Abstract
Rationale
Increasing evidence shows that imidazoline I2 receptor agonists enhance opioid-induced analgesia, suggesting that the combination of I2 receptor agonists with opioids could be a favorable strategy for pain control. However, the effect of I2 receptor agonists on the abuse liability of opioids is unknown. This study examined the impact of the I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI on some abuse-related behavioral effects of the opioid morphine in rats.
Objectives
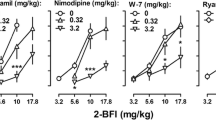
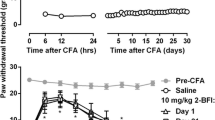
The von Frey filament test was used to determine the antinociceptive effects of 2-BFI (intravenous, i.v.) in a rat model of complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain. IV self-administration was used to assess the reinforcing effects of 2-BFI alone and to assess the effects of non-contingent injections of 2-BFI (i.p.) on morphine self-administration. A two-lever drug discrimination paradigm in which rats were trained to discriminate 3.2 mg/kg morphine (i.p.) from saline was used to examine whether 2-BFI or another I2 receptor agonist 2-(4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-yl)quinoline hydrochloride (BU224) affected the discriminative stimulus effects of morphine.
Results
2-BFI could not maintain reliable self-administration behavior in rats with no pain or CFA-treated inflammatory pain. However, pretreatment with 2-BFI (i.p.) produced dose-dependent decreases in the dose-effect curve of morphine self-administration. Both 2-BFI and BU224 did not substitute for morphine but significantly attenuated the discriminative stimulus effects of morphine.
Conclusions
These results suggest that I2 receptor agonists do not enhance, but in fact appear to decrease, the abuse liability of opioids, further supporting the potential utility of I2 receptor agonist-opioid combination therapy for pain control.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
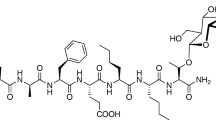
- 2-BFI:
-
2-(2-Benzofuranyl)-2-imidazoline
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BU224:
-
2-(4,5-Dihydroimidazol-2-yl)quinoline hydrochloride
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s adjuvant
- FR:
-
Fixed ratio
- PWT:
-
Paw withdrawal threshold
References
An XF, Zhang Y, Winter JC, Li JX (2012) Effects of imidazoline I(2) receptor agonists and morphine on schedule-controlled responding in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101:354–359
Bedin A, CaldartBedin RA, Vieira JE, Ashmawi HA (2016) Duloxetine as an analgesic reduces opioid consumption after spine surgery: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Clin J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000471
Chou R, Turner JA, Devine EB, Hansen RN, Sullivan SD, Blazina I, Dana T, Bougatsos C, Deyo RA (2015) The effectiveness and risks of long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain: a systematic review for a National Institutes of Health Pathways to Prevention Workshop. Ann Intern Med 162:276–286
DeWire SM, Yamashita DS, Rominger DH, Liu G, Cowan CL, Graczyk TM, Chen X-T, Pitis PM, Gotchev D, Yuan C, Koblish M, Lark MW, Violin JD (2013) A G protein-biased ligand at the μ-opioid receptor is potently analgesic with reduced gastrointestinal and respiratory dysfunction compared with morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344:708–717
Ferrari F, Fiorentino S, Mennuni L, Garofalo P, Letari O, Mandelli S, Giordani A, Lanza M, Caselli G (2011) Analgesic efficacy of CR4056, a novel imidazoline-2 receptor ligand, in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 4:111–125
Higgins GA, Wang Y, Corrigall WA, Sellers EM (1994) Influence of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists and the indirect 5-HT agonist, dexfenfluramine, on heroin self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 114:611–619
Ishihara M, Togo H (2007) Direct oxidative conversion of aldehydes and alcohols to 2-imidazolines and 2-oxazolines using molecular iodine. Tetrahedron 63:1474–1480
Kissin I (2010) The development of new analgesics over the past 50 years: a lack of real breakthrough drugs. Anesth Analg 110:780–789
Lanza M, Ferrari F, Menghetti I, Tremolada D, Caselli G (2014) Modulation of imidazoline I2 binding sites by CR4056 relieves postoperative hyperalgesia in male and female rats. Br J Pharmacol 171:3693–3701
Li JX, McMahon LR, France CP (2008) Comparison of naltrexone, 6alpha-naltrexol, and 6beta-naltrexol in morphine-dependent and in nondependent rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 195:479–486
Li JX, Zhang Y, Winter JC (2011) Morphine-induced antinociception in the rat: supra-additive interactions with imidazoline I(2) receptor ligands. Eur J Pharmacol 669:59–65
Li JX, Shah AP, Patel SK, Rice KC, France CP (2013) Modification of the behavioral effects of morphine in rats by serotonin 5-HT(1)A and 5-HT(2)A receptor agonists: antinociception, drug discrimination, and locomotor activity. Psychopharmacology 225:791–801
Li J-X, Thorn DA, Qiu Y, Peng B-W, Zhang Y (2014) Antihyperalgesic effects of imidazoline I(2) receptor ligands in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Brit J Pharmacol 171:1580–1590
