisik HB. Bio-monitoring of cadmium, lead, arsenic and mercury in industrial districts of Izmir, Turkey by using honey bees, propolis and pine tree leaves. Ecol Eng. 2016;90:331–5.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (FONCYT) (Projects PICT-2013-0072-BID and PICT-2016-2506-BID), and Universidad Nacional de Cuyo (Project 06/M099) (Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Ionic Liquids as Tunable Materials in (Bio)Analytical Chemistry with guest editors Jared L. Anderson and Kevin D. Clark.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 111 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorentini, E.F., Escudero, L.B. & Wuilloud, R.G. Magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique for preconcentration and ultra-trace determination of Cd in honey. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 4715–4723 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1050-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1050-6