Abstract
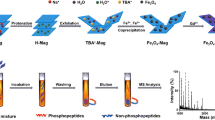
In this study, we describe a method for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides with multifunctional chitosan–glycidyl methacrylate (GMA)–iminodiacetic acid (IDA)–Fe (III) nanospheres for direct analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption–ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). This is the first time that chitosan has been used to create nanospheres support material for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides by modification with GMA, derivatization with IDA, and loading with Fe (III) ions. Chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe (III) nanospheres with a diameter of 20 to 100 nm have multifunctional chemical moieties which confer unique properties, good dispersibility in highly acidic binding buffers, as well as good biocompatibility and chemical stability which improves their specific interaction with phosphopeptides using various types of acid binding buffers. The process of enrichment is very simple, quick, efficient, and specific. Its high specificity and efficiency for purification of phosphopeptides is reflected in the very low and substoichiometric amounts of phosphopeptides which can be detected, in quantities as low as 1:3,000 M ratios. Compared with other state-of the-art technologies such as the use of conventional Fe3+-IMAC and TiO2, these chitosan nanosphere techniques show superior specificity and sensitivity. Moreover, the resultant chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe3+ nanosphere-absorbed phosphopeptides can be either directly analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS analysis or eluted and further analyzed by nano-LC-MS/MS.

A method for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides with novel multifunctional chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe (III) nanospheres for direct analysis by matrix assisted laser desorption-ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graves JD, Krebs EG (1999) Pharmacol Ther 82:111–121
Cohen P (2001) Eur J Biochem 268:5001–5010
Schmelzle K, White FM (2006) Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(4):406–414
Houseman BT, Huh JH, Kron SJ, Mrksich M (2002) Nat Biotechnol 20:270–274
Zhou H, Watts JD, Aebersold R (2001) Nat Biotechnol 19:375–378
McLachlin DT, Chait BT (2001) Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:591–602
Han G, Ye M, Zou H (2008) Analyst 133:1128–1138
Dunn JD, Reid GE, Bruening ML (2010) Mass Spectrom Rev 29:29–54
Andersson L, Porath J (1986) Anal Biochem 154:250–254
Posewitz MC, Tempst P (1999) Anal Chem 71:2883–2892
Pinkse MW, Uitto PM, Hilhorst MJ, Ooms B, Heck A (2004) J Anal Chem 76:3935–3943
Zhou H, Ye M, Dong J, Han G, Jiang X, Wu R, Zou H (2008) J Proteome Res 7:3957–3967
Ficarro SB, McCleland ML, Stukenberg PT, Burke DJ, Ross MM, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, White FM (2002) Nat Biotechnol 20:301–305
Smith JC, Figeys D (2006) Mol Biosyst 2:364–370
Mazanek M, Mituloviae G, Herzog F, Stingl C, Hutchins JR, Peters JM, Mechtler K (2007) Nat Protoc 2:1059–1069
Kweon HK, Hakansson K (2006) Anal Chem 78:1743–1749
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jørgensen TJD (2005) Mol Cell Proteomics 4:873–886
Li Y, Leng T, Lin H, Deng C, Xu X, Yao N, Yang P, Zhang X (2007) J Proteome Res 6:4498–4510
Eriksson A, Bergquist J, Edwards K, Hagfeldt A, Malmström D, Hernandez AV (2010) Anal Chem 82(11):4577–4583
Thingholm TE, Larsen MR (2009) Methods Mol Biol 527:57–66
Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Robinson PJ, Larsen MR (2008) Mol Cell Proteomics 7:661–671
Hoang T, Roth U, Kowalewski K, Belisle C, Steinert K, Karas M (2010) Anal Chem 82:219–228
Wu J, Shakey Q, Liu W, Schuller A, Follettie MT (2007) J Proteome Res 6:4684–4689
Muszynska G, Andersson L, Porath J (1986) Biochemistry 25:6850–6853
Feuerstein I, Morandell S, Stecher G, Huck CW, Stasyk T, Huang H-L, Huber LA, Bonn GK (2005) Proteomics 5(1):46–54
Chaga GS (2001) J Biochem Biophys Methods 49:313–334
Aprilita NH, Huck CW, Bakry R, Feuerstein I, Stecher G, Morandell S, Huang HL, Stasyk T, Huber LA, Bonn GK (2005) J Proteome Res 4(6):2312–2319
Mourya VK, Inamdar NN (2008) React Funct Polym 68:1013–1051
Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Reis RL, Mano JF (2005) Carbohydr Polym 62:142–158
Prabaharan M (2008) J Biomater Appl 23:5–36
Zou X, Zhong L, Liu D, Yang B, Lou Y, Rainer M, Najam-ul-Haq M, Huck CW, Bonn GK, Yin Y (2011) Anal Bioanal Chem 400:747–756
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the “985 project” of China. We thank Shimadzu Group Company for supporting the MALDI-TOF MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 266 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, X., Liu, D., Zhong, L. et al. Highly specific capture and direct MALDI-MS analysis of phosphorylated peptides using novel multifunctional chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe (III) nanosphere. Anal Bioanal Chem 401, 1251–1261 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5186-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5186-x