Liu JF, Thorn DA, Zhang Y, Li JX (2016) Effects of trace amine-associated receptor 1 agonists on the expression, reconsolidation, and extinction of cocaine reward memory. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 19(7):pyw009
NIH (2013) Pain in America NINDS Chronic Pain Information Page. Bethesda, MD
Nutt DJ, French N, Handley S, Hudson A, Husbands S, Jackson H, Jordan S, Lalies MD, Lewis J, Lione L et al (1995) Functional studies of specific imidazoline-2 receptor ligands. Ann N Y Acad Sci 763:125–139
Qiu Y, He XH, Zhang Y, Li JX (2014) Discriminative stimulus effects of the novel imidazoline I(2) receptor ligand CR4056 in rats. Sci Rep 4:6605
Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Li JX (2015) Discriminative stimulus effects of the imidazoline I2 receptor ligands BU224 and phenyzoline in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 749:133–141
Rovati LC, Brambilla N, Blicharski T, Connell J, Vitalini C, Bonazzi A, Giacovelli G, Girolami F, D’Amato M (2020) Efficacy and safety of the first-in-class imidazoline-2 receptor ligand CR4056 in pain from knee osteoarthritis and disease phenotypes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Osteoarthr Cartil 28:22–30
Shen F, Tsuruda PR, Smith JA, Obedencio GP, Martin WJ (2013) Relative contributions of norepinephrine and serotonin transporters to antinociceptive synergy between monoamine reuptake inhibitors and morphine in the rat formalin model. PLoS ONE 8:e74891
Siemian JN, Li J, Zhang Y, Li JX (2016a) Interactions between imidazoline I2 receptor ligands and acetaminophen in adult male rats: antinociception and schedule-controlled responding. Psychopharmacology 233:873–882
Siemian JN, Obeng S, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li JX (2016b) Antinociceptive interactions between the imidazoline I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI and opioids in rats: role of efficacy at the mu-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 357:509–519
Siemian JN, Wang K, Zhang Y, Li JX (2018) Mechanisms of imidazoline I(2) receptor agonist-induced antinociception in rats: involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission. Br J Pharmacol 175:1519–1534
Soergel DG, Subach RA, Burnham N, Lark MW, James IE, Sadler BM, Skobieranda F, Violin JD, Webster LR (2014) Biased agonism of the μ-opioid receptor by TRV130 increases analgesia and reduces on-target adverse effects versus morphine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy volunteers. PAIN® 155:1829–1835
Sullivan MD, Howe CQ (2013) Opioid therapy for chronic pain in the United States: promises and perils. Pain 154(Suppl 1):S94-100
Tanda G, Mereu M, Hiranita T, Quarterman JC, Coggiano M, Katz JL (2016) Lack of specific involvement of (+)-naloxone and (+)-naltrexone on the reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cocaine and opioids. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 41:2772–2781
Thorn DA, Zhang Y, Peng BW, Winter JC, Li JX (2011) Effects of imidazoline I(2) receptor ligands on morphine- and tramadol-induced antinociception in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 670:435–440
Thorn DA, An X-F, Zhang Y, Pigini M, Li J-X (2012) Characterization of the hypothermic effects of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists in rats. Br J Pharmacol 166:1936–1945
Thorn DA, Jing L, Qiu Y, Gancarz-Kausch AM, Galuska CM, Dietz DM, Zhang Y, Li JX (2014) Effects of the trace amine-associated receptor 1 agonist RO5263397 on abuse-related effects of cocaine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 39:2309–2316
Thorn DA, Siemian JN, Zhang Y, Li JX (2015) Anti-hyperalgesic effects of imidazoline I2 receptor ligands in a rat model of inflammatory pain: interactions with oxycodone. Psychopharmacology 232:3309–3318
Thorn DA, Zhang Y, Li JX (2016) Effects of the imidazoline I receptor agonist 2-BFI on the development of tolerance and behavioral/physical dependence to morphine in rats. Br J Pharmacol 173:1363–1372
Turk DC, Wilson HD, Cahana A (2011) Treatment of chronic non-cancer pain. Lancet 377:2226–2235
Ugedo L, Pineda J, Martin-Ruiz R, Ruiz-Ortega JA, Artigas F (1999) Imidazoline-induced inhibition of firing rate of 5-HT neurons in rat dorsal raphe by modulation of extracellular 5-HT levels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 881:365–368
Wang Y, Joharchi N, Fletcher PJ, Sellers EM, Higgins GA (1995) Further studies to examine the nature of dexfenfluramine-induced suppression of heroin self-administration. Psychopharmacology 120:134–141
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health (Award no. R01DA034806). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The main idea of this study was from JS and J-XL. JS and J-XL designed the study, conducted the data analysis, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. KW performed the pain tests. JS and DHL performed the self-administration experiments. KW performed the drug discrimination experiments. YZ provided 2-BFI and BU224. All authors contributed to and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Siemian, J.N., Woodhouse, K., Liu, D.H. et al. The imidazoline I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI reduces abuse-related effects of morphine: self-administration and drug discrimination. Psychopharmacology 241, 479–487 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06524-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06524-